Measurement of Infiltration
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Infiltrometer Methods Overview
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss infiltrometers. Can anyone tell me what an infiltrometer is used for?

Is it to measure how fast water can seep into the ground?

Exactly! There are mainly two types: the double ring infiltrometer and the single ring infiltrometer. The double ring helps eliminate lateral flow, which can skew our results. A good way to remember it is 'Double is Accurate'—DA for infiltrometer.

Can the single ring still give us useful data?

It certainly can, but remember it’s simpler and less accurate. Use 'Single is Simple'—SIS to recall that point.

In summary, the double ring is more precise, while the single ring is easier to use.
Basin or Flooding Method
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, let's discuss the basin or flooding method. What do you know about measuring infiltration using a basin?

You put a known amount of water in a container, and measure how deep it gets over time, right?

Exactly! This method tracks how quickly water infiltrates an area. Remember, it’s helpful in understanding large water management systems. Use 'Basin for Big Data'—BBD to keep this in mind.

Is it used often in real-life situations?

Yes, very much! It's essential for planning irrigation and drainage systems.

In short, the basin method provides a straightforward approach to measuring how quickly water moves into the soil.
Soil Moisture Accounting Method
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s analyze the soil moisture accounting method—is everyone familiar with this approach?

Aren't we looking at how soil moisture changes before and after it rains?

Correct! By monitoring soil moisture profiles, we can estimate how much water has infiltrated. It's useful in long-term water management. A memory aid here could be 'Moisture Moves'—MM.

And does it give immediate results like the infiltrometers?

Not quite. It's more about gathering data over time rather than instantaneous measurements.

So, to summarize, soil moisture accounting is important for long-term planning and understanding infiltration patterns.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the different techniques used to measure soil infiltration rates, including infiltrometer methods, the basin or flooding method, and soil moisture accounting methods. Each method provides valuable insights into the infiltration capacity of soils, which is crucial for effective water management.
Detailed
Measurement of Infiltration
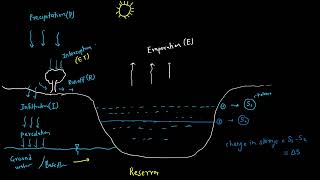
Infiltration measurement is a crucial aspect of hydrology and civil engineering as it helps determine how much water is absorbed by the soil during rainfall or irrigation. There are several techniques used to measure infiltration rates, generally categorized as follows:
1. Infiltrometer Methods
- Double Ring Infiltrometer: This method involves two concentric rings. Water is maintained in both, but the measurement is focused on the inner ring to reduce the effects of lateral flow, providing more accurate results.
- Single Ring Infiltrometer: A simpler technique that uses a single ring. While easier to implement, it is less accurate due to potential lateral water movement.
2. Basin or Flooding Method
In this approach, a known volume of water is applied to a designated area. The change in water depth over time is then used to calculate the infiltration rate, offering a practical means to assess the soil's absorption capabilities.
3. Soil Moisture Accounting Method
This method assesses changes in soil moisture levels before and after a rainfall event to estimate infiltration rates. It relies on monitoring moisture profiles to deduce infiltration behavior.
The accurate measurement of infiltration is essential for various applications in water resources engineering, including irrigation planning, drainage solutions, flood management, and groundwater recharge strategies.
Youtube Videos






![WRE Module2 [PART02]- Infiltration indices: phi-index and w-index, runoff by infiltration method](https://img.youtube.com/vi/TS6Mem4j-qY/mqdefault.jpg)

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Infiltrometer Methods Overview
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Various field methods are used to measure infiltration rates:
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration can be measured using different field methods. These methods are crucial for understanding how quickly water moves into the soil and can be applied in different contexts based on local conditions and needs. The three primary methods mentioned are infiltrometer methods, basin or flooding methods, and soil moisture accounting methods.
Examples & Analogies
Think of measuring how fast a sponge absorbs water. Just like you might use different containers or methods to see which one allows the sponge to soak up more water in a specific time, these methods help researchers determine how quickly various soils can absorb water.
Infiltrometer Methods Explained
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
26.4.1 Infiltrometer Methods
(a) Double Ring Infiltrometer
- Consists of two concentric rings.
- Water is maintained in both rings; infiltration from the inner ring is measured.
- Reduces lateral flow effects.
(b) Single Ring Infiltrometer
- Simpler but less accurate due to lateral water movement.
Detailed Explanation
Infiltrometer methods are specifically designed to measure how water infiltrates through soil. The double ring infiltrometer uses two rings: an inner ring where water is measured and an outer ring to minimize discrepancies from lateral flow (water moving sideways rather than down). This method provides a more accurate measure of infiltration. The single ring infiltrometer is easier to use but can lead to less precise measurements because it doesn’t account as well for lateral water movement, which can skew the results.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to measure how quickly a sponge absorbs water by placing it in a shallow dish versus a bowl with high sides. The dish (single ring) may let water spill over the sides easily, making it harder to know its true absorption rate. A bowl with a narrower top (double ring) helps keep the water focused around the sponge, giving a clearer picture of its absorbing ability.
Basin or Flooding Method
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
26.4.2 Basin or Flooding Method
- A known quantity of water is applied to a bounded area.
- Change in depth over time gives the infiltration rate.
Detailed Explanation
The basin or flooding method involves applying a specific volume of water to a contained area (a basin) and then monitoring how much the water level decreases over time. This drop indicates how quickly the soil is absorbing the water, providing a clear measure of the infiltration rate. It's a straightforward method that visually demonstrates how different soil types can handle water.
Examples & Analogies
Think of filling a bathtub and noticing how quickly the water level lowers after you stop adding water. If the drain is clogged, the water will stay higher longer, just like soil that can’t absorb water efficiently. This method helps us observe how quickly different soils can soak up that 'water' over time.
Soil Moisture Accounting Method
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
26.4.3 Soil Moisture Accounting Method
- Based on changes in soil moisture profiles before and after rainfall.
Detailed Explanation
The soil moisture accounting method tracks how much water is retained in the soil by comparing the moisture levels before and after it rains. By analyzing these changes, we can gain insights into how quickly water infiltrates into the ground and how much is being retained for plant use or contributing to runoff.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine checking how wet and dry a sponge feels before and after you've poured water on it. This method is like measuring those moisture levels to understand how much water the sponge (or soil) can hold at different times. It gives us a detailed view of water movement in the soil, which is critical for managing agricultural practices and ensuring crops get enough water.
Key Concepts
-
Infiltrometer: A tool used for measuring infiltration rates.
-
Basin Method: A technique to measure infiltration by applying water to a defined area.
-
Soil Moisture Accounting: A method for estimating infiltration based on changes in soil moisture.
Examples & Applications
A researcher uses a double-ring infiltrometer to obtain precise infiltration rates for a study on wetland restoration.
Farmers apply the basin method to determine the absorption capacity of their fields before choosing irrigation methods.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water in, water out, that's what the infiltrometers shout!
Stories
Imagine a sponge (the soil) sitting in a puddle (the basin). Over time, it soaks up the water, and we see how full it gets—this is how we measure infiltration!
Memory Tools
Remember 'Basin for Big Data' (BBD) for understanding the basin method's capacity to gather useful information.
Acronyms
D.A. for 'Double is Accurate' to remember the double ring infiltrometer's advantage.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltrometer
A device used to measure the rate of water infiltration into soil.
- Infiltration Rate
The speed at which water enters the soil, usually measured in mm/hr.
- Cumulative Infiltration
The total volume of water that has infiltrated per unit area over time.
- Soil Moisture Accounting
A method that measures changes in soil moisture to determine infiltration.
- Basin Method
A technique that applies a known quantity of water to a bounded area to measure infiltration.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
