Hydro-Power Energy
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Hydro-Power Energy Generation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we will delve into hydro-power energy. Can anyone tell me what hydro-power is?

Isn't it energy generated from water?

Exactly right! Hydro-power generates electricity by converting the kinetic energy of moving water, primarily through turbines in hydroelectric dams. These turbines then drive generators. Remember the acronym 'KITE'—Kinetic energy, Into Turbines, to Electricity.

What happens to the water after it turns the turbines?

Great question! After turning the turbines, the water continues downstream. It’s important to remember that this process doesn't use up water; it just harnesses its flow. And now, why do you think hydro-power is popular?

Because it’s renewable?

Exactly! Hydro-power is renewable as it uses the natural water cycle. Let's sum up: hydro-power converts the kinetic energy of water into electrical energy—a sustainable practice with incredible benefits!
Environmental Challenges of Hydro-Power
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, while hydro-power has great benefits, we must also consider its environmental impact. Can anyone think of some negative effects?

Doesn't building a dam destroy fish habitats?

Absolutely! Dams can disrupt ecosystems, displacing species and destroying natural habitats. Let’s remember 'DARE'—Dams Affect River Ecosystems.

What about human communities? Do they get affected?

Yes! Sometimes, entire communities need to relocate when rivers are dammed. This can lead to cultural loss, too. Let’s reflect: while hydro-power helps meet energy needs, we have to balance that with the health of our ecosystems and communities. What strategies can help mitigate these impacts?

Maybe we can create fish ladders in dams?

Correct! Fish ladders are a great example of an engineering solution to help fish navigate around dams. We've covered the importance and challenges of hydro-power—let’s keep these factors in mind!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains hydro-power energy generation, detailing how the kinetic energy of moving water is transformed into electrical power via turbines. The discussion highlights the ecological consequences of hydroelectric projects, such as habitat destruction and deforestation.
Detailed
Hydro-Power Energy
Hydro-power energy is a significant component of renewable energy resources, utilizing the kinetic energy of flowing water to generate electricity. This process takes place in hydroelectric projects where dams are constructed across rivers.
Key Concepts:
- Energy Conversion: The kinetic energy of water is initially converted into mechanical energy using turbines. These turbines are then connected to generators, which transform the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Environmental Impact: Despite its benefits as a renewable energy source, hydro-power projects can lead to severe environmental consequences, including the destruction of aquatic habitats, deforestation due to dam construction, and the relocation of communities.
- Importance of Energy: Hydro power is a pivotal aspect of energy sustainability, contributing to a nation's energy mix while raising concerns over ecological integrity.
Through understanding hydro-power energy, we can assess its role in our energy strategies and weigh its benefits against potential ecological impacts.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Hydro-Power Energy
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
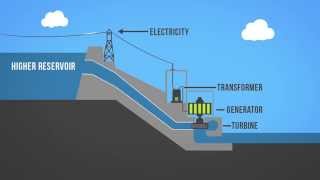
Electrical power is generated by hydro-electric projects in which dams are constructed across the river.
Detailed Explanation
Hydro-power energy is a form of renewable energy generated from moving water. Hydro-electric projects typically involve the construction of dams across rivers. These dams trap water, and as the water is released, it flows through turbines, turning them and generating electricity. Essentially, kinetic energy from the water is converted into mechanical energy as the turbines spin, and this mechanical energy is then transformed into electrical energy by generators.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water wheel at a traditional mill. Just as the flow of water makes the wheel turn which then helps grind grain, hydro-power plants harness flowing river water to spin turbines and generate electricity.
Conversion of Kinetic Energy
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The kinetic energy of water is converted into mechanical energy by means of turbines and in turn, the mechanical energy is transferred into electrical energy by generators.
Detailed Explanation
In hydro-power plants, the process begins with water falling or flowing down from a height. This motion gives the water kinetic energy. Turbines are strategically positioned to capture this energy. As water flows over turbines, it causes them to rotate. This rotation provides mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy through generators attached to the turbines. Thus, the energy of moving water becomes usable electricity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a child playing with a pinwheel on a windy day. As the wind (which is like the moving water) pushes against the pinwheel, it spins (similar to how a turbine spins) generating excitement (analogous to generating electricity).
Environmental Impacts of Hydro-Power
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hydro power projects lead to several environmental problems like destruction of animal habitats, deforestation, migration of people etc.
Detailed Explanation
While hydro-power is a renewable energy source, it can also have significant environmental consequences. The construction of dams often leads to the flooding of large areas, which can destroy local wildlife habitats and disrupt ecosystems. Additionally, the creation of reservoirs can result in deforestation as trees are cleared to make way for the water. The people living in these areas may also be displaced from their homes, leading to social concerns alongside environmental impacts.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a large swimming pool in your backyard; to do so, you might have to remove trees and plants, which would harm local wildlife that lives in those plants. Similarly, large dams create reservoirs that can drastically change the landscape and displace both animals and people.
Key Concepts
-
Energy Conversion: The kinetic energy of water is initially converted into mechanical energy using turbines. These turbines are then connected to generators, which transform the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
-
Environmental Impact: Despite its benefits as a renewable energy source, hydro-power projects can lead to severe environmental consequences, including the destruction of aquatic habitats, deforestation due to dam construction, and the relocation of communities.
-
Importance of Energy: Hydro power is a pivotal aspect of energy sustainability, contributing to a nation's energy mix while raising concerns over ecological integrity.
-
Through understanding hydro-power energy, we can assess its role in our energy strategies and weigh its benefits against potential ecological impacts.
Examples & Applications
The Hoover Dam, a prime example of hydroelectric power generation, supplies electricity to millions while also impacting local ecosystems.
In Brazil, the Belo Monte Dam has generated controversy due to its effects on indigenous communities and biodiversity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Flowing rivers turn and spin, turning water into light within.
Stories
Once in a valley, there was a majestic river. As it rushed over stones, it called out for a chance to power the world. Engineers built a dam, making the water spin turbines and light up cities, but they had to remember to care for the land and its creatures.
Memory Tools
Remember the word ‘FLOW’ for hydro-power: Flowing water, Leading to power, Offering energy, Wise planning for eco-care.
Acronyms
D.E.A.L. for understanding hydro-power
Dams block water
Energy is generated
Affects the ecosystem
Land must be considered.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hydropower
Energy generated by converting the kinetic energy of flowing water into electricity.
- Turbine
A machine for generating rotary motion from a fluid flow, essential in hydroelectric power generation.
- Generator
A device that converts mechanical energy from turbines into electrical energy.
- Dam
A barrier constructed to hold back water, often leading to the formation of a reservoir and used in hydro-power generation.
- Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
