Application of Consistency Checks in Engineering
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Consistency Checks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss the significance of consistency checks in engineering, specifically regarding rainfall records. Why do you think accuracy is so important?

Inaccurate data can lead to poor design decisions!

Exactly! If our flood estimations are off, we could face major disasters. Can anyone give me an example of where this might happen?

If a dam is built based on incorrect flooding data, it might not hold up during heavy rain.

Great point! This can lead to catastrophic failures. Remember the acronym A.C.E., which stands for Accurate, Consistent, Effective, to remind us of the importance of data integrity in engineering.

So how is consistency checked?
Applications of Consistency Checks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into specific applications. How do you think rainfall consistency affects flood estimation?

Inconsistent data could underestimate the potential flood, right?

Exactly! Flood estimates rely on accurate rainfall data. Moving on, what role does data consistency play in reservoir operations?

If the data is off, we might not store enough water or could release too much!

Well said! Efficient reservoir management is critical for supply management. Remember the mnemonic D.E.C., which stands for Design, Evaluate, Control, highlighting the process.

Got it! And what about urban hydrology?
Consistency in Climate Change Research
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's discuss climate change research. Why do we need consistent data for this?

To identify real trends without misinformation!

Exactly! Valid trends are essential for understanding environmental changes. Let's conclude with a quick summary. What's the key takeaway from our discussions?

Consistency checks are vital for safe and effective engineering decisions!

Absolutely! Remember, the integrity of our engineering work hinges on reliable data!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Consistency checks are vital in engineering to ensure the reliability of rainfall data used for various applications such as flood estimations, reservoir operations, urban hydrology, and climate change research. Inconsistent data can lead to significant design flaws and misinformed decisions.
Detailed
Application of Consistency Checks in Engineering
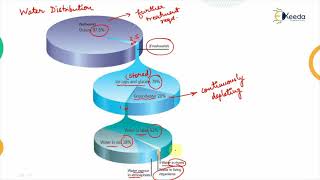
Consistency checks are essential for accurate rainfall data, which is crucial in various engineering applications. This section highlights four key applications where consistent data is paramount:
- Design Flood Estimation: Accurate flood estimation depends on reliable rainfall data; inconsistent figures may lead to underestimating or overestimating flood risks, impacting infrastructure durability.
- Reservoir Operation Studies: Historical rainfall data's reliability is vital for effective reservoir management, influencing decision-making regarding water storage, release patterns, and maintaining ecological balance.
- Urban Hydrology: In urban settings, drainage systems must be designed with precise intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves based on consistent rainfall data to prevent flooding and ensure public safety.
- Climate Change Research: Long-term climate studies require homogenized data to establish valid trends and patterns. Inconsistencies can skew interpretations affecting policy and conservation efforts.
Addressing these concerns involves systematic application of consistency checks to maintain data integrity for sound engineering practices.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Design Flood Estimation
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Inconsistent data can underestimate or overestimate flood magnitudes.
Detailed Explanation
When estimating potential flood scenarios for engineering projects, it's crucial to rely on accurate rainfall data. If this data is inconsistent, engineers risk either underestimating the severity of floods, which can lead to insufficient drainage capacity, or overestimating them, which can result in unnecessarily expensive infrastructure. Thus, consistency checks ensure that the data used in modeling flood risks is dependable.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a weather forecast that has been wildly inconsistent – one day it predicts sunny weather, and the next day it warns of a torrential downpour. If city planners based their flood defenses on 'sunny' data, they might face disastrous flooding when the downpour occurs. This highlights why maintaining consistent data is crucial for accurate flood estimation.
Reservoir Operation Studies
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Reliability depends on historical rainfall input.
Detailed Explanation
Reservoir designs and operations depend heavily on historical rainfall data. For example, if historical records show that a reservoir has been filled to certain levels during high rainfall years but those records are inconsistent, the engineers may either miscalculate the reservoir's capacity or misjudge the necessary outflow strategies during heavy rainfall. Consistency checks enhance the reliability of this historical data, which in turn informs better operational strategies.
Examples & Analogies
Think about managing your savings account. If you often miscalculate your monthly income, you might either save too little or spend too much, leading to financial trouble. In the same way, reservoir operations rely on precise rainfall data to ensure water supply and flood safety.
Urban Hydrology
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Design of drainage systems needs accurate intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves.
Detailed Explanation
Urban areas require effective drainage systems that can handle rainfall events without causing floods. The design of these systems often relies on IDF curves, which represent the relationship between the intensity, duration, and frequency of rainfall events. If the rainfall data that feeds into these calculations is inconsistent, it can result in drainage systems that are either overbuilt, wasting resources, or underbuilt, leading to potential flooding. Therefore, ensuring the consistency of rainfall data is essential for creating effective urban drainage solutions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sponge that’s designed to soak up water. If you know how much water to expect based on past rain, you can make a perfect sponge. But if your rain data is unreliable, the sponge might be too small or too big, leading to water spills regardless. This is akin to urban drainage systems relying on precise data to function effectively.
Climate Change Research
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Long-term studies need homogenized data for validity.
Detailed Explanation
Climate change research often depends on historical weather patterns to detect trends over time. Inconsistent data can obscure true climate signals, making it challenging to draw accurate conclusions about changes in weather and rainfall over decades. Therefore, homogenizing data—correcting inconsistencies—is crucial for credible long-term climate studies, ensuring that scientists can reliably assess changes and make informed predictions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of climate change research like piecing together a jigsaw puzzle. If you have pieces that don't quite fit together because their shapes are inconsistent, the complete picture will always look distorted. Homogenizing data is like smoothing the edges of those puzzle pieces to ensure they create a clear and accurate picture of our climate.
Key Concepts
-
Design Flood Estimation: Ensures structures can withstand potential flooding events.
-
Reservoir Operation Studies: Relies on historical data to manage water resources effectively.
-
Urban Hydrology: Accurate data leads to effective drainage and flood prevention.
-
Climate Change Research: Consistent data is critical for understanding long-term climate patterns.
Examples & Applications
Using corrected rainfall data to prevent overflow in reservoir designs.
Employing consistent rainfall records to create reliable urban drainage systems that prevent flooding.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Data must be true and clear, or build we might in fear!
Stories
Imagine a builder relying on faulty blueprints, the entire structure collapsing. This illustrates why consistent checks are essential in engineering.
Memory Tools
C.A.R.E - Consistency Assures Reliable Engineering.
Acronyms
D.E.R.C. - Design, Evaluate, Revise, Correct for effective engineering outcomes.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Consistency Checks
Procedures used to evaluate the reliability and accuracy of data, particularly in rainfall records.
- Design Flood Estimation
The process of predicting potential flood magnitudes that an engineering project must withstand.
- Reservoir Operations
The management of water levels and storage in reservoirs to meet demands and ecological needs.
- Urban Hydrology
The study of water movement and quality in urban environments, focusing on drainage and flood management.
- Climate Change Research
The scientific study of climatic trends and their impacts on ecosystems and human activities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
