Soil and Natural Vegetation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Types of Soils in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the different types of soils in India. Can anyone tell me about alluvial soil?

Isn't alluvial soil found in the Indo-Gangetic plains and is really fertile?

That's correct! Alluvial soil is indeed very fertile and supports a lot of agriculture. Now, what about black soil?

It’s from the Deccan Plateau and is used for growing cotton, right?

Well done! It's rich in minerals. This soil is very important for cotton cultivation. Let’s summarize this - A for Alluvial is Fertile, B for Black is Best for Cotton!
Other Soil Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, can anyone explain what red soil is? Where is it typically found?

Red soil is found in Eastern and Southern India and gets its color from iron oxide!

Excellent! Red soil is indeed characterized by a reddish color. How about laterite soil?

Laterite soil is found in the Western Ghats, and it’s usually leached and has low fertility.

Great observation! For laterite soil, remember 'L for Laterite is Low in nutrients!' What about desert soil?

It’s in Rajasthan and is dry, supporting very little vegetation.
Natural Vegetation in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's shift our focus to natural vegetation. Who can tell me where we find tropical rainforests in India?

They are in the Western Ghats and northeastern states!

Exactly! These forests are incredibly diverse. Now, how about deciduous forests?

They are in Central India, and the trees there shed their leaves seasonally.

Correct! Remember, Deciduous - D for Drop their leaves in fall! What about mangroves?

The Sundarbans! That’s where they are found.
Desert Vegetation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about desert vegetation. Where is it mainly found?

It's found in the Thar Desert!

Exactly! Can anyone tell me how these plants adapt to survive in such harsh conditions?

They are often xerophytes, meaning they need very little water!

Very good! Remember, Xerophytes are heroes of the desert! Let’s recap all soils and vegetation types once more.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
It provides a thorough overview of different soil types such as alluvial, black, red, laterite, and desert soils, alongside corresponding natural vegetation like tropical rainforests, deciduous forests, mangroves, and desert vegetation, illuminating their ecological significance within India's geography.
Detailed
Soil and Natural Vegetation
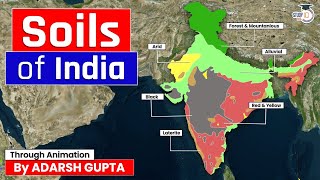
This section explores the diverse types of soils and natural vegetation prevalent across India. The primary soil types discussed include:
- Alluvial Soil: Found in the Indo-Gangetic plains, this soil is fertile and supports intensive agriculture.
- Black Soil: Associated with the Deccan Plateau, it is rich in minerals and ideal for cotton cultivation.
- Red Soil: Predominantly located in Eastern and Southern India, it has a distinct reddish hue due to iron oxide.
- Laterite Soil: Commonly found in the Western Ghats, it is leached of nutrients and often used for bricks.
- Desert/Arid Soil: Characteristic of Rajasthan, it is dry and lacks nutrients, supporting minimal vegetation.
The section further examines the types of vegetation:
- Tropical Rainforest: Found in the Western Ghats and northeastern states, these forests are rich in biodiversity.
- Deciduous Forest: Located in Central India, they shed leaves seasonally adapting to climate variations.
- Mangroves: Specifically the Sundarbans, these forests are crucial for coastal protection and biodiversity.
- Desert Vegetation: Thriving in the Thar Desert, it includes xerophytes that endure extreme aridity.
Understanding soil types and vegetation is vital for agricultural planning, biodiversity conservation, and ecological stability.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Soil Types in India
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Soils:
● Alluvial: Indo-Gangetic plains
● Black: Deccan Plateau
● Red: Eastern and Southern India
● Laterite: Western Ghats
● Desert/Arid: Rajasthan
Detailed Explanation
This section discusses the various types of soils found in India and where they are predominantly located. Each type of soil has unique characteristics that make it suitable for different types of vegetation and agricultural practices:
- Alluvial Soil: This type is found mainly in the Indo-Gangetic plains and is formed by the deposition of sediments carried by rivers. It is very fertile and supports diverse crops.
- Black Soil: Predominantly found in the Deccan Plateau, this soil is rich in minerals and ideal for growing cotton, making it particularly important for the cotton industry.
- Red Soil: Found in Eastern and Southern India, red soil is less fertile than alluvial soil due to its low phosphorus content. However, it can be improved with fertilizers for agriculture.
- Laterite Soil: Located primarily in the Western Ghats, laterite soil forms in tropical areas with heavy rainfall. It is characterized by high iron and aluminum content and is typically not very fertile.
- Desert/Arid Soil: Found in Rajasthan, this soil is dry and often poor in nutrients. Its primary use is for arid vegetation and limited farming activities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the different types of soil like different types of cake. Just as some cakes are moist (like alluvial soil), while others are dry and crumble easily (like desert soil), each soil type supports different kinds of crops, much like how different cakes can be served at various occasions!
Natural Vegetation Types in India
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Vegetation:
● Tropical Rainforest: Western Ghats, NE states
● Deciduous Forest: Central India
● Mangroves: Sundarbans
● Desert Vegetation: Thar Desert
Detailed Explanation
This part elaborates on the variety of natural vegetation found across different regions of India:
- Tropical Rainforest: These are dense forests found in areas like the Western Ghats and Northeast states of India. They have a high level of biodiversity and are lush throughout the year, thanks to heavy rainfall.
- Deciduous Forest: This type of forest is located in Central India and is characterized by trees that shed their leaves in the dry season, which helps them conserve water.
- Mangroves: Found in coastal regions like the Sundarbans, mangroves are unique as they grow in saline (salty) conditions. They are crucial for protecting coastal areas from erosion and providing habitat to a wide range of wildlife.
- Desert Vegetation: The Thar Desert is home to desert vegetation, characterized by drought-resistant plants like cacti and shrubs. This vegetation has adapted to survive in arid conditions with limited water supply.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the different types of vegetation as a wardrobe of clothing for different weather. The tropical rainforest is like a summer outfit worn in warm, wet weather, while deciduous forests represent the seasonal wear, shedding clothes in winter, and the mangroves function like water-resistant gear protecting you from coastal storms. Lastly, desert vegetation is akin to tough, weatherproof clothing designed for extreme dryness and harsh conditions.
Key Concepts
-
Soil Types: There are different types of soil in India including alluvial, black, red, laterite, and desert soil, each with unique properties.
-
Natural Vegetation: India has diverse vegetation types including tropical rainforests, deciduous forests, mangroves, and desert vegetation.
Examples & Applications
Alluvial soil is highly fertile and located in the Indo-Gangetic plains, making it suitable for growing rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
The Sundarbans mangroves serve as a critical barrier against coastal erosion and support a variety of marine life.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In valleys deep, alluvial thrives, fertile and lush, where life derives.
Stories
Once in a land where rivers flowed, alluvial soil brought crops to grow, while in the hills black soil glowed, cotton and dreams, in sun and show.
Memory Tools
A for Alluvial, B for Black, R for Red, L for Laterite, D for Desert!
Acronyms
SAND
for Soil
for Alluvial
for Nature (Vegetation)
for Desert.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Soil
The upper layer of earth in which plants grow.
- Alluvial Soil
Fertile soil deposited by rivers.
- Black Soil
Soil ideal for cotton cultivation, found in the Deccan Plateau.
- Red Soil
Soil that has a reddish color due to iron content, found in Eastern and Southern India.
- Laterite Soil
Soil rich in iron and aluminum, formed in tropical areas.
- Desert/Arid Soil
Dry and nutrient-poor soil found in desert regions.
- Tropical Rainforest
Densely wooded and lush area found in warm tropical regions.
- Deciduous Forest
Forests wherein trees shed leaves seasonally.
- Mangroves
Coastal vegetation found in brackish water areas, often in estuaries.
- Desert Vegetation
Vegetation adapted to survive in arid desert climates.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
