Extraction of Aluminium (Important Example)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Aluminium Extraction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're focusing on the extraction of aluminium from bauxite, a critical process in metallurgy. Why do you think aluminium is so widely used in our daily lives?

I think it's because aluminium is lightweight and durable.

Also, it doesn't rust easily, right?

Exactly! Its properties make it ideal for various applications. Now, what do you think is the first step in extracting aluminium?

We need to start with the ore, bauxite.

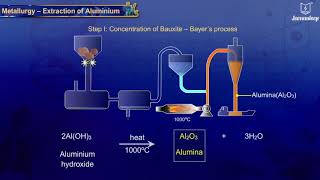
Correct, we extract aluminium from bauxite, which has the chemical formula Al₂O₃·2H₂O.
Electrolytic Reduction Method
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Aluminium extraction involves electrolytic reduction. Can anyone describe what this means?

It means using electric current to reduce the alumina to aluminium?

Yes, and we dissolve the alumina in cryolite to improve the process. Why do you think that is important?

It lowers the melting point, making it easier to conduct the process!

Exactly! Let's discuss the reactions happening at the electrodes. At the cathode, what do we get from Al³⁺ ions?

We get aluminium metal!
Electrolysis Reaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at the electrolysis reactions. What happens at the anode?

O²⁻ ions are converted into oxygen gas!

Right! We say: O²⁻ → ½O₂ + 2e⁻. This reaction emphasizes the balance of electric charges. Can anyone tell me why we need to remove the oxygen as a byproduct?

To keep the process going efficiently and avoid reactions that could stop the extraction!

Exactly! We must manage the byproducts carefully. How about summarizing the key processes we learned today?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Aluminium is extracted from bauxite (Al₂O₃·2H₂O) using the electrolytic reduction method, where molten alumina is dissolved in cryolite. Key electrolysis reactions at the cathode and anode are also explored.
Detailed
Extraction of Aluminium (Important Example)
Aluminium is primarily extracted from the ore bauxite, chemically represented as Al₂O₃·2H₂O. The extraction process involves electrolytic reduction, which is significant due to aluminium's extensive applications in technology and industry. The method consists of dissolving molten alumina in cryolite to lower the melting point and enhance conductivity. The electrolysis process involves two key reactions:
- At the Cathode:
Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al (Reducing aluminium ions to form aluminium metal)
- At the Anode:
O²⁻ → ½O₂ + 2e⁻ (Oxidizing oxide ions to form oxygen gas)
The electrolysis of alumina plays a crucial role in meeting global aluminium demand, making the understanding of this process essential in metallurgy.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Aluminium Ore - Bauxite
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Ore: Bauxite (Al₂O₃·2H₂O)
Detailed Explanation
The primary ore used for the extraction of aluminium is Bauxite, which is chemically represented as Al₂O₃·2H₂O. This compound consists of aluminium oxide combined with water. Understanding this chemical formula is crucial since it indicates the presence of aluminium that can be extracted.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine Bauxite as a treasure chest that contains precious aluminium. Just like you would need a map and tools to find and open a treasure chest, specific methods are needed to extract the valuable aluminium from its ore.
Method of Extraction - Electrolytic Reduction
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Method: Electrolytic reduction of molten alumina dissolved in cryolite.
Detailed Explanation
To extract aluminium from bauxite, a process called electrolytic reduction is used. This involves dissolving alumina (the aluminium-bearing compound from bauxite) in another compound called cryolite, which lowers the melting point and improves the conductivity. The mixture is then subjected to an electric current, allowing for efficient extraction of aluminium.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the process as baking in a well-prepared oven. Just like how specific temperatures and ingredients lead to a successful cake, using cryolite and electric current creates the right conditions to extract aluminium effectively.
Electrolysis Reactions
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electrolysis Reactions:
● Cathode: Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al
● Anode: O²⁻ → ½O₂ + 2e⁻
Detailed Explanation
During the electrolysis process, two key reactions occur. At the cathode (negative electrode), aluminium ions (Al³⁺) gain electrons and are reduced to form aluminium metal (Al). This reaction shows the reduction process where ions are transformed into a solid metal. At the anode (positive electrode), oxide ions (O²⁻) lose electrons to form oxygen gas (½O₂). These reactions are essential for understanding how aluminium is produced.
Examples & Analogies
This can be compared to a race: at the cathode, aluminium ions 'run' to meet electrons and become solid metal, while at the anode, oxide ions 'release' oxygen gas into the air, just as runners pass the finish line simultaneously creating a lively atmosphere.
Key Concepts
-
Bauxite: The primary ore used to extract aluminium.
-
Electrolytic Reduction: A method where electric current is utilized to extract metals from ores.
-
Cryolite: A substance that dissolves alumina, enhancing the efficiency of the extraction process.
-
Electrolysis Reaction: The chemical transformations at the cathode and anode during the extraction of aluminium.
Examples & Applications
The extraction of aluminium from bauxite using electrolytic reduction is a significant industrial process.
During the electrolysis of alumina, aluminium is deposited at the cathode while oxygen gas is released at the anode.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To extract the aluminium, bauxite we delve, electrolyze with cryolite, watch the metal proudly shelve!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a factory bustling with activity, workers solved the mystery of extracting aluminium from bauxite. They discovered how to use the magic of electrolysis with cryolite as their trusty companion, leading to shiny aluminium that everyone adored.
Memory Tools
Remember B.E.C.O. for Aluminium Extraction: Bauxite, Electrolysis, Cryolite, Oxygen.
Acronyms
Use the acronym A.O.C. to remember
- Aluminium
- Oxygen
- Cryolite.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bauxite
The primary ore of aluminium, consisting mainly of aluminium oxide and water.
- Electrolytic Reduction
A process that uses electrical current to drive a chemical reaction, extracting metals from their ores.
- Cryolite
A mineral used to dissolve alumina in the extraction process to reduce the melting point and improve conductivity.
- Electrode
A conductor through which electricity enters or leaves an electrolyte in the electrolysis process.
- Electrolysis
The process of using electric current to drive a chemical reaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
