Fossil Fuels
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Fossil Fuels
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into fossil fuels. Can anyone tell me what fossil fuels are?

Are they just regular fuels we find on Earth?

Not quite! Fossil fuels are actually formed from ancient plants and animals, and they include coal, crude oil, and natural gas. They are key energy resources today. Does anyone know how they are formed?

Isn't it something about geological processes?

Exactly! Over millions of years, organic matter gets buried and transformed by heat and pressure. This process turns them into the carbon-rich fuels we use. Can anyone think of the main types of fossil fuels?

Coal, oil, and gas!

Great! Remember the acronym 'C.O.G' for Coal, Oil, Gas to help you remember. Now, can you each explain a bit about one of these fuels?

I can start with coal! It's a solid fuel made primarily from plant materials.

And I know crude oil is a liquid fossil fuel used in cars and factories!

Natural gas is the cleanest burning fossil fuel, right?

Exactly! Excellent participation, everyone. To summarize: fossil fuels are ancient organic materials transformed into coal, oil, and gas, which are vital for energy but come with environmental costs.
Environmental Impact of Fossil Fuels
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered what fossil fuels are, let's discuss their impacts. What do you think some environmental issues are related to their use?

Maybe air pollution from burning them?

Correct! Burning fossil fuels releases CO2, contributing to climate change and global warming. What else might happen?

I think it can also contaminate soil and water.

Yes! Mining and drilling can lead to significant land degradation and pollution. Can anyone share why these impacts are concerning?

Because they affect human health and the environment.

Exactly right! Let’s remember this as the 'H.E.E.' acronym for Health, Environment, and Emissions. Why do you think we should transition to renewable energy sources?

To reduce these negative impacts and help the planet!

Well said! To recap, fossil fuel use leads to serious air and soil pollution, directly impacting health and the environment.
Fossil Fuels and Energy Production
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's connect fossil fuels to energy production. Why is energy important for economic growth?

Because we need energy for industries and transportation!

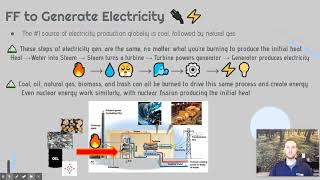
That's spot on! Energy is crucial for manufacturing, agriculture, and daily life. Can anyone tell me the percentage of energy that comes from fossil fuels?

Is it about 80% globally?

Yes, it's close to that! And that shows how reliant we are on them. With reliance, what does that mean for future energy strategies?

We should find alternatives that are cleaner and sustainable.

Correct! It's crucial for sustainable development. Remember the term 'Sustainable Shift' to think about moving towards renewable energy. Let’s wrap up by noting the balance we must find between energy needs and environmental protection.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Fossil fuels, including coal, crude oil, and natural gas, are derived from ancient biological materials and pose significant environmental challenges such as pollution and resource depletion. The section outlines the processes involved in obtaining these fuels and discusses their role in energy production and economic growth.
Detailed
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are the remnants of ancient plants and animals that have transformed over millions of years due to geological processes into carbon-rich resources found in the Earth’s crust. There are three main types of fossil fuels: coal, crude oil, and natural gas. Coal, primarily a solid form of fuel, comes from plant material, while crude oil is a liquid obtained from various hydrocarbons, and natural gas is a gaseous form that emits less CO2 during combustion.
Types of Fossil Fuels
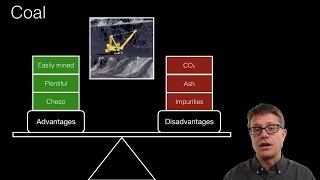
- Coal: Formed from buried plant material altered by geological forces, it is mined for energy but poses risks such as greenhouse gas emissions and pollution.
- Crude Oil: Processed in refineries to produce fuels and other materials. It is widely used for transportation and industrial applications.
- Natural Gas: Extracted from subsurface formations, it is considered cleaner than other fossil fuels due to lower emissions.
Environmental Impacts
The extraction and use of fossil fuels contribute significantly to environmental degradation, including but not limited to:
- Air pollution leading to health issues and climate change.
- Soil contamination and water issues resulting from mining and drilling operations.
- The greenhouse effect exacerbated by CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels.
Overall, while fossil fuels remain essential for economic growth and energy needs, their environmental impact necessitates a critical look towards sustainable alternatives.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Fossil Fuels
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fossil fuels: Fossil means the remains of an animal or a plant which have become hard and turned into rock. All these found in earth’s crusts which have been formed in the past by the geological processes. Fossil fuels are solid coal (lignite), liquid (crude oil / petroleum) and gases (natural gas).
Detailed Explanation
Fossil fuels are natural energy sources formed from the decomposed remains of ancient plants and animals. Over millions of years, heat and pressure transformed these organic materials into three main types of fuels: solid, liquid, and gas. The solid form is coal, the liquid form is crude oil (or petroleum), and the gaseous form is natural gas. These fuels are found in the Earth's crust and are non-renewable, meaning they take millions of years to form and cannot be readily replaced once depleted.
Examples & Analogies
Think of fossil fuels like a time capsule buried underground—inside are the remains of ancient plants and animals that, over time, have been subjected to immense pressure and heat, changing them into the energy sources we use today, much like how a treasure can be hidden away but takes time to be uncovered.
Coal
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Coal: Huge quantity of plant materials buried under the earth's crust and altered by geological processes and converted into carbon-rich fuel. It is a non-renewable source because it takes a very long period (millions of years) for its formation. Coal is extracted by the process of mining and involves accidents due to mine collapse, ground water pollution, accumulation of poisonous material, explosive gases etc cause diseases. CO2 pollution leads to greenhouse effect (global warming).
Detailed Explanation
Coal is created from ancient plant matter that has been buried under layers of rock and sediment. Over time, the heat and pressure transform this organic material into a carbon-rich substance we can burn for energy. However, coal mining can be dangerous due to risks like mine collapses and toxic gas accumulation. Additionally, burning coal releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and affecting climate change.
Examples & Analogies
Picture coal as the fossilized remains of a lush forest from hundreds of millions of years ago. When we extract and burn it, we're not just getting energy; we're releasing ancient carbon back into the atmosphere, similar to opening a time capsule and sending all of its contents into the air.
Crude Oil
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Crude oil: It is obtained in the form of liquid. The crude oil is heated up to 600°C in the oil refinery and condenses the vapors of hydrocarbons. Petrol and other petroleum products are refined fuels from crude oil. Petroleum products are used in large quantities in the manufacture of detergents, plastics, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, synthetic rubber, etc. The transport sector consumes about 40% of diesel; 25% industries; 19% households; and the rest 16% agriculture and other sectors.
Detailed Explanation
Crude oil is a thick, black liquid extracted from underground reservoirs. Once obtained, it undergoes a refining process, involving heating it to extremely high temperatures (about 600°C). This process breaks down the oil into various components or products, such as gasoline (petrol), diesel, and many industrial chemicals. Crude oil is crucial for modern society and is used not only as fuel but also as a raw material for countless everyday products.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine crude oil like a massive chocolate cake that, when sliced (refined), reveals different layers (products) such as frosting (fuel) and cake (plastics). Each slice is essential for various uses, just as each product derived from crude oil is crucial for daily life.
Natural Gas
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Natural Gas: Gas deposits are trapped from the sedimentary formations by means of drilling holes into the rock formations. While burning of natural gas, the emission of CO2 is less and thus reduces the greenhouse effect and global warming. A total of 734 billion cubic meters of gas is estimated as proven reserves.
Detailed Explanation
Natural gas is a fossil fuel found in underground rock formations, composed primarily of methane. To access it, geologists drill into the Earth, tapping into these gas reserves. Unlike coal and oil, burning natural gas produces less carbon dioxide, making it a comparatively cleaner energy source. The significant reserves indicate its potential for long-term energy supply; however, it is still a non-renewable resource.
Examples & Analogies
Think of natural gas as a clean-burning campfire compared to smoky logs. When you use a campfire (natural gas), it produces less smoke and cleaner air than burning wood (coal), making it a better choice for reducing pollution.
Key Concepts
-
Formation of Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels are formed from the decomposition of ancient organic matter over millions of years.
-
Types of Fossil Fuels: The main types are coal, crude oil, and natural gas, each with unique extraction and usage processes.
-
Environmental Impact: Fossil fuel usage leads to pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource exploitation.
Examples & Applications
Coal is often mined from underground seams, which can lead to land degradation and habitat destruction.
Crude oil extraction can result in oil spills, which have devastating effects on marine ecosystems.
Natural gas is commonly used in households for heating and cooking, but its leakage contributes to climate change.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Fuels from ages past, in the ground they'll last, coal, oil, and gas, that's fossil fuels amassed!
Stories
Imagine a lush forest that slowly gets buried under layers of sediment. Over millions of years, it transforms into coal, while oceans fill with tiny sea creatures that become oil. This is nature’s tale of fossil fuels!
Memory Tools
C.O.G for Coal, Oil, Gas helps remember the three fossil fuels.
Acronyms
H.E.E. for Health, Environment, Emissions to remember the key impacts of fossil fuels.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fossil Fuels
Energy resources made from ancient organic materials that have undergone geological processes, including coal, crude oil, and natural gas.
- Coal
A solid fossil fuel formed from plant remains, used primarily for energy production.
- Crude Oil
A liquid fossil fuel composed of hydrocarbons, refined for use in transportation and manufacturing.
- Natural Gas
A gaseous fossil fuel that burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, often used for heating and electricity generation.
- Greenhouse Gases
Gases, such as CO2, that trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
