Techniques to Improve Infiltration
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Soil Amendment
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the techniques we can use to improve infiltration is soil amendment. Can anyone tell me what that might involve?

It involves adding things like compost or mulch to the soil!

Exactly! Adding organic matter increases soil texture and structure, what’s the benefit of that for infiltration?

It helps the soil hold more water!

Great point! The more porous and nutrient-rich the soil, the better the infiltration.

So this means we can also improve plant growth?

Yes! Healthy plants create better soil structure, which leads to enhanced infiltration.

Remember: Organic Matter Improves Infiltration — OMII!
Contour Bunding and Trenches
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Another method is contour bunding. Can someone explain what that is?

It's when you build barriers along the slopes of the land, right?

Exactly! And why do we want to create barriers?

To slow down runoff so water can soak into the soil!

Right! This technique is crucial for preventing erosion and enhancing water retention.

Does it work well for all types of soil?

Great question! It's especially effective in areas with sloped terrain where runoff is a concern.

Remember: Bunding to Absorb Water — BAWW!
Artificial Recharge
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Artificial recharge can play a significant role in enhancing infiltration. Who can tell me what that means?

It involves creating setups like recharge wells or basins to improve water absorption.

Great! How does this help out the groundwater?

It allows for more water to seep into the ground and replenish aquifers!

Exactly! This technique is crucial in water-stressed areas. High tech helps low water!
Vegetative Measures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now talk about vegetative measures. How do they improve infiltration?

Plants help hold the soil together and trap water.

Correct! What else do cover crops do for the soil?

They add organic matter and nutrients to the soil!

Exactly! Healthy soil with lots of plant cover has significantly improved infiltration rates. Plants are powerful!

Remember: Plants Protect and Promote Infiltration — PPI!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Civil engineers implement several techniques to improve infiltration, including soil amendments, contour bunding, artificial recharge, and vegetative measures. These strategies help increase water absorption by soil, reduce runoff, and improve groundwater recharge, playing a vital role in water management and irrigation design.
Detailed
Techniques to Improve Infiltration
Infiltration is a critical process influencing groundwater recharge and surface runoff, making its enhancement vital in civil engineering. This section outlines several effective techniques that can be applied to improve soil infiltration:
- Soil Amendment: The addition of organic matter to improve soil texture and structure, thus enhancing its water-holding capacity. Organic materials increase porosity and provide nutrients essential for plant growth, which in turn help sustain soil structure.
- Contour Bunding and Trenches: Techniques that involve creating physical barriers along the contours of the land. These bunds help slow down surface runoff, allowing water to infiltrate the soil rather than flowing away, thereby effectively increasing infiltration rates.
- Artificial Recharge: The use of infiltration basins and recharge wells designed specifically to enhance the natural infiltration process. By channeling water into these systems, it can penetrate the soil more efficiently, facilitating groundwater replenishment.
- Vegetative Measures: Implementing cover crops and agroforestry systems enhances the soil's ability to retain water. Vegetative cover leads to reduced surface erosion, improved soil structure, and increased organic matter, all of which contribute to better infiltration rates.
These techniques are especially important in urban studies and agriculture, where efficient water management is crucial for sustainable practices.
Youtube Videos




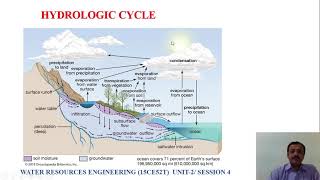


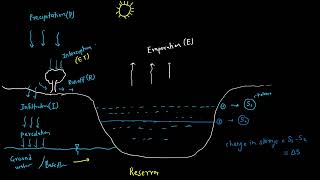
![WRE Module2 [PART02]- Infiltration indices: phi-index and w-index, runoff by infiltration method](https://img.youtube.com/vi/TS6Mem4j-qY/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Soil Amendment
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Soil Amendment: Adding organic matter.
Detailed Explanation
Soil amendment involves enhancing the soil structure and its ability to retain moisture by adding organic materials such as compost, manure, or peat. Organic matter improves soil porosity and increases its ability to hold water and nutrients. This leads to better infiltration as the soil becomes more receptive to water, allowing it to percolate down rather than running off the surface.
Examples & Analogies
Think of soil amendment like adding a sponge to a dry towel. When you add water to the towel, it quickly gets soaked up by the sponge, which helps improve its moisture retention. Likewise, organic matter in soil acts like that sponge, helping it absorb more water effectively.
Contour Bunding and Trenches
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Contour Bunding and Trenches: Reducing surface runoff velocity.
Detailed Explanation
Contour bunding involves creating earthen barriers or bunds along the contours of the land. This technique helps slow down water flow over the surface, allowing it more time to infiltrate into the soil. Trenching, which creates channels for water, can also capture and direct water to areas where it can be absorbed, reducing the speed at which water runs off. Both methods aim to improve water infiltration and minimize soil erosion.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine placing speed bumps on a road. Just as speed bumps slow down cars and give them time to process the road, contour bunds and trenches slow down water flow, giving it time to settle into the ground instead of rushing off.
Artificial Recharge
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Artificial Recharge: Infiltration basins and recharge wells.
Detailed Explanation
Artificial recharge involves human-made structures designed to enhance the natural process of groundwater recharge. Infiltration basins are shallow depressions that capture rainwater, allowing it to seep into the ground. Recharge wells are drilled holes where excess water can be injected underground, facilitating the replenishment of aquifers. These techniques are especially useful in areas where natural groundwater recharge is insufficient due to impervious surfaces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of artificial recharge like using a funnel to pour water into a bottle. The funnel directs the water into the bottle, ensuring that it gets in quickly and effectively. Similarly, infiltration basins and recharge wells channel excess water into the soil, enhancing water availability underground.
Vegetative Measures
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Vegetative Measures: Cover crops, agroforestry.
Detailed Explanation
Vegetative measures involve using plants to enhance soil structure and water infiltration. Cover crops, which are planted during the off-season, protect the soil from erosion and improve its organic matter content. Agroforestry combines agriculture with forestry practices, leading to more complex interactions between trees and crops that enhance soil health. Both practices increase the soil's infiltration capacity by improving its structure and reducing surface runoff.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a friendly neighborhood gathering as an analogy. Just like different friends bring diverse perspectives and fun activities that enhance the group dynamic, various types of plants in vegetative measures work together to improve soil health and water retention, creating a more resilient environment.
Key Concepts
-
Soil Amendment: Enhancing soil with organic materials.
-
Contour Bunding: Creating barriers along land slopes to reduce runoff.
-
Artificial Recharge: Artificially enhancing groundwater while aiding infiltration.
-
Vegetative Measures: Using plants to improve soil moisture retention.
Examples & Applications
Using compost to increase the organic matter content of soil.
Implementing contour bunding on a hillside farm to prevent erosion and promote water infiltration.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To add some organic matter, soil’s a little fatter; bunds will keep water, make it go longer and not scatter.
Stories
Once upon a time in a dry land, a farmer learned that by adding compost, building bunds, and planting trees, water could stay in the soil longer, nourishing the land.
Memory Tools
SOFA - Soil Organic Fertility Amendment!
Acronyms
BRAIN - Bunds Reduce And Improve Navigation (of water in soil).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Soil Amendment
The process of adding organic matter to soil to enhance its structure and nutrient content.
- Contour Bunding
The construction of embankments along the contour lines of the land to slow down water runoff.
- Artificial Recharge
Methods that facilitate the infiltration of water into the ground to replenish groundwater supplies.
- Vegetative Measures
Practices that utilize plants to improve soil structure and moisture retention.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
