Food Shortages and Hunger
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Climate Change Effects on Agriculture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss how climate change affects agriculture. Can anyone tell me what happens to crops when temperatures rise?

Crops might not grow as well because it could be too hot for them.

Exactly! Increased temperatures can stress plants. Also, as precipitation patterns change, we may see either too much or too little water for crops. Let's remember the acronym *WATE* which stands for Water Availability, Temperature effects, and Ecosystem impacts. What else might fluctuate?

Maybe pests and diseases could increase?

Right! Warmer climates can lead to more pests. This is why understanding these factors is essential for food security.

So, is climate change the only reason for food shortages?

Not the only reason, but it's a significant one. We must consider social, economic, and political issues too. To summarize today's session, climate change affects water availability and may stress crops, thus threatening food security.
Regional Impacts of Food Shortages
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into which areas might face the worst food shortages. Can anyone think of regions particularly vulnerable to these changes?

This might apply to regions that already struggle with water shortages, like some parts of Africa.

Absolutely, regions like Sub-Saharan Africa are likely to face significant challenges. These areas have a high reliance on agriculture for livelihoods and can be severely impacted by climate variability. Remember our mnemonic ***DROUGHT***: Drought Risk, Overall agricultural dependency, Unequal access to resources, Affected regions, and Timing of crop cycles.

What about places like Southeast Asia, where rice is essential?

Good point! The rice paddies there could be vulnerable, especially with flooding and changing rainfall patterns. So, it's critical we look at both physical and socio-economic factors.

What can be done to help these regions?

That’s an essential question. We can explore adaptive agricultural practices designed to withstand climatic variations in our next session.
Adaptive Agricultural Practices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let’s discuss adaptive agricultural practices. Who can give me an example of a method that could help farmers face climate changes?

Drought-resistant crops?

Exactly! Drought-resistant crops are one strategy that allows farmers to maintain yields even under water-scarce conditions. We can use the acronym *CROP* for Climate resilience, Resource management, Outreach for local knowledge, and Pest management. Why is outreach significant?

Farmers need support and knowledge about new methods!

Indeed! Education and training empower them to adopt better farming practices. What else can help?

Better irrigation systems could support water use.

Yes, improved irrigation is vital! To recap, adaptive practices include using drought-resistant crops, improving irrigation, and providing education to farmers.
Global Food Security and Policy Implications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our final session, let's look at global policies affecting food security. Can someone explain why policy matters in this context?

Policies can influence agricultural practices and funding for crop research!

Exactly! Policies shape funding and investment into resilience programs. We might consider the acronym *AGRICULTURE* which stands for Agricultural Grants, Resources, International Cooperation, Uplifting local economies, Climate action, and Technical support for farmers. How does cooperation help?

It can unify efforts across borders for shared technology!

Right! Collaborative efforts bolster strategies addressing climate impacts on food systems. To summarize today, effective policies and international cooperation are essential for maintaining global food security.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
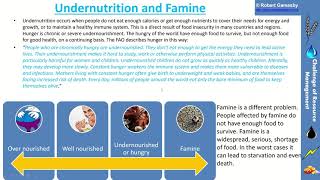
As climate change alters precipitation and evaporation patterns globally, the agricultural output is threatened, posing risks to food security. This is likely to result in food shortages and increased hunger in some regions, as highlighted in the implications of climate change on food systems.
Detailed
Food Shortages and Hunger
The section emphasizes the critical impacts of climate change on food security. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns evolve, the availability of water resources is increasingly at risk due to altered precipitation and evaporation rates. This variability in water resources is likely to affect agricultural productivity, challenging the stability of food systems worldwide.
The implications are profound, with certain regions expected to experience significant food shortages and increased hunger as a direct consequence of these environmental changes. The complexities of these challenges underscore the interconnectedness of climate impacts and food security, highlighting the need for adaptive measures to support agricultural resilience in the face of ongoing climatic shifts.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Water resources will be affected as precipitation and evaporation patterns change around the world.
Detailed Explanation
Climate change impacts the weather systems that govern precipitation and evaporation. As global temperatures rise, some regions may experience more rainfall while others may face droughts. This inconsistency can complicate water supply and availability, making it difficult for communities to access the water they need for drinking, sanitation, and agriculture.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge that can only hold a certain amount of water. If you pour water too quickly, it will overflow, just like regions with heavy rainfall. Conversely, regions that receive less water during a drought struggle, similar to a sponge that dries out and cannot absorb more water.
Effect on Agricultural Output
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This will affect agricultural output. Food security is likely to be threatened and some regions are likely to experience food shortages and hunger.
Detailed Explanation
Changes in water availability lead directly to changes in agricultural productivity. Crops depend on reliable water supplies, and if farmers cannot depend on seasonal rains or experience extreme weather events like floods or droughts, crop yields may drop. This directly affects food security, meaning there is not enough food available for the population. Regions that already struggle with food access may be hit hardest.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a farmer who relies on seasonal rain for their crops. If this rain starts to come unpredictably, the farmer may find their fields dry when they need to plant or flooded when it's time to harvest. This unpredictability can lead to reduced harvests similar to relying on a vending machine that sometimes gets jammed and doesn't dispense food.
Key Concepts
-
Food Security: Physical and economic access to safe food.
-
Climate Change: Long-term alteration of climate patterns.
-
Water Resource Variability: Changing patterns affecting agricultural output.
-
Drought-Resistant Crops: Crops developed to withstand environmental stresses.
Examples & Applications
Rice cultivation in Southeast Asia is vulnerable to changing rainfall patterns, potentially leading to food shortages.
Sub-Saharan Africa's extreme reliance on climate-sensitive agriculture increases its risk of food security challenges.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To grow and thrive, crops must survive, in water or sun, they need to run.
Stories
The farmer faced a challenge as the rains fell short, he learned to plant seeds that could withstand the drought.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym CROP: Climate resilience, Resource management, Outreach, Pest management.
Acronyms
WATE
Water Availability
Temperature effects
Ecosystem impacts.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Food Security
The state when all people have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs.
- Climate Change
Long-term alteration in temperature and typical weather patterns in a place, often attributed to human activities.
- Droughtresistant Crops
Crop varieties specifically bred to withstand low water availability.
- Water Resources
Natural resources of water that are essential for human and ecological needs.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
