Roasting and Calcination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Roasting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about roasting. Can anyone tell me what roasting involves?

Is it the process of heating ore?

Exactly! Roasting involves heating sulfide ores in the presence of air to convert them into oxides. This is important because oxides are easier to reduce later to extract metals.

What types of ores are commonly roasted?

Great question! Common examples include sulfur ores like Zinc Sulfide, ZnS. Remember, we need the air to facilitate the reaction!

What happens to the sulfur?

In the roasting process, sulfur is released as sulfur dioxide gas. Any guesses on why that’s significant?

Maybe it helps in purifying the metal?

Correct! The removal of sulfur makes the subsequent reduction process much cleaner.

### Summary: Roasting involves heating sulfide ores in air to convert them to oxides, essential for metal extraction.
Understanding Calcination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss calcination. Who can explain what calcination involves?

Is it heating ores too?

Yes, but it’s different! Calcination occurs in the absence of air and targets carbonate ores. The goal is to remove volatile impurities like carbon dioxide.

Can you give us an example of a carbonate ore?

Sure! A common example is Zinc Carbonate, ZnCO₃. When we heat this, we drive off CO₂, leaving us with zinc oxide.

Why do we need to remove CO₂?

Removing CO₂ makes the product purer and ready for the reduction process, where the oxide can be further reduced to obtain the metal.

### Summary: Calcination involves heating carbonate ores in the absence of air to remove CO₂, preparing them for metal extraction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Roasting involves heating sulfide ores in the presence of air to convert them into oxides, whereas calcination entails heating carbonate ores in the absence of air to remove volatile impurities. These processes are essential for preparing ores for subsequent reduction to yield metals.
Detailed
Roasting and Calcination
Roasting and calcination are fundamental processes in metallurgy that prepare ores for the extraction of metals. Both methods involve heating ores but under different conditions.
Roasting
- Definition: The process of heating ore in the presence of air.
- Purpose: To convert sulfide ores into their respective oxides, which are easier to reduce in later stages of metal extraction.
- Commonly Used For: Sulfide ores such as Zinc Sulfide (ZnS).
Calcination
- Definition: The process of heating ore in the absence of air.
- Purpose: To remove volatile impurities, particularly carbon dioxide from carbonate ores.
- Commonly Used For: Carbonate ores like Zinc Carbonate (ZnCO₃).
In summary, both roasting and calcination are critical in the metallurgy of metals, setting the stage for subsequent metal extraction methods.
Youtube Videos


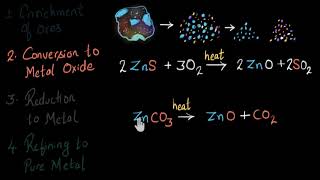





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Roasting Process
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Roasting
Heating ore in presence of air
Converts sulfides to oxides
Used for: Sulfide ores (e.g., ZnS)
Detailed Explanation
Roasting is a metallurgical process that involves heating ore in the presence of air. The main goal of roasting is to convert sulfide minerals into oxides. For instance, when zinc sulfide (ZnS) is roasted, it transforms into zinc oxide (ZnO) along with the release of sulfur dioxide gas (SO₂). This step is important because it prepares the metal for further extraction processes, such as reduction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of roasting as similar to cooking. When you roast marshmallows over a fire, the heat changes their texture and flavor, making them more enjoyable to eat. In a similar manner, roasting changes the chemical structure of sulfide ores, making them more suitable for extracting the desired metal.
Calcination Process
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Calcination
Heating ore in absence of air
Removes volatile impurities
Used for: Carbonate ores (e.g., ZnCO₃)
Detailed Explanation
Calcination is the process of heating ore without air, which allows it to lose volatile components, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂). For example, when zinc carbonate (ZnCO₃) is heated, it decomposes into zinc oxide (ZnO) and carbon dioxide. This is particularly useful for carbonate ores, as it helps in the purification of the material and prepares it for the subsequent steps in metal extraction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a pot of water with pasta boiling in it. If you keep it cooking without the lid, the water evaporates away, leaving the pasta cooked and ready to eat. Similarly, calcination removes unwanted gases from carbonate ores, leaving behind the solid metal oxide necessary for further extraction.
Key Concepts
-
Roasting: Process of heating sulfide ores in air to convert them to oxides.
-
Calcination: Process of heating carbonate ores in absence of air to remove CO₂.
-
Sulfide Ores: Ores containing metals combined with sulfur.
-
Carbonate Ores: Ores containing metals combined with carbonate.
Examples & Applications
Example of Roasting: Heating Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) in air results in Zinc Oxide (ZnO) and Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂).
Example of Calcination: Heating Zinc Carbonate (ZnCO₃) in absence of air produces Zinc Oxide (ZnO) and Carbon Dioxide (CO₂).
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the furnace, we roast with air, converting sulfur; it's only fair.
Stories
Imagine a miner uncovering zinc ores. He heats them with a breath of fresh air, turns sulfide into oxide, ready for the next stage of extracting the shiny metal.
Memory Tools
R.O.C - Roasting Ores in the air, Calcination Ores without air.
Acronyms
R.O.C.
Roasting (with air)
Calcination (without air).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Roasting
The process of heating sulfide ores in the presence of air to convert them into oxides.
- Calcination
The process of heating carbonate ores in the absence of air to remove volatile impurities like carbon dioxide.
- Sulfide Ores
Ores that contain metal combined with sulfur, such as zinc sulfide (ZnS).
- Carbonate Ores
Ores that contain metal combined with carbonate, such as zinc carbonate (ZnCO₃).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
