Infiltration in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Issue of Soil Crust Formation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss how soil crust formation affects water infiltration in arid and semi-arid regions. Can anyone tell me what they think a 'soil crust' is?

Is it like a hard layer that forms on top of the soil?

Exactly! This hard layer can block water from soaking into the soil. This can cause water to run off instead of being absorbed. Why do you think this is a problem?

It can lead to less water going into the ground, which can hurt plants.

Correct! Reduced water availability can affect plant growth and overall ecosystem health. Now, let's explore how we can manage this.
Management Strategies to Enhance Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To combat the effects of soil crusting, we can employ various management strategies. One effective method is contour bunding. Can anyone share what they know about it?

I think it involves building barriers along the land's contour?

Right! This helps to slow down water runoff and allows for more absorption into the soil. What about mulching? What benefits does it provide?

Mulching can help retain moisture and keep the soil temperature consistent, right?

Exactly! Mulching helps reduce evaporation and protects the soil. Finally, we have check dams. Why do we build these?

To capture water and help it soak into the ground more?

That's correct! Check dams slow down runoff and promote infiltration. Well done, everyone! Let's summarize.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Infiltration in arid and semi-arid regions is significantly affected by soil crust formation that reduces water absorption. To enhance infiltration, management strategies such as contour bunding, mulching, and constructing check dams are essential. These strategies help in efficiently capturing and utilizing scarce water resources.
Detailed
Infiltration in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions
In arid and semi-arid regions, soil conditions present unique challenges to water infiltration. Crust formation on the surface of soils often inhibits the ability of water to penetrate effectively, leading to increased run-off and reduced soil moisture. This phenomenon can significantly affect agricultural productivity and water resource management in these areas.
To address these challenges, various management strategies are employed:
1. Contour Bunding: This involves creating barriers along the contour lines of the land, which helps in slowing down water flow and enhances water absorption into the soil.
2. Mulching: Applying a layer of organic or inorganic materials on the soil surface can help retain moisture, moderate soil temperature, and reduce evaporation.
3. Check Dams: These small dams are constructed to intercept and retain rainwater or runoff, facilitating increased percolation into the ground.
These infiltration management strategies are crucial as they can significantly improve water retention in landscapes that are inherently fragile and prone to degradation.
Youtube Videos





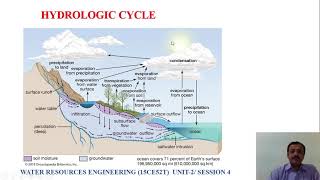



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Crust Formation in Soils
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Soils often have crust formation, reducing infiltration.
Detailed Explanation
In arid and semi-arid regions, soil can develop a crust on its surface when it dries out. This crust can create a barrier that prevents water from easily penetrating the soil. Because of this formation, the ability of the soil to absorb water effectively is significantly hindered. Crusts can form from factors like intense sunlight, wind, and low moisture, which compact the surface layer.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the crust on a pie. Just as the pie's crust can prevent liquid fillings from flowing out easily, the crust on the soil blocks water from soaking in. If you pour water on the crusted soil, much of it will run off rather than be absorbed.
Management Strategies to Enhance Infiltration
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Management strategies include contour bunding, mulching, and check dams to enhance infiltration.
Detailed Explanation
To combat the problem of reduced infiltration in arid and semi-arid regions, various management strategies are implemented. Contour bunding involves creating barriers along the contours of the land to slow water movement and encourage infiltration. Mulching, which involves covering the soil with organic materials, helps retain moisture and protect the soil surface from crust formation. Check dams are small barriers built across waterways to slow down water flow, allowing more time for it to infiltrate into the ground.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge trying to soak up water. If you place it on a flat surface, it may not absorb much water, as the liquid just runs off. However, if you tilt the surface slightly (like contour bunding), the sponge has a chance to soak up the water more efficiently. Similarly, using mulch and check dams helps soil absorb and retain moisture.
Key Concepts
-
Soil Crust: A hard surface layer restricting infiltration.
-
Contour Bunding: A method to enhance water absorption by constructing barriers.
-
Mulching: A technique used to conserve moisture and reduce evaporation.
-
Check Dams: Structures built to promote infiltration by capturing runoff.
Examples & Applications
In many arid regions, such as the deserts of the southwestern United States, crust formation significantly impacts rainfall absorption.
Farmers in semi-arid areas often use mulching to enhance soil moisture retention and improve crop yields.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In arid lands where soil is tough, keep water in with bunds, that's enough!
Stories
Once in a dry valley, farmers struggled to grow due to the hard crust on their soil. They learned about contour bunds and started planting with mulching. Soon, their crops thrived, watering the valley's hopes!
Memory Tools
Remember 'MCC' for managing infiltration: Mulching, Contour Bunding, Check Dams.
Acronyms
C.E.C. for Contour, Evaporation reduction with Covering (Mulch), and Capped with Dams.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Soil Crust
A hard layer on the soil surface that impedes water infiltration.
- Contour Bunding
A practice of building barriers along the contour lines of the land to enhance water absorption.
- Mulching
The application of organic or inorganic materials on the soil surface to retain moisture.
- Check Dam
A small dam built to intercept and retain runoff, facilitating water percolation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
