Importance in Water Resources Engineering
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Role of Infiltration in Drainage Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing how infiltration affects the design of drainage systems. Why is understanding infiltration important in this context?

Because if we know how much water the soil can absorb, we can design systems to handle excess runoff better!

Yeah! It helps prevent flooding and waterlogging!

Exactly! We can think of infiltration as our first line of defense against excessive surface runoff. Remember, we often say 'the sponge absorbs rain'—that's a good way to remember its role!

Is there a way to measure how much water the soil can soak up?

Great question! We use methods like infiltrometers to get a good estimate of the infiltration rate. Who remembers what that might look like?

I think it's like a ring that holds water, right? So, we can see how quickly the water disappears!

Absolutely! Now, let’s summarize: Infiltration is crucial for drainage design as it prevents flooding and assists in effective water management.
Groundwater Recharge and Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s look at infiltration’s role in groundwater recharge. How do you think this influences our water supply?

If water infiltrates well, then more water gets into aquifers, right?

So, it could help during dry seasons when we rely on groundwater!

That's correct! Properly estimating percolation rates allows us to sustain groundwater levels, essential for our water supply system. Think of infiltration as 'the lifeblood of our aquifers.'

So, improving infiltration could mean better water availability!

Yes! Thus summarizing: Infiltration is vital for groundwater recharge, ensuring sustainable water supplies. Remember, every bit that infiltrates is a contribution to our drinking water sources.
Irrigation Efficiency and Scheduling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now talk about how infiltration relates to irrigation design and efficiency. What have you learned about this connection?

It helps us know when to water our crops so we don’t waste water!

And we can adjust how much we apply based on how fast the soil absorbs it!

Exactly, saving both water and costs! A good saying here is 'water wisely, thrive abundantly.' Because if infiltration is high, we save watering time and resources!

What about during heavy rains? Can infiltration help then?

Yes! Higher infiltration reduces runoff during heavy rains, protecting fields from flooding. So let's conclude: Infiltration enhances irrigation scheduling and can be pivotal in managing rainfall effectively.
Soil Conservation Practices with Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about how improving infiltration can help with soil conservation. Why do you think this matters?

It can keep nutrients in the soil and reduce erosion!

Yes! Erosion can wash away soil and crops, so anything that helps keep it in place is good!

Correct! We often say, 'Soil is wealth.' Enhancing infiltration allows for better moisture retention and prevents erosion, fostering healthier soils.

So using things like contour bunding could help, right?

Definitely! To summarize today: Improving infiltration plays a significant role in soil conservation, directly impacting agricultural productivity and ecological health.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
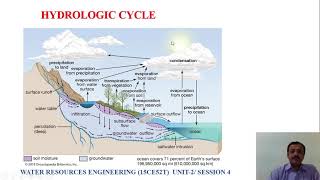
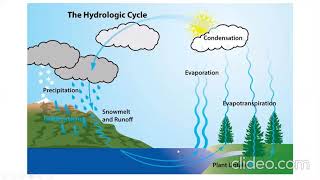
Infiltration is vital for effective water management in engineering, influencing design aspects of drainage systems, irrigation practices, and urban planning. By understanding and enhancing infiltration, engineers can mitigate waterlogging, optimize groundwater recharge, and implement erosion control strategies.
Detailed
Infiltration plays a pivotal role in water resources engineering due to its influence on hydrology and soil management. Key applications in this field include:
- Design of Drainage Systems: Effective management of water logging and surface runoff is critical for urban areas and agricultural lands.
- Groundwater Recharge Studies: Estimating percolation rates helps maintain sustainable groundwater levels.
- Irrigation Design: Scheduling and determining application efficiency is essential for effective resource utilization and conservation.
- Soil Conservation: Enhancing infiltration assists in reducing soil erosion, protecting the land's fertility.
- Urban Planning: Implementation of pervious pavements and rain gardens can greatly improve urban water management.
Each of these applications showcases the integral connection between infiltration processes and the practical challenges faced in civil engineering and sustainable resource management.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Design of Drainage Systems
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Design of Drainage Systems: Reducing waterlogging and surface runoff.
Detailed Explanation
Drainage systems are essential for efficiently managing excess water on land. When rain falls, some water seeps into the ground, but the rest can create puddles or even severe flooding. A well-designed drainage system collects this excess water and channels it away from where it can cause problems, such as agricultural fields or roads. This process helps prevent soils from becoming waterlogged, which can damage crops and create hazardous driving conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge sitting in a pool of water. If the sponge gets too full, water sits on top of it, making a mess. A drainage system is like creating small holes in the sponge to let excess water flow out, ensuring it doesn’t stay too wet.
Groundwater Recharge Studies
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Groundwater Recharge Studies: Estimating percolation rates.
Detailed Explanation
Groundwater recharge is the process by which water moves downward from the surface to fill the groundwater aquifers. Estimating percolation rates helps engineers understand how quickly water can infiltrate the soil and reach the underground water sources. This is crucial for maintaining a sustainable water supply, especially in areas prone to drought where there is a need for careful water management.
Examples & Analogies
Think about filling a bathtub with water. If the drain is open, the water flows out quickly. But if the drain is blocked, the water fills up fast. Understanding infiltration and percolation rates helps ensure that our 'bathtub' of groundwater remains filled and doesn't overflow or dry up.
Irrigation Design
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Irrigation Design: Scheduling and determining application efficiency.
Detailed Explanation
Efficient irrigation systems are crucial for providing crops with adequate water. By understanding infiltration rates, engineers can determine how much water to apply, when to do it, and how often this should occur. This minimizes water waste and ensures that crops receive just the right amount of irrigation necessary for their growth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a gardener who waters their plants without knowing how much water the soil can absorb. If they overwater, the plants may flood and die. If they under-water, the plants become thirsty and wilt. Proper irrigation design is like using a measuring cup to give each plant the perfect amount of water.
Soil Conservation
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Soil Conservation: Preventing erosion through infiltration enhancement.
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration plays a key role in maintaining soil health and preventing erosion. By allowing more water to infiltrate, soil structure improves, and the risk of erosion by surface runoff decreases. This not only protects the soil but also supports healthy plant growth and maintains the ecosystem.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sandcastle by the sea. If waves wash over it without soaking into the sand, the castle collapses. However, if the sand can absorb water, it becomes more stable and can resist the waves. Similarly, soil that can absorb water is less likely to wash away.
Urban Planning
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Urban Planning: Designing pervious pavements and rain gardens.
Detailed Explanation
In urban areas, managing stormwater is critical to reduce flooding and improve water quality. Engineers design features like pervious pavements and rain gardens that allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground rather than running off into sewer systems. This not only alleviates pressure on drainage systems but also helps recharge groundwater.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a parking lot covered in concrete. When it rains, the water quickly flows off, creating puddles. Now picture a similar parking area filled with special stones that let water seep through. This creates a mini-reservoir that nourishes the ground below instead of merely creating a slippery surface.
Key Concepts
-
Infiltration: The movement of water from the surface into the soil.
-
Drainage Design: Engineering practices to manage excess water and prevent flooding.
-
Groundwater Recharge: The process through which water makes its way back into aquifers.
-
Irrigation Efficiency: The effectiveness of water application in agriculture.
-
Soil Conservation: Practices that protect soil from erosion and degradation.
Examples & Applications
Implementing pervious pavements in urban areas to allow rainwater to infiltrate and recharge groundwater.
Using contour bunding in agricultural fields to enhance soil moisture retention and reduce runoff.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Infiltration, a helpful notion, keeps our land full of water's potion.
Stories
Imagine a sponge soaking up rainwater; similarly, soil absorbs water to nourish crops and prevent floods.
Memory Tools
Remember R.G.I.S - Recharge, Groundwater, Infiltration, Soil conservation, to recall the importance of water infrastructure.
Acronyms
DRAIN - Design, Recharge, Agriculture, Infiltration, Nature - highlights key focus areas for engineers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltration
The process by which water enters the soil from the surface.
- Groundwater Recharge
The process of water filtering down into aquifers from the surface.
- Drainage Systems
Structures designed to remove excess water from a given area.
- Irrigation Efficiency
A measure of how well irrigation systems supply water to crops without waste.
- Soil Conservation
Practices aimed at preventing soil erosion and maintaining soil health.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
