Infiltration and Watershed Models
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Watershed Models
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into how infiltration models support watershed management. Can anyone tell me why infiltration is crucial in this context?

Infiltration helps determine how much water enters the soil rather than running off into streams.

Exactly! Infiltration is key to managing water resources. We use models to predict how water behaves in a watershed. Can anyone name a hydrologic model?

I think SWAT is one of them!

Correct! SWAT stands for Soil and Water Assessment Tool. It's great for predicting the impact of land management practices on water, sediment, and agricultural chemical yields.

Are there other models we should know about?

Yes, we also have HEC-HMS, which stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center - Hydrologic Modeling System. Let's remember these two key models: SWAT and HEC-HMS, or we can call them SWAT and HEC for short!

In summary, infiltration models like SWAT and HEC are critical in estimating how much water will infiltrate and how much will runoff.
Factors in Demographics and Modeling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss what factors these models consider when estimating infiltration. Why is it important to account for land use?

Different land uses can affect how quickly water soaks into the ground or runs off.

Exactly! Urban areas with lots of impervious surfaces lead to higher runoff. What about soil type?

Different soils have different infiltration capacities. Sandy soil holds less water than clay.

Right! Soil types significantly influence both infiltration rates and water retention. Finally, what is antecedent moisture?

It's the moisture in the soil before new rainfall, which affects how much water can infiltrate during a storm.

Excellent point! To summarize, key factors in infiltration models include land use, soil type, and antecedent moisture—let’s call them the 'big three'!
Benefits of Infiltration Models
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, why do you think it's essential to use accurate infiltration models in practice?

It helps us predict and manage flooding risks better.

Also, it guides decision-making for agricultural practices!

Absolutely! Accurate models are vital for flood management, agricultural planning, and conserving groundwater. They allow us to simulate different scenarios. How can we ensure the accuracy of these models?

By using real data to calibrate them!

Exactly right! Calibration with real data optimizes model parameters, ensuring better predictions. Summarizing this session, accurate infiltration models are crucial for managing resources effectively, making us all aware of their importance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Infiltration models are essential to hydrologic models, such as SWAT and HEC-HMS. These models incorporate various factors to estimate infiltration and runoff, helping in effective water resource management and planning.
Detailed
Infiltration and Watershed Models
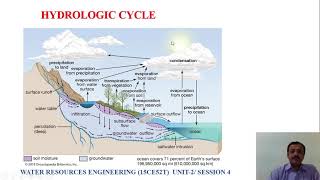
Infiltration models are a critical component of hydrologic modeling, helping to understand and predict how water moves through a watershed. Watershed management relies on accurate infiltration assessments to optimize water resource use and mitigate issues like flooding and soil erosion. This section highlights key models used in watershed management, such as the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) and the Hydrologic Engineering Center - Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS).
These models consider vital factors including land use, soil type, and antecedent moisture conditions to accurately estimate infiltration rates and subsequent runoff from precipitation events. Understanding these models allows hydrologists and engineers to develop effective strategies for flood management, irrigation, groundwater recharge, and overall watershed health.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Integration of Infiltration Models
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Infiltration models are integrated into hydrologic models like:
- SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool)
- HEC-HMS (Hydrologic Engineering Center - Hydrologic Modeling System)
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration models play a crucial role in hydrologic modeling, which refers to the simulation of water movement within an area. Specifically, two significant models are mentioned: SWAT and HEC-HMS.
- SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool): This model is used to assess the impact of land management practices on water, sediment, and agricultural chemical yields in large, complex watersheds. It integrates various processes such as rainfall, runoff, soil erosion, and plant growth to provide a comprehensive understanding of water balance within a watershed.
- HEC-HMS (Hydrologic Engineering Center - Hydrologic Modeling System): This model helps engineers and planners in stormwater management and flood forecasting. HEC-HMS simulates the rainfall-runoff processes, allowing users to analyze how different factors, including land use and soil properties, affect how water infiltrates and moves across the landscape.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to bake a cake without a proper recipe. You have your ingredients (water, soil, land use) but without knowing how they interact and how much of each you need, the result could be a disaster. Just like a recipe guides you to create the perfect cake, hydrologic models like SWAT and HEC-HMS guide water managers to understand and manage water in different landscapes effectively. These models allow scientists and engineers to predict how water flows and see the effects of different environmental conditions just as a recipe helps ensure a cake rises perfectly.
Methods for Estimating Infiltration and Runoff
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
SCS Curve Number Method, which accounts for land use, soil type, and antecedent moisture to estimate infiltration and runoff.
Detailed Explanation
The SCS Curve Number Method is a well-established approach for estimating runoff from a given rainfall event by considering various factors. Here’s how it works:
- Land Use: Different types of land cover, such as forests, urban areas, or agriculture, influence how much water can infiltrate the soil and how much will run off. For example, a forested area typically has higher infiltration than a paved parking lot.
- Soil Type: The physical characteristics of the soil, like texture and structure, determine its ability to absorb water. Sandy soils tend to allow more infiltration than clayey soils, which can become compacted and lead to increased runoff.
- Antecedent Moisture: This factor considers the amount of moisture already present in the soil before a rainfall event. If the soil is already saturated, less water will infiltrate and more will run off.
By integrating these components into the curve number calculation, land managers can make informed decisions about stormwater management and infrastructure planning.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge sitting in water. If the sponge is already soaked, it can’t hold any more water. Similarly, if the ground is wet before it rains (antecedent moisture), it won’t be able to soak up much more water, causing excess runoff. The SCS Curve Number Method is like a recipe that tells you how much water a sponge (or the ground) can absorb based on its condition, helping us understand how to manage water during storms effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Infiltration Models: Tools for predicting how water enters the soil, crucial for watershed management.
-
SWAT and HEC-HMS: Key hydrologic models used to estimate infiltration and runoff, taking into account various environmental factors.
-
Importance of Calibration: Using real data to refine model predictions enhances accuracy.
Examples & Applications
Using SWAT for predicting the impact of changing land use on local waterways.
Implementing HEC-HMS for flood risk management in urban planning.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
SWAT and HEC, models that we see, help water flow, as easy as can be.
Stories
Imagine a farmer using SWAT to decide when to water crops. He checks the soil moisture and the land use to optimize water use, ensuring his crops grow healthy.
Memory Tools
Remember SWAT and HEC - S for Soil, W for Water, A for Assessment, T for Tool; H for Hydrologic, E for Engineering, C for Center.
Acronyms
Use 'SWHEC' to remember both models
for SWAT
for Water
for Hydrologic
for Engineering
and C for HEC.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltration
The process of water entering the soil from the land surface.
- Watershed
An area of land where all precipitation collects and drains into a common outlet.
- SWAT
Soil and Water Assessment Tool, a model used for predicting water yield, sediment transport, and chemical yields in a watershed.
- HECHMS
Hydrologic Engineering Center - Hydrologic Modeling System, a model used for simulating rainfall-runoff processes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
