Limit State Design Approach Using PGA
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Limit State Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the Limit State Design approach, which is crucial for ensuring safety in structures during earthquakes. Does anyone know what the Limit State signifies?

I think it refers to the maximum condition we expect a structure to withstand without failing.

Exactly, Student_1! The Limit State indicates conditions under which the safety of structures is compromised. What do you think governs this state during an earthquake?

Is it the Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA)?

Spot on! PGA is indeed a vital parameter. It reflects the maximum acceleration the ground experiences during an earthquake. This is crucial for determining how much force a structure needs to withstand.
Understanding Safety Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Great insight! In Limit State Design, we apply partial safety factors to the seismic loads based on PGA. Can anyone explain why these factors are important?

I think they provide a safety margin to accommodate uncertainties in the design.

That's correct, Student_3! These factors account for uncertainties in our estimations of loads, material behaviors, and eventual outcomes. Any idea what determines the safety factors' values?

Is it based on the PGA and the importance of the structure?

Exactly, Student_4! More critical structures receive higher safety factors. This ensures a high level of safety, especially in essential buildings like hospitals.
Real-World Implications of Using PGA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss the real-world implications. Why do you think using PGA in designs is crucial?

It helps in accurately predicting how much shaking a structure can handle.

Correct, Student_1! By using PGA, engineers can make informed decisions when designing buildings to ensure they remain safe during earthquakes. Any examples that come to mind of structures designed with this in mind?

What about tall buildings in earthquake-prone areas like Japan? They likely consider PGA in their designs.

Absolutely! Japan is a great example where PGA significantly influences building codes to enhance seismic resilience.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In Limit State Design, PGA serves as a critical parameter for establishing the Ultimate Limit State (ULS) during seismic events. It involves applying partial safety factors that depend on both the level of PGA and the importance of the structure, ensuring that designs effectively account for potential seismic impacts.
Detailed
Limit State Design Approach Using PGA
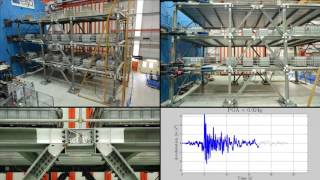
In earthquake engineering, the reliability and performance of structures during seismic events are paramount. The Limit State Design approach prioritizes safety through the application of Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA) as it governs the Ultimate Limit State (ULS) for seismic loads.
Key Points:
- Ultimate Limit State (ULS): This denotes the maximum load that a structure can sustain without failure. In seismic terms, this includes the forces experienced from ground shaking.
- PGA Application: Partial safety factors are applied to the seismic loads based on the measured or estimated PGA at the design site. The importance of the structure (e.g., a hospital versus a parking garage) also influences these factors.
- Seismic Safety: The use of PGA in this approach ensures that engineers design buildings and infrastructures that can withstand extreme seismic forces, ultimately safeguarding lives and property.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Ultimate Limit State (ULS) Governed by PGA
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In Limit State Design, PGA governs the Ultimate Limit State (ULS) for seismic loading.
Detailed Explanation
In the context of structural engineering, the Limit State Design (LSD) approach focuses on ensuring that the structure can withstand certain loads without failing. The Ultimate Limit State (ULS) is a condition beyond which the structure ceases to fulfill its intended purpose, typically associated with catastrophic failure. Here, the Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA) is a critical factor; it helps define the maximum seismic force that the structure might experience during an earthquake. Thus, when engineers design buildings, they take into account the PGA to ensure the structure can resist these forces safely.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a tall building in an earthquake-prone area. Engineers must ensure that the building can stand strong against the shaking caused by an earthquake. They use PGA to calculate how much the ground will shake and design the building accordingly, much like a bridge needs to be built sturdy enough to hold heavy traffic without collapsing.
Application of Partial Safety Factors
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Partial safety factors applied to seismic loads depend on PGA and structural importance.
Detailed Explanation
In engineering, partial safety factors are used to account for uncertainty and variability in loads and material properties. When calculating the effects of seismic forces in Limit State Design, engineers apply these safety factors based on the projected PGA and how crucial the structure is to public safety. For instance, a hospital might have higher safety factors compared to a parking garage because it is more critical for human safety and services during and after an earthquake.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cooking with a recipe. If you know that your measurements can vary slightly or the ingredients may not be exactly the same, you might add a little extra flavoring to ensure your dish turns out well. Similarly, engineers add safety factors to their calculations to ensure that their structures are safe, even if the real-world conditions aren't exactly as planned.
Key Concepts
-
PGA governs structural safety in earthquake design.
-
Partial safety factors account for uncertainties in seismic loading.
-
Ultimate Limit State signifies maximum load before failure.
Examples & Applications
Designing a hospital in a high seismic zone using PGA for structural integrity.
Applying calculated safety factors to a bridge based on its importance to urban infrastructure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
PGA’s the key in seismic plight, keeps buildings standing upright.
Stories
Imagine a tall hospital standing firm in an earthquake. Engineers use PGA to calculate the safest way to keep it standing. Their calculations give it the strength to withstand shaking, just like a tree swaying but never breaking.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SAGE' for seismic design: Safety factors, Acceleration measured, Ground importance, Effective limits.
Acronyms
Use 'PGA' - for Peak Ground Acceleration in seismic assessments.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Limit State Design
An approach that ensures structures are designed to meet safety requirements for various loading conditions, including seismic loads.
- Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA)
The maximum acceleration recorded at a specific location during an earthquake, crucial for determining seismic load effects.
- Ultimate Limit State (ULS)
The condition beyond which a structure is deemed to fail and is no longer safe for use.
- Partial Safety Factors
Factors applied during design to account for uncertainties in loads, material strengths, and future conditions.
- Seismic Resilience
The ability of a structure to withstand seismic forces and remain functional following an earthquake.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
