MVC Pattern (Model-View-Controller)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to MVC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the MVC pattern. Does anyone know what MVC stands for?

Model, View, Controller!

Exactly! The MVC pattern divides our application into three key components. Let's start with the Model. Can anyone tell me what role the Model plays?

The Model represents the data and the business logic of the application, right?

Spot on! It manages the data, logic, and business rules. Now, what about the View?

The View is what the user interacts with, displaying the data in a user-friendly way.

Yes! And finally, what does the Controller do?

It processes user inputs, works with the Model, and updates the View!

Great recap! The MVC pattern allows for flexibility, easier maintenance, and clear role separation. Remember: M for data, V for display, and C for control! This structure helps keep applications organized and manageable.
Benefits of MVC Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the components, let’s discuss the benefits of using the MVC pattern. What do you think is a major advantage?

I think it allows for better organization and separation of concerns.

Correct! This separation makes it easier to update and manage complex applications. Can anyone think of another benefit?

It also improves scalability, right? Each component can be developed independently.

Exactly! And what about testing — how does MVC help with that?

Testing individual components becomes more manageable because they are decoupled!

Yes! So, remember: MVC's separation promotes better organization, scalability, and testing. To help remember this, think of MVC as 'Manageable, Scalable, Testable'.
Real-world Applications of MVC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at how MVC is used in real-world applications. Can anyone provide an example of a framework that utilizes MVC?

I think Ruby on Rails uses the MVC pattern!

That's right! Rails is a perfect example. What about in the PHP world?

Laravel also follows the MVC architecture!

Yes! Almost every popular web framework has some form of the MVC pattern integrated. Can anyone think of an advantage this gives developers using those frameworks?

It standardizes the way we build applications, making it easier to onboard new developers.

Exactly! Familiarity with MVC helps teams work together more effectively. Remember: MVC is widely used because it simplifies complexity through separation. Think of it as a 'Map for Code'!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern is a software architectural pattern that separates an application into three main components: Model, View, and Controller. This separation enhances modularity, making it easier to manage complexity, update code, and test applications. Each component has its own responsibilities, which facilitates independent development and scalability.
Detailed
MVC Pattern (Model-View-Controller)
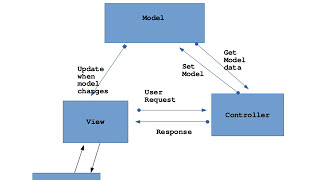
The MVC design pattern is a widely used architectural pattern for developing web applications. It divides an application into three interconnected components:
- Model: This is the core of the application, representing the data and the business logic. It manages the data, logic, and rules of the application.
- View: This component is responsible for rendering the user interface and displaying data to the user. It takes input from users and presents it in a format that is consumable.
- Controller: Acting as an intermediary between Model and View, the controller processes user inputs from the View, interacts with the Model to retrieve or modify data, and updates the View accordingly.
Significance
The MVC pattern facilitates a decoupled architecture where each component can be developed and tested independently. This separation simplifies management of complex applications, enhances scalability, and encourages code reuse. The pattern also aids teams in organizing their code structure by offering clear pathways of interaction via defined contracts between components.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
The Role of the Model
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Model: Represents the data layer and logic.
Detailed Explanation
The Model in the MVC pattern acts as the source of data and business logic in an application. It handles data processing, storage, and retrieval, ensuring that the data is accurate and up-to-date. When changes occur in the Model (for instance, a database update), it notifies the View to reflect these changes accordingly.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Model as a library. Just like a library holds books (data), and you can retrieve or update your knowledge there, the Model manages all the application's data and logic. When you need a specific book (data), the librarian (Model) helps you find it, and if a new book is added, the library system updates its catalog (notifies the View).
The Role of the View
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• View: Represents the UI components.
Detailed Explanation
The View is responsible for displaying the data provided by the Model to the user. It ensures that the user interface is engaging and accessible by presenting the information in a visually appealing format. The View listens to the Model for any updates and refreshes the display accordingly to keep the user informed.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are watching a cooking show. The View is like the television screen that presents everything happening in the kitchen (data from the Model). If the chef cooks something new, the camera (View) adjusts to show it clearly to the audience. When there are changes in the kitchen (Model updates), the View updates the display for everyone watching.
The Role of the Controller
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Controller: Coordinates the interaction between the Model and View.
Detailed Explanation
The Controller acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View. It processes user inputs, makes decisions based on those inputs, and updates the Model accordingly. When the Model changes, the Controller also informs the View so that it can display the updated data to the user. This separation of concerns allows for a clean and organized application structure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Controller as the director of a play. The director (Controller) communicates with both the actors (Model) and the stage crew (View). When the director receives feedback from the audience (user input), they decide whether to adjust the performance (update the Model) and instruct the stage crew on how to change the scenery (update the View).
Key Concepts
-
Model: Represents the data and logic of the application.
-
View: Represents the user interface that displays data.
-
Controller: Manages the flow of data between Model and View.
-
Separation of Concerns: Principle of dividing application into distinct components.
-
Scalability: The ability for an application to grow and handle increased demand.
Examples & Applications
In an e-commerce web application, the Model might handle user data and orders, the View could present the catalog to users, and the Controller would manage interactions like adding items to the cart.
In a blogging platform, the Model could manage articles and user comments, the View would render these to the user interface, and the Controller would process user submissions like new comments or articles.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Model's the data, View’s for the show, Controller’s the link, making it flow!
Stories
Imagine MVC as a theater: the Model is backstage managing scripts (data), the View is the actor performing on stage (UI), and the Controller is the director coordinating the scene (user actions).
Memory Tools
Remember: M for Managing Data, V for Visualizing Output, and C for Controlling Interactions - 'MVC'.
Acronyms
MVC
for Model
for View
for Controller - remember it as the foundation for organized coding.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Model
The data layer that represents the core of the application's data and logic.
- View
The user interface component that presents data to the user.
- Controller
The intermediary that processes user input, interacts with the model, and updates the view.
- Separation of Concerns
The principle of organizing code into distinct sections, each managing its own area of responsibility.
- Scalability
The ability of a system to handle growth, such as increased loads or expanding features, efficiently.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
