Definition of Evaporation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Evaporation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are delving into the process of evaporation. Can anyone tell me how you would define evaporation?

Is it when water turns into vapor, like when you boil water?

Exactly! Evaporation occurs when water changes from a liquid state to a vapor phase due to energy absorption, primarily from sunlight. This is crucial in the hydrological cycle. Let's remember this key point with the acronym 'DREAM' - 'D' for 'direct energy', 'R' for 'redistribution', 'E' for 'evaporation', 'A' for 'atmospheric importance', and 'M' for 'moist soils'.

So, it happens at the surface of lakes and wet soil, right?

Correct! The process predominantly occurs at the surface of water bodies and moist soils, meaning that where water meets air, evaporation can take place.
Influencing Factors of Evaporation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've defined evaporation, let's talk about what influences its rate. Who can name a factor affecting evaporation?

Does temperature affect it?

Yes! Higher temperatures increase the rate of evaporation. Warm air can hold more moisture. If we remember the acronym 'SHWAP' - 'S' for 'Solar radiation', 'H' for 'Humidity', 'W' for 'Wind speed', 'A' for 'Atmospheric pressure', and 'P' for 'Temperature', we can easily recall these factors. Can anyone describe how wind speed affects evaporation?

Wind helps by moving the saturated air away from the surface, right?

Exactly! Wind increases evaporation rates because it maintains a high vapor pressure gradient. Excellent participation, everyone!
Why Understanding Evaporation Matters
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s reflect on why understanding evaporation is vital. Can anyone think of a real-world application related to agriculture or engineering?

It's important for irrigation planning, right? We need to know how much water is lost through evaporation.

Absolutely! Accurate knowledge of evaporation rates helps in estimating water losses, thus aiding in effective irrigation planning. Remember the phrase 'Every Drop Counts'. What does that mean for both agricultural practices and water conservation measures?

If we know how much water evaporates, we can better manage our water supplies!

Precisely! Proper management ensures sustainable use of our water resources. Great discussion today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Evaporation refers to the transformation of water from a liquid state to vapor, facilitated by energy absorption, predominantly from solar radiation. This process occurs at the surface of water bodies and moist soils and is influenced by various climatic factors.
Detailed
Definition of Evaporation
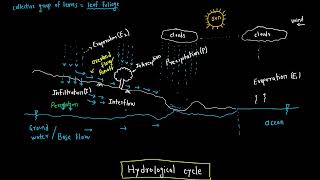
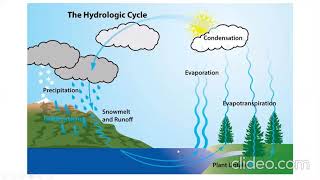
Evaporation is a critical process in the hydrological cycle, referring to the phase change of water from liquid to vapor. This transformation results primarily from the absorption of energy, typically from solar radiation. Evaporation predominantly occurs at the air-water interface of lakes, oceans, and moist soils, playing a vital role in the redistribution of water on Earth. The rate of evaporation varies based on several climatic conditions including temperature, solar radiation, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. Understanding evaporation is essential for effective water resource management, agricultural planning, and environmental engineering.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is Evaporation?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Evaporation is the process by which water changes from liquid to vapor phase due to the absorption of energy (usually from solar radiation).
Detailed Explanation
Evaporation is a natural process where water transitions from being a liquid to a gas (vapor). This change requires energy, which commonly comes from the sun's radiation. When solar energy heats up the water, it provides the necessary energy to overcome the forces holding the water molecules together in liquid form, allowing them to escape into the air as vapor.
Examples & Analogies
Think of evaporation like boiling water. When you heat water on the stove, the water heats up and turns into steam. In a similar way, when the sun heats a body of water, like a lake or puddle, the energy allows water molecules to break free and rise into the air.
Where Does Evaporation Occur?
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It primarily occurs at the surface of water bodies and moist soils.
Detailed Explanation
Evaporation mainly takes place at the surface of water bodies (like oceans, lakes, and rivers) and on moist soil. The reason it occurs at the surface is that it is here where the water molecules are most exposed to the air and sunlight, which provides the energy needed for the evaporation process.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine putting a small drop of water on a countertop. Over time, that drop will shrink and disappear as it evaporates. This happens because the energy from the surrounding environment causes the water to turn into vapor, similar to how puddles dry up after a rainstorm.
Factors Affecting Evaporation Rate
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The rate of evaporation depends on climatic conditions and surface characteristics.
Detailed Explanation
The amount of evaporation that occurs is influenced by several factors including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and the characteristics of the surface from which the evaporation is taking place. For example, higher temperatures typically increase evaporation rates because warm air can hold more moisture. Conversely, high humidity can slow down evaporation because the air is already saturated with moisture.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a hot summer day versus a cool, humid day. On a sunny summer day, you'll notice that a puddle dries up quickly because the heat encourages water to evaporate. However, on a humid day, even if it's warm, puddles may linger longer because the air is already full of moisture and can't absorb much more.
Key Concepts
-
Evaporation: The phase change of water from liquid to vapor.
-
Hydrological Cycle: The continuous cycle of water movement in the environment.
-
Factors Affecting Evaporation: Includes temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation.
Examples & Applications
A puddle on a sunny day evaporates faster due to higher temperatures and increased solar radiation.
Water on a smooth lake surface evaporates more slowly than on a wind-exposed area, demonstrating the effect of wind speed.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the sun is high and the air is dry, water goes up to wave goodbye.
Stories
Imagine a sunny day at the beach; the sun warms the ocean, causing waves to dance and evaporate, forming clouds in the sky.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SHWAP' for factors of evaporation: Solar radiation, Humidity, Wind speed, Atmospheric pressure, and Temperature.
Acronyms
DREAM for evaporation's importance
Direct energy
Redistribution
Evaporation
Atmospheric dynamics
Moist soil interactions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Evaporation
The process by which water changes from liquid to vapor phase due to energy absorption.
- Hydrological Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
- Solar Radiation
Energy emitted by the sun, crucial for the evaporation process.
- Vapor Pressure Gradient
The difference in vapor pressure between the water surface and the air above it, driving evaporation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
