Grading Scale Example (for each Criterion)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Grading Scale
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the grading scale used in MYP Year 5 Design. This scale helps us understand how your work is evaluated across four criteria. Can anyone tell me what those criteria are?

Is it Inquiring and Analysing, Developing Ideas, Creating the Solution, and Evaluating?

Exactly, great job! Each criterion is scored from 0 to 8. For instance, a score of 0 means not meeting any standards. Remember the acronym: *MEAN*—Minimal, Early, Average, Notable—for the levels from 1 to 4.

What about a score of 5 to 8?

Scores from 5 to 6 show competent performance that's detailed. Scores of 7 to 8 represent high-quality work. By understanding this scale, you can better aim for clarity and insight in your solutions.

So, our goal should be to reach levels 7 or 8, right?

Exactly! Always aim for high-quality work. Remember to reflect on your project as you progress, which leads us to our next session.
Applying the Grading Scale
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our next session, let's talk about how you can apply this grading scale to assess your work and the work of your peers. Why do you think that might be important?

It helps us understand our strengths and weaknesses, right?

Absolutely! Self-assessment using the scale can provide insight into which areas you excel and where you need improvement. Can anyone give me an example of a project aspect you might evaluate?

Maybe how well we identified the need for a solution?

Great example! Evaluating how well you explained and justified that need could be based on Criterion A. Using the scale helps you focus on quality and offers a path for improvement!

Would it help our groups as well?

Definitely! Peer feedback is invaluable as it encourages collaborative learning and improvement. Let's take this knowledge into our practice!
Reflecting on Quality Work
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our final session, let's focus on why aiming for high-quality work in design projects is vital. What impact can this have on your future endeavors?

If we make high-quality work now, we’ll be better prepared for real-world situations?

Exactly! High-quality work showcases your problem-solving skills and creativity. High scores reflect your effort and understanding of innovation and technology.

How can we ensure we reach those high scores?

By continually referring back to the grading scale! Use it to check your progress, ask for feedback, and refine your ideas. This solidifies your learning and output.

So we should keep the grading scale in mind throughout our projects?

Very much so! Think of it as your roadmap to success in designing. Keep practicing these skills, and you'll excel!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
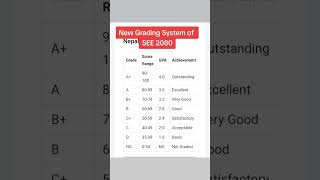
This section outlines the grading scale for assessing MYP Year 5 Design projects across four specific criteria. Each criterion is scored from 0 to 8, fostering a comprehensive evaluation system that aids students in understanding their performance and expectations.
Detailed
Grading Scale Example (for each Criterion)
In the assessment of MYP Year 5 Design, the grading scale is broken down into a clear framework for evaluating students' work across four criteria: Inquiring and Analysing, Developing Ideas, Creating the Solution, and Evaluating. Each criterion is graded on a scale from 0 to 8, offering a total possible score of 32 points.
Grading Levels:
- Level 0: Indicates that the work does not meet any of the established standards.
- Levels 1-2: Represents minimal achievement where the work is underdeveloped and lacks completeness.
- Levels 3-4: Demonstrates a basic understanding with some clarity and logic evident in parts of the work.
- Levels 5-6: Signifies competent performance, featuring appropriate detail and explanation throughout.
- Levels 7-8: Reflects high-quality work characterized by consistency, thoroughness, and insightful connections.
This structured grading system empowers students to engage in a comprehensive design process, enhancing their ability to problem-solve, think critically, and showcase innovation.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Grading Scale Levels
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Level Descriptor Summary (General)
0 Does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors.
1–2 Minimal achievement; work is underdeveloped and incomplete.
3–4 Basic understanding; some clarity and logic in parts.
5–6 Competent performance; appropriate detail and explanation.
7–8 High-quality work; consistent and thorough, showing insight.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines the grading scale for the assessment criteria in the MYP Year 5 Design programme. The scale ranges from 0 to 8, with different levels of achievement:
- 0 means the student did not meet any of the expected standards.
- 1-2 indicates that the work is very basic and incomplete, showing minimal effort.
- 3-4 suggests a fundamental understanding where some parts may be clear but lacks depth in logic.
- 5-6 represents competent performance where the student's work is thoughtful and includes appropriate levels of detail.
- 7-8 is the highest level of achievement, indicating thorough and insightful work, demonstrating a high quality of understanding and execution.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this grading scale like a sports competition. In a race:
- If a runner finishes last and doesn't meet the required distance, that's similar to a level 0.
- If a runner crosses the finish line but only barely makes it, that's like a level 1-2.
- A runner who finishes within a certain time shows some understanding of technique, similar to level 3-4.
- If a runner performs well and consistently meets their training goals, that’s like level 5-6.
- Finally, if they break a personal record or outperform the competition with skill, that’s comparable to level 7-8.
Key Concepts
-
Assessment Criteria: Standards established for evaluating student work.
-
Grading Scale: The method of scoring student performance on a range of 0 to 8.
-
Quality Work: The importance of producing thorough and insightful designs.
-
Reflection: The ongoing process of assessing one's work continually to achieve high standards.
Examples & Applications
When evaluating a project, a student may identify a specific need for improvement in a community, which would relate directly to Criterion A.
A student using 3D modeling software to present their design reflects the importance of Criterion B.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To score the best, put in your zest, from zero to eight, strive for the great!
Stories
Imagine a student named Alex who aimed for an 8 in their design project. Each week, he reflected on his work, got feedback, and made improvements, eventually achieving that goal!
Memory Tools
R.I.S.E. - Reflect, Improve, Score, Excel; a way to remember how to enhance work quality.
Acronyms
C.A.R.E. - Clarity, Analysis, Reflection, and Execution; key elements for high-quality design projects.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Assessment Criteria
The specific standards and components used to evaluate student work in the MYP Year 5 Design course.
- Grading Scale
A structured system ranging from 0 to 8 to evaluate student performance across four specified design criteria.
- Inquiring and Analysing
Criterion A emphasizes the identification of a problem and the need for research to inform a design solution.
- Developing Ideas
Criterion B focuses on creating feasible, innovative ideas and designs based on research.
- Creating the Solution
Criterion C entails demonstrating technical skills and producing a functional design solution.
- Evaluating
Criterion D requires testing and assessing a solution against established design specifications.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
