Modified Compaction Test
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Compaction Testing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the Modified Compaction Test. Can someone tell me why soil compaction is important in construction?

I think it's to prevent things like settlement in buildings.

Exactly! Compaction reduces voids in the soil, which minimizes swelling and shrinkage. Who can explain what happens when soil is compacted dry of optimum moisture?

It has greater swell and swell pressure!

Great point! We can remember that with the acronym 'SWELL' — Swelling When Engaged in Low moisture.

Does that mean wet soil is better for compaction?

Yes, generally! Wet soil allows for better particle orientation. To summarize, soil compaction is critical for stability, minimizes voids, and helps control swell.
Understanding the Apparatus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the equipment used for the Modified Compaction Test. Can anyone name the components?

There's a cylindrical metal mould and a rammer!

Correct! The mould has specific dimensions: 101.6 mm diameter and 116.8 mm height. Why do you think we need to use a detachable base plate and collar?

To hold the soil in place while we compact it?

Absolutely right! And each layer is compacted with 25 uniform blows. This consistency is critical for accurate results. Can someone summarize why each step might be important?

It ensures the soil is compacted evenly, so we get a reliable density measurement.

Exactly! Consistency is key.
Procedure of the Modified Compaction Test
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s walk through the procedure of the Modified Compaction Test. First, how much soil do we need to start with?

About 3 kg of dry soil, right?

Correct! And why do we need to pulverize the soil?

To make sure there are no lumps that would affect the compaction?

Exactly! Next, we mix in water. The amount of water changes based on the soil type. Why do you think we need to test multiple water contents?

To find the optimal moisture level for the best compaction?

Spot on! Each trial helps us determine the best conditions for compaction. Anyone remember how many trials we should conduct?

At least six trials, and some should be after decreasing bulk density.

Great summary! Remember, testing thoroughly gives us the best data.
Significance of the Modified Compaction Test
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think the Modified Compaction Test was developed during World War II?

Maybe to help build airfields that could support heavy planes?

That's correct! The Army needed safe, dependable runways. The test remains relevant today in civil engineering for building strong foundations. Can anyone provide an example of where this might apply?

Airports and highways need to ensure the soil can carry heavy loads.

Exactly! The understanding of soil structure is essential in many fields. Remember, 'SOIL' - Stability Of Infrastructure Lies in compaction!

That's a good way to remember it!

To recap, the Modified Compaction Test is about ensuring soil stability for various constructions, stemming from military needs to civilian applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Developed during World War II, the Modified Compaction Test reflects advancements in soil engineering, particularly in achieving better compaction for airfields. The test minimizes void space, which significantly reduces soil swelling and shrinkage.
Detailed
Modified Compaction Test
The Modified Compaction Test is a vital procedure that allows engineers to assess the compaction of soil for various construction applications. This test was developed during World War II by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to ensure that airfields could support heavy aircraft. By reducing void spaces within the soil, the test effectively minimizes swelling and shrinkage, critical issues in the stability of soil foundations.
Key apparatus for the test includes a cylindrical metal mold, a detachable base plate, and a rammer. The procedure involves compacting dry soil that passes through a 4.75 mm sieve, mixing it with water in controlled amounts, and applying specific compactive efforts to achieve the desired density. Understanding this test is crucial for civil engineers when constructing stable and durable structures.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Modified Compaction Test
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In early days, compaction achieved in field was relatively less. With improvement in knowledge and technology, higher compaction became a necessity in field.
Detailed Explanation
The Modified Compaction Test emerged because earlier methods of achieving soil compaction were inadequate for modern engineering standards. As engineers gained more understanding of soil behavior and with advancements in construction technologies, there was a pressing need to achieve higher levels of soil compaction to support larger structures, particularly airfields.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge that is dry and fluffy versus one that is wet and compacted. Initially, when we tried to use the dry sponge for something heavy, it couldn’t support the weight well. However, after knowing how to wet it, squeeze it, and then it can hold much more without losing shape. Similarly, as our knowledge improved, engineers found better ways to compact soil.
Development and Purpose of the Test
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hence Modified Compaction Test became relevant. It was developed during World War II by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineering to better represent the compaction required for airfield to support heavy aircraft.
Detailed Explanation
The need for the Modified Compaction Test was identified during World War II. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers realized that for airfields, which needed to support heavy military aircraft, it was crucial to ensure the ground was solid enough. This led to the creation of a testing method that could accurately reflect the compaction necessary for such demands.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a parking lot for a fleet of large trucks. If you just laid the surface without checking how strong it was, heavy trucks might drive over it and sink or get stuck. The Modified Compaction Test is like a rigorous check to ensure that the surface can withstand that weight without failing.
Key Concepts
-
Modified Compaction Test: A procedure developed for better soil compaction that minimizes void space.
-
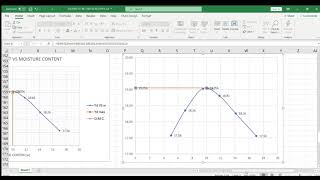
Optimum Moisture Content: The ideal water content for achieving maximum compaction density in soil.
-
Compaction Procedure: Involves weighing soil, mixing with water, layering in a mold, and applying blows of force.
-
Historical Significance: Developed for military applications, essential for building airfields.
Examples & Applications
Airports use the Modified Compaction Test to ensure runway stability under heavy aircraft.
Road construction utilizes the test to guarantee longevity and safety in vehicular traffic.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Compaction's key, listen well, / It keeps structures safe, can't you tell?
Stories
Once there was a runway needing support. Engineers mixed earth and water, compacting with a strong rapport, ensuring planes wouldn’t fall or sways, allowing flights on sunny days.
Memory Tools
To remember the steps of the compaction test, think 'Mold, Mix, Measure, Compact!'
Acronyms
Remember 'SWELL' for soil compaction
Stability With Effective Layering.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Compaction
The process of denser packing of soil which minimizes voids, enhancing stability.
- Swell Pressure
Pressure exerted by soil when it absorbs water and expands.
- Optimum Moisture Content
The moisture level at which soil achieves maximum density upon compaction.
- Bulk Density
Mass of a given volume of soil, determining its compactness.
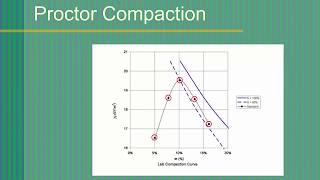
- Proctor Test
A standard laboratory test used to determine the optimum moisture content and maximum dry density of soil.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
