Microservices Architecture
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Microservices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're focusing on Microservices Architecture. Can anyone tell me how a microservices approach differs from a monolithic architecture?

In monolithic architecture, everything is in one codebase, right?

Exactly, that's a key point! In microservices, we have decoupled services. Can anyone explain what a decoupled service means?

It means that each service operates independently, so they don't affect each other directly!

Great! And that independence allows for faster deployment cycles. Why is that beneficial, do you think?

If one service needs an update, we can do it without messing up the whole app?

Exactly! Independently deploying services allows teams to work concurrently and rapidly.

To remember this, think of 'DIP'. It stands for Decoupled, Independent, and Parallel deployment!

That’s a helpful mnemonic!

Before we conclude, can anyone summarize what we learned about microservices?

Microservices break apps into independent parts allowing for easier management and scaling!
Key Characteristics of Microservices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into the key characteristics of Microservices. First, can someone explain what scalability means in this context?

It means we can add more instances of a service as the demand increases.

Excellent! This scalability allows better resource utilization. What about management – why can this be challenging with microservices?

Because there are many services to manage, and coordinating them can be complex.

Correct! Complexity can increase, especially at scale. Remember 'MICE' to stress management complexity: Multiple Indpendent Components Exist!

That's a cool way to remember it!

So what benefits do you see for teams working with microservices, and what challenges might they face?

The benefits include faster deployments and better scalability, but it can be tougher to manage everything.

Perfect summary!
When to Use Microservices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss when it's best to implement microservices. Can someone give me an example of a scenario that requires high availability?

A financial application that needs to be online all the time!

Exactly! High availability is crucial in such cases. Any other scenarios come to mind?

Large-scale systems that experience heavy traffic would also need microservices, right?

Absolutely! Any others?

When multiple teams are working on different parts of the system.

Yes, that's a perfect example! Each team can manage its own service without stepping on each other’s toes. Remember the acronym 'LMT' for Large systems, Multiple teams, and Traffic!

That’s easy to remember!

Before we finish, can you summarize when microservices should be used?

Microservices are ideal for large applications needing high availability and where multiple teams are involved.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
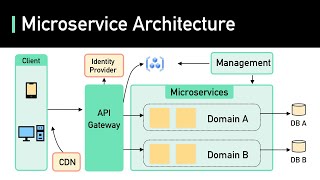
Microservices Architecture is a modern approach to application development where large applications are divided into smaller, self-contained services. Each service operates independently, communicates through APIs, and can be deployed and scaled independently. This architecture is ideal for large applications and those requiring high availability.
Detailed
Microservices Architecture
Microservices Architecture represents a significant shift from traditional monolithic designs, wherein applications are built as cohesive units. Instead, microservices structure applications as a collection of loosely coupled services, each responsible for a specific business function. These services communicate through APIs, allowing for easier integration and flexibility.
Key Characteristics
- Decoupled Services: Each service can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently, enhancing the overall resilience of the application.
- Independent Deployment Cycles: Services can be updated without affecting other parts of the application, leading to faster iterations.
- Scalability: As demand increases, additional instances of the services can be deployed, optimizing resource utilization.
- Complex Management: While microservices improve modularity, managing and deploying multiple services can become complex, especially at scale.
When to Use Microservices
- Large Applications: Ideal for systems that need to manage high traffic and scale efficiently.
- Multiple Development Teams: Projects with various teams working on different services can benefit from independent service management.
- High Availability & Fault Tolerance: Systems requiring continuous uptime perform better with microservices, as issues in one service do not halt the entire system.
Microservices thus enhance the flexibility and maintainability of full-stack applications, setting the stage for more robust projects.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Microservices Architecture
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Microservices is a more modular approach where an application is broken down into smaller, independent services, each responsible for a specific function. These services communicate with each other via APIs, and each service can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Detailed Explanation
Microservices architecture is a design approach that partitions an application into multiple services. Each service performs a specific role within the application and operates independently. This means that if you want to update a service or add new features, you can do so without affecting the entire application. They typically communicate using APIs, which are standard methods for allowing different services to exchange data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant where each chef specializes in a different dish—one chef makes pasta, another does desserts, and a third handles salads. If a new dessert becomes popular, the dessert chef can create it without needing to ask the pasta chef to change anything. This is similar to how microservices operate in that each service can evolve independently.
Key Characteristics of Microservices
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Key Characteristics:
- Decoupled services
- Independent deployment cycles
- Scalable by adding more instances of services
- Complex to manage and deploy, especially at scale
Detailed Explanation
The microservices architecture has several important characteristics:
- Decoupled services: Each service can function independently from the others, which makes the system easier to manage and update.
- Independent deployment cycles: Since services are autonomous, they can be deployed at different times without requiring the entire application to go down.
- Scalability: You can scale individual services based on demand. For example, if one part of the application, like user authentication, needs more resources, only that service can be scaled up rather than the whole application.
- Complex management: Although the modular approach has its advantages, managing many independent services can be challenging due to the need for coordination and monitoring.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a large concert where each performer plays a different instrument. If the drummer needs to practice more often, they can do that separately without making the guitarist stop playing. However, the concert organizers need to coordinate between all musicians to ensure the entire performance goes smoothly, reflecting the complexity of managing many stakeholders in microservices.
When to Use Microservices
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When to use:
- Large applications that need to scale efficiently
- Projects with multiple teams working on different parts of the system
- Systems that require high availability and fault tolerance
Detailed Explanation
Microservices are particularly beneficial in certain situations:
- For large applications that require flexibility and scalability, microservices allow developers to build and deploy parts of the application independently, adapting to user needs as they grow.
- Multiple teams can work in parallel on different services without stepping on each other's toes, speeding up development and facilitating continuous integration.
- High availability and fault tolerance are critical for applications that must be operational at all times. Microservices can reroute traffic if one service fails, hence minimizing downtime.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a hospital where different departments like emergency, radiology, and surgery operate independently but must communicate when a patient is referred. If one department is overloaded, it doesn’t halt the entire hospital's operations. Similarly, with microservices, if one service runs into issues, other services can continue to function flawlessly.
Key Concepts
-
Microservices: An architectural style structuring applications as collections of loosely coupled services.
-
Scalability: The ability to efficiently increase capacity to handle growth in demand.
-
Fault Tolerance: A system's ability to maintain operational functionality despite failures.
Examples & Applications
An e-commerce application utilizing microservices for user management, product catalog, and payment processing.
A large-scale news website where each section (sports, politics, entertainment) is handled by individual microservices.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Microservices break apart, for scaling's where we start!
Stories
A team of developers built an app, but they found it too complex. They divided it into microservices – user management, payment, and notifications – and suddenly everything scaled smoothly!
Memory Tools
DIP - Decoupled, Independent, Parallel for remembering microservices traits.
Acronyms
LMT - Large systems, Multiple teams, Traffic signify when to use microservices.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Microservices
An architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services.
- Decoupled Services
Independent components of an application that interact through APIs, allowing for modularity and scalability.
- APIs
Application Programming Interfaces that allow different software components to communicate.
- Scalability
The capability of a system to increase in performance under an increased load.
- Fault Tolerance
The ability of a system to continue operating properly in the event of a failure of some of its components.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
