Uses of Energy
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Energy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss why energy is vital for our economy and daily activities. Can anyone share how energy impacts our lives?

Energy is used for transportation, like cars and buses!

Exactly! Without energy, we wouldn't be able to power our vehicles. Energy also drives industries. What do you think about energy consumption in different countries?

I think developed countries use more energy because they have more factories.

Right! In fact, higher energy consumption often reflects a country's material advancement. Great observation!

Let's remember the acronym E.A.T for 'Energy, Advancement, and Transportation'—it highlights why energy is so crucial!
Types of Non-renewable Resources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now we'll explore non-renewable energy resources. Can anyone name a non-renewable resource?

Coal? I’ve heard it’s used a lot.

Correct! Coal is one of the primary fossil fuels. But it has drawbacks like pollution. What about crude oil?

Crude oil is used for making petrol and for heating.

Yes, and it’s vital for many products. Remember, all these resources contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. A mnemonic to recall them is 'C.O.N'—Coal, Oil, Natural gas.

What are some environmental concerns associated with these fuels?

They can cause pollution and climate change!
Renewable Resources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift to renewable resources. Can anyone tell me their benefits?

They are sustainable and don’t pollute as much!

Great! Solar energy is a significant renewable source. How does it work?

It uses panels to convert sunlight into electricity!

Exactly! The acronym S.O.L.A.R reminds us of its functions: Sunlight, Output, Light Conversion, and Absorption, and Recycling!

Are wind and hydro energy also renewable?

Yes! Wind captures kinetic energy while water flow generates mechanical energy. Excellent question!
Comparison of Energy Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s compare non-renewable and renewable energy. What’s a key difference?

Non-renewable resources will run out, but renewable ones won’t!

Correct! Non-renewables can contribute to climate change too. Any potential disadvantages of renewables?

Weather can affect their reliability, like solar during rainy days.

Exactly! Remember R.E.N.E.W for 'Reliant, Ever-present, New, Energy-wise and Wind-powered'. These factors help us understand their usability!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses the importance of energy as a fundamental resource for economic growth and everyday activities. It outlines the different forms of energy, such as renewable and non-renewable sources, and highlights how human activities can affect the availability and efficiency of these energy forms.
Detailed
Uses of Energy
Energy is integral to both economic growth and daily activities. It comes in various forms, like mechanical and thermal, and can't be created or destroyed, only transformed. Energy production is crucial for industrial and domestic needs, contributing significantly to a nation's advancement.
1. Importance of Energy:
- Each sector, including agriculture, transport, and commerce, heavily relies on energy.
- Per capita energy consumption acts as an indicator of a country's material progress.
2. Types of Energy Resources:
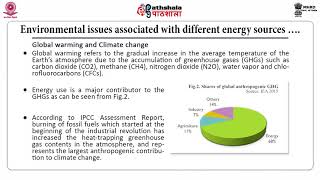
- Non-renewable Resources: These include fossil fuels like coal, crude oil, and natural gas, which, while efficient, have substantial environmental impacts through pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Coal: Long-term formation leads to mining risks and environmental damage.
- Crude Oil: Refined for multiple uses, but its extraction and processing involve pollution effects on ecosystems.
- Natural Gas: Considered cleaner than coal and oil, yet extraction and transportation pose risks.
- Renewable Resources: These are constantly replenished and generally have lower environmental impacts compared to non-renewable resources.
- Solar Energy: Can be harnessed directly through photovoltaic cells for electricity or through thermal collectors for heating. Efficiency can be hindered by weather.
- Hydropower: Generated from water flow, although it can disrupt ecosystems.
- Geothermal Energy: Taps into Earth's heat, but faces pollution challenges.
- Wind Energy: Clean and renewable, yet dependent on location and wind patterns.
- Ocean Energy: Includes tidal and thermal conversion.
- Bioenergy: Derived from organic materials, considered sustainable but may compete with food resources.
- Nuclear Energy: Produces significant energy but poses waste management issues.
3. Final Thoughts:
- Energy sources are multifaceted, necessitating careful consideration of sustainability and environmental impacts. Human activities continue to shape energy usage and thus require a focus on conservation and innovation.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Energy
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Energy is a primary input in any industrial operation.
- It is also a major input in sectors such as commerce, transport, tele-communications etc.
- The wide range of services required in the household and industrial sectors.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the critical role that energy plays in different sectors. Firstly, in industrial operations, energy acts as a vital resource needed for manufacturing processes. Secondly, it highlights the necessity of energy in commerce, transport, and telecommunications, indicating that without energy, these industries can't function properly. Finally, it touches on how households also rely on energy for daily tasks, showing that energy is a fundamental part of modern life.
Examples & Analogies
Think of energy as the fuel for a car. Just like a car needs fuel to move, industries and households need energy to operate. For example, imagine trying to cook dinner without electricity or gas; it would be nearly impossible for most people, illustrating just how essential energy is in daily life.
Types of Energy Resources
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There are three main types of energy: A. Non-renewable, B. Renewable, C. Nuclear energy.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk categorizes energy resources into three main types: non-renewable, renewable, and nuclear. Non-renewable resources, like fossil fuels, cannot be replenished quickly and include coal, oil, and natural gas. Renewable resources, such as solar, wind, and hydro energy, can naturally replenish and are more sustainable. Lastly, nuclear energy comes from atomic reactions and is a powerful, albeit complex, source of power.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bank account: non-renewable resources are like spending your savings; once they're gone, they're gone. Renewable resources are like earning money—the more you conserve, the more you have in the future. Nuclear energy, on the other hand, is like investing in stocks; it has the potential for high rewards but requires careful management.
Non-renewable Energy Resources
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A. Non-renewable energy resources include: Fossil fuels such as coal, crude oil, and natural gas.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses non-renewable energy resources, specifically fossil fuels. These are formed from ancient organic matter over millions of years and are found deep within the Earth. The extraction of these fuels involves mining for coal and drilling for oil and gas. While they are currently the most significant sources of energy, their usage leads to environmental issues, such as pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a campfire that uses logs for fuel. The logs represent coal, oil, and gas. Once you burn through them, you can’t just replace them instantly; you have to go out and find more logs, which isn't a quick process. Similarly, once non-renewable energy sources are used, they're depleted, making it essential to look for alternative energy solutions.
Renewable Energy Resources
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
B. Renewable energy resources include: Solar energy, Hydro-power, Geothermal energy, Wind energy.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk presents renewable energy resources, which are resources that can naturally replenish within a short timeline. Solar energy harnesses sunlight to produce electricity or heat. Hydro-power uses flowing water to generate electricity. Geothermal energy utilizes heat from the Earth, and wind energy captures the movement of air to create power. These resources are crucial for sustainable energy practices, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these renewable resources as a garden. Just like you can plant seeds and harvest crops repeatedly every season, renewable energy resources can be 'harvested' constantly without depleting their source. For instance, as long as the sun shines, we can collect solar energy without harming the environment.
Nuclear Energy
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
C. Nuclear Energy or Atomic power is the energy which is trapped inside the atom. It is non-renewable source of energy released during fission or fusion.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk covers nuclear energy, highlighting its origin from atomic reactions. Nuclear energy can be produced through fission, where the nucleus of an atom is split, or fusion, where nuclei combine. Nuclear power provides large quantities of energy but also poses challenges, such as the management of radioactive waste, making it a topic of considerable debate concerning safety and environmental impact.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small firecracker; when lit, it releases a burst of energy quickly. Nuclear energy operates similarly, except on a much larger and controlled scale. While it can produce large amounts of power efficiently, it also requires careful handling, just like ensuring that firecrackers are used safely to prevent accidents.
The Role of Research in Energy
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Owing to the far-reaching changes in the forms of energy and their respective roles in supporting human activities, research and training on various aspects of energy and environment have assumed great significance.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk underscores the importance of research related to energy resources and environmental impacts. As society undergoes changes in energy consumption and technology, understanding these shifts through research is essential for sustainable development and environmental protection. Research helps innovate new energy solutions, improve efficiency, and mitigate negative environmental impacts.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how scientists research medicine to find cures for diseases. Similarly, research in energy aims to find innovative ways to generate and use energy sustainably. Just as medicine improves health, responsible energy practices can lead to a healthier planet.
Key Concepts
-
Energy is essential for economic growth and daily activities.
-
Non-renewable resources include fossil fuels that are limited and contribute to environmental issues.
-
Renewable energy sources are sustainable and help reduce pollution.
Examples & Applications
Coal, natural gas, and crude oil are examples of non-renewable energy sources.
Solar panels and wind turbines are examples of renewable energy technologies.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Energy flows, it goes, in forms we know, from sun to coal, to where we grow.
Stories
Imagine a world powered solely by the sun's rays and wind's embrace, harmoniously energizing our lives without pollution.
Memory Tools
R.E.N.E.W for Renewable: Replenishing, Efficient, Naturally sourced, Energy-wise, Wind-powered.
Acronyms
C.O.N for Non-renewable
Coal
Oil
Natural gas.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Energy
The capacity to do work, existing in various forms like mechanical, thermal, and chemical.
- Nonrenewable resources
Energy sources that cannot be replenished in a short amount of time, such as fossil fuels.
- Renewable resources
Energy sources that are replenished naturally and can be used indefinitely, such as solar and wind energy.
- Greenhouse gases
Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming.
- Fossil Fuels
Natural resources formed from the remains of ancient organisms, including coal, oil, and natural gas.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
