Rivers and Water Bodies
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Major Rivers of India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the major rivers of India. Who can tell me one major river that flows through northern India?

Is it the Ganga?

Correct! The Ganga is not only crucial for irrigation but also holds religious importance. Can anyone name some other important rivers?

The Yamuna and Brahmaputra!

Yes, both are vital. Remember: 'YB' for Yamuna and Brahmaputra! Now, do these rivers flow into the sea or merge into other rivers?

They flow into the sea.

Exactly! The Ganga and Brahmaputra eventually flow into the Bay of Bengal. Let's summarize: Ganga is important for agriculture, while the Brahmaputra is significant for its vast basin.
Significance of Lakes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss lakes. What is the largest coastal lagoon in India?

Chilika Lake?

Exactly! Chilika Lake is also known for its biodiversity. Who can tell me another lake?

Wular Lake?

Good job! Wular Lake is the largest freshwater lake. These lakes play crucial ecological roles, from providing habitats to supporting local economies through fishing. Let's recap: Chilika is coastal and biodiverse, while Wular is freshwater.
Understanding Dams
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about dams. Can anyone name a significant dam in India?

The Bhakra-Nangal Dam!

Correct! The Bhakra-Nangal Dam is vital for irrigation and hydroelectric power. Why are dams important?

They store water and help in energy generation.

Exactly! Let's remember: ‘B-H-H’ for Bhakra, Hirakud, and Nagarjuna Sagar dams. Each of these plays a significant role in India's water management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the prominent rivers of India, such as the Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra, alongside important lakes like Chilika Lake, and significant dams like Bhakra-Nangal. Understanding these water bodies is crucial for comprehending India's geography and hydrology.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Rivers and Water Bodies
In the Indian subcontinent, rivers, lakes, and dams play a vital role in shaping the geographical and ecological aspects of the region. This section focuses on marking and understanding the following key features:
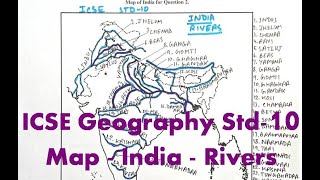
Major Rivers:
- Ganga: One of the most significant rivers in terms of religion and agriculture, it flows through northern India.
- Yamuna: A major tributary of the Ganga, it flows through several states and forms the boundary between Delhi and Uttar Pradesh.
- Brahmaputra: Known for its vast basin, it flows through Assam and is one of the primary rivers in northeastern India.
- Godavari: The second longest river in India, it flows from the Western Ghats.
- Krishna: Situated in the southern part of India, it is vital for irrigation.
- Narmada and Tapi: Both rivers flow westward, and their valleys are known for their distinct features.
- Mahanadi: Flows through Odisha, known for its fertile basin.
- Indus: Primarily flows through northern India and into Pakistan, significant for its historical context.
Lakes:
- Chilika Lake: The largest coastal lagoon in India, located on the eastern coast, renowned for its biodiversity.
- Wular Lake: One of the largest freshwater lakes in India, located in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Pulicat Lake: A brackish coastal lagoon, it is situated on the border of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Sambhar Lake: The largest inland salt lake in India, known for salt production.
Dams:
- Bhakra-Nangal Dam: A significant multipurpose dam on the Sutlej River that contributes to irrigation and hydroelectric power.
- Hirakud Dam: Built across the Mahanadi River in Odisha, it was one of the first major multipurpose river valley projects in India.
- Nagarjuna Sagar Dam: Constructed on the Krishna River, it is among the largest dams in the country.
Understanding these rivers, lakes, and dams is crucial for comprehending the hydrology of India and its impact on agriculture, economy, and ecology. By marking these features on maps, students gain foundational knowledge essential for advanced geographical studies.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Major Rivers of India
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Rivers: Ganga, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, Indus
Detailed Explanation
This chunk focuses on the major rivers of India. The rivers mentioned are significant as they play crucial roles in the geography, culture, and economy of the country. For instance, the Ganga is known as a sacred river in Hinduism and is also vital for irrigation and water supply. Each river has its unique characteristics and influences the regions through which it flows.
Examples & Analogies
Think of rivers as the lifelines of a country, similar to how blood vessels nourish different parts of the body. Just as blood flow is essential for our health, rivers provide water for agriculture, drinking, and sanitation, sustaining life in numerous ways across India.
Significant Lakes
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Lakes: Chilika Lake, Wular Lake, Pulicat Lake, Sambhar Lake
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines significant lakes in India. Each lake is unique in its ecosystem and geographical importance. For instance, Chilika Lake is one of the largest coastal lagoons in India, providing a habitat for various species and supporting local fishing communities. Similarly, Wular Lake is among the largest freshwater lakes, playing a crucial role in regulating water levels and supporting biodiversity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine lakes as reservoirs of life, much like a grocery store that provides a variety of fresh products. Just as a grocery store supplies food for people, lakes support diverse wildlife and provide resources for communities living nearby.
Important Dams
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Dams: Bhakra-Nangal, Hirakud, Nagarjuna Sagar
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces important dams in India. Dams are critical for managing water resources, generating electricity, and preventing floods. The Bhakra-Nangal Dam, for example, is one of the highest gravity dams in India and is vital for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation. Each dam contributes significantly to the regional economy and supports agriculture through water supply.
Examples & Analogies
Think of dams like a water bottle that you fill to stay hydrated throughout the day. Dams store water for various purposes like irrigation, drinking and energy production, much like how a water bottle provides hydration when you need it.
Key Concepts
-
Ganga: A major river flowing through northern India, essential for agriculture and religious practices.
-
Brahmaputra: Noted for its vast basin and importance in the northeastern region of India.
-
Chilika Lake: A significant coastal lagoon known for its ecological diversity.
-
Dams: Structures that store water, aid in irrigation, and generate hydroelectric power.
Examples & Applications
The Krishna River flows from the Western Ghats and is crucial for irrigation in southern India.
Wular Lake is renowned for its diverse aquatic life and is essential for local fishing communities.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In India’s rivers, Ganga flows free, with Brahmaputra's vast legacy.
Stories
Once, the Ganga and Brahmaputra met in a vast riverboat race; the Ganga claimed speed, while Brahmaputra boasted of breadth, showing that every river has its unique strength and story.
Memory Tools
Remember 'GBK' for Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Krishna – key rivers in India.
Acronyms
Use 'Chilika' for C-H-I-L-I-K-A
Coastal
Habitat
Important
Lagoon
India
Key
Aquatic.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ganga
A major river in northern India, significant for agriculture and religion.
- Brahmaputra
A major river in northeastern India, known for its vast basin.
- Chilika Lake
The largest coastal lagoon in India, located on the eastern coast.
- BhakraNangal Dam
A significant multipurpose dam on the Sutlej River that contributes to irrigation and hydroelectric power.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
