Physical Features
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Mountains of India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's explore the majestic mountains of India. Can anyone tell me the names of prominent mountain ranges?

The Himalayas, right?

Exactly! The Himalayas are the tallest mountains in the world. Remember, they stretch across the northern border of India. Can anyone think of another mountain range?

What about the Aravalli Range?

Great point! The Aravalli Range is one of the oldest mountain ranges and runs across several states in western India. Can anyone share what significance these mountains have?

They affect our climate and are important for water sources.

Absolutely! The Himalayas, in particular, act as a barrier against cold winds and are vital for the monsoon. Let's remember: *Himalayas = Largest, Aravalli = Oldest*.
Plateaus of India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to plateaus. Who can name some major plateaus in India?

The Deccan Plateau is one of them.

Right! The Deccan Plateau occupies a large part of southern India and influences the regional climate. Can someone tell me another plateau?

The Chotanagpur Plateau is also significant because it has rich mineral resources.

Exactly, Student_1! The Chotanagpur Plateau is known as the 'granary of India' due to its fertility. Let’s remember: *Deccan = Major, Chotanagpur = Mineral-rich*.
Deserts of India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about deserts. Who knows which desert is the most well-known in India?

The Thar Desert!

Correct! The Thar Desert is the only major desert in India and is unique for its dunes and desert ecosystems. What challenges does life face in the Thar Desert?

Water scarcity and extreme temperatures.

Exactly! Remember, the Thar Desert is not just about its dryness; it's a unique habitat. Let's summarize: *Thar = Largest desert, challenges = Water scarcity, extremes*.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
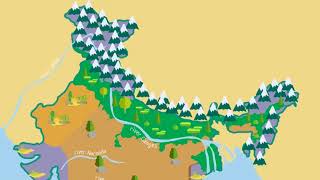
In this section, students will explore the key physical features of India, including its major mountains, peaks, plateaus, and deserts, which are essential for understanding the country’s geography. Some notable features include the Himalayas, the Deccan Plateau, and the Thar Desert.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In this section, we will delve into the physical features of India, which play a crucial role in defining the landscape and ecology of the country. Key categories covered include:
- Mountains: The section highlights prominent mountain ranges like the Himalayas, known for their towering peaks and significance to climate and cultures; the Aravalli, one of the world's oldest mountain ranges; and the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats, which are vital for biodiversity and agriculture.
- Peaks: The only specific peak mentioned is Mt. K2 (Godwin Austen), recognized as the second highest mountain in the world, which is significant for climbers and geographers alike.
- Plateaus: The section lists major plateaus including the Deccan Plateau, a vast volcanic plateau that influences weather patterns, the Chotanagpur Plateau rich in minerals, and the Malwa Plateau known for its agricultural produce.
- Deserts: The Thar Desert, situated in the northwest region of India, is characterized by its arid climate and unique ecosystems.
Understanding these physical features is essential for studying India's geographical diversity, human settlements, and resource distribution.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Mountains
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Mountains: Himalayas, Aravalli, Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats
Detailed Explanation
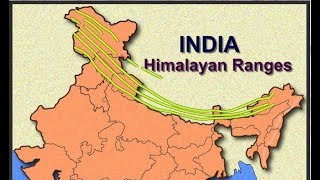
India is home to several major mountain ranges. The Himalayas are the tallest and most famous, forming a natural boundary between India and its northern neighbors. The Aravalli range runs from northwest to southeast, while the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats are two distinct ranges running parallel to India's western and eastern coasts, respectively. These mountains play crucial roles in influencing the climate and biodiversity of the regions where they are located.
Examples & Analogies
Think of mountains as the spine of the country, providing essential support and structure. Just like how our spine affects our posture and balance, mountains influence weather patterns and provide habitats for many species.
Peaks
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Peaks: Mt. K2 (Godwin Austen)
Detailed Explanation
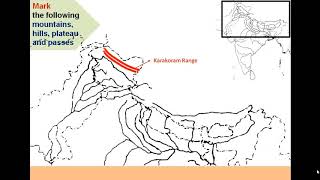
One of the notable peaks in India is Mt. K2, also known as Godwin Austen. It is the second highest mountain in the world and is part of the Karakoram range. While K2 is located in Pakistan, it is significant for Indian geography and is often referenced in discussions about the country's highest peaks.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine reaching for the stars—Mt. K2 is like a symbol of that ambition, representing the highest aspirations we have, much like how climbers strive to reach the top of the tallest peaks.
Plateaus
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Plateaus: Deccan Plateau, Chotanagpur Plateau, Malwa Plateau
Detailed Explanation
Plateaus are elevated flatlands that rise significantly above the surrounding areas. The Deccan Plateau is the largest, located in southern India, known for its rich mineral resources. The Chotanagpur Plateau is famous for its coal mines, while the Malwa Plateau is notable for its fertile farmland. These plateaus’ unique topography influences agriculture, water availability, and settlements.
Examples & Analogies
Consider plateaus as the 'tables' of the earth; just like a dining table serves as a solid platform for placing food, plateaus provide solid ground for various activities like farming and mining.
Deserts
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Desert: Thar Desert
Detailed Explanation
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is located in the northwestern part of India, primarily in Rajasthan. It is characterized by sand dunes, sparse vegetation, and extreme temperatures. The desert's unique ecosystem supports a variety of wildlife adapted to harsh conditions, and it plays a critical role in the cultural identity of the region.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Thar Desert like a giant ocean of sand. Just like a sea has its own unique creatures and plants capable of surviving harsh saltwater, the Thar is home to life forms that thrive in dry, sandy conditions.
Key Concepts
-
Himalayas: The tallest mountain range in India, influencing climate and ecosystems.
-
Deccan Plateau: A significant plateau characterized by its volcanic soil, impacting agriculture.
-
Thar Desert: The largest desert in India, known for its unique flora and fauna.
Examples & Applications
The Himalayas form a natural barrier that affects the monsoon patterns in India.
The Deccan Plateau's fertile volcanic soil gives rise to a diverse agriculture economy.
The harsh conditions in the Thar Desert require innovative adaptations for water conservation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the Himalayas, the heights ascend, / While on the Thar's sands, the challenges never end.
Stories
Once, a traveler climbed the Himalayas, saw the beauty and grace. He then crossed the vast Thar Desert, learning to adapt to its harsh face.
Memory Tools
H.A.D. - Himalayas (tallest), Aravalli (old), Deccan (fertile).
Acronyms
M.P.D. - Mountains, Plateaus, Deserts for the physical features of India.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Himalayas
The tallest mountain range in the world, located in northern India.
- Aravalli
One of the oldest mountain ranges in India, stretching across western states.
- Deccan Plateau
A large plateau in southern India known for its volcanic origin.
- Chotanagpur Plateau
A plateau rich in minerals located in eastern India.
- Thar Desert
A major desert located in northwestern India, known for its arid environment.
- Eastern Ghats
A mountain range along the eastern coast of India, less extensive than the Western Ghats.
- Western Ghats
A mountain range along the western coast of India, recognized for its biodiversity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
