Electromotive Force (EMF)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding EMF
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss Electromotive Force, or EMF. Who can tell me what they think EMF stands for?

Is it about how the electric current moves?

That's a good start! EMF represents the total energy supplied by a cell for every coulomb of charge. It’s measured in volts. Can anyone tell me how this relates to the battery's performance?

Does it mean how much energy the battery can provide?

Exactly! EMF indicates the potential difference you would measure when no current is flowing. It shows the maximum energy output of the battery.

So, when the battery is charged, that’s the EMF?

Correct! Think of EMF as the battery's 'capacity' to push charge through a circuit.

In summary, EMF is crucial for understanding how batteries work and their role in electric circuits.
Significance of EMF
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about why EMF is important. Can anyone think of some everyday applications that might rely on EMF?

Electric cars? They need batteries!

Exactly! The EMF determines how far an electric car can travel on a full charge. What else?

Smartphones! They use batteries too.

You're right! In smartphones, the EMF of the battery influences how long the device can operate before needing a recharge. Remember the acronym E for Energy, M for Maximizing, and F for Functionality to help recall EMF's purpose!

Will all batteries have the same EMF?

Great question! No, the EMF will vary based on the battery type and its chemistry.

To summarize, EMF is significant in understanding how effectively batteries power various devices.
Measuring EMF
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, how can we measure EMF? Who knows the devices we use for that?

Isn’t it a voltmeter?

Yes! A voltmeter measures the potential difference, or EMF, across the terminals of a battery when it's not connected in a circuit. What’s crucial to remember is the state of the battery when taking this measurement.

It should be not conducting current, right?

Exactly! If current flows, the measured voltage won't reflect the true EMF due to internal resistance. Keep that in mind!

So we always measure it when the device is off?

Correct! To reinforce, we measure EMF with a voltmeter when no current is flowing to get an accurate reading.

In summary, accurate EMF measurement is essential for understanding battery performance in real-world applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
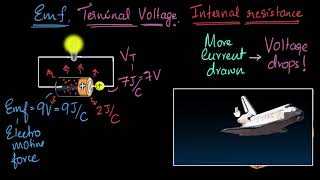
This section discusses the concept of Electromotive Force (EMF), defined as the total energy provided by a source per coulomb of charge. EMF represents the maximum potential difference between the terminals of a battery or cell when it is not conducting current.
Detailed
Electromotive Force (EMF)
Electromotive Force, or EMF, is a critical concept in the study of electricity, particularly in understanding how batteries and cells operate. EMF refers to the total energy supplied by a cell or battery for every coulomb of charge that passes through it. Essentially, it indicates the potential difference that may be observed across the terminals of a battery when no current is being drawn.
In practical terms, EMF can be viewed as the 'drive' behind electric current within a circuit. It is typically measured in volts (V), coherent with the defined unit of potential difference. When a battery is fully charged and not connected in a circuit (i.e., no current flowing), the voltage measured between its terminals reflects its EMF.
Understanding EMF is crucial in various applications, from power distribution systems to electronic devices, as it affects how devices function based on the energy supplied by their sources. This section sets the stage for further discussions on electric circuits and the principles governing electric flow.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of EMF
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● EMF is the total energy supplied by the cell or battery per coulomb of charge.
Detailed Explanation
Electromotive Force (EMF) refers to the amount of energy that a battery or a cell provides to each coulomb of electric charge that flows through it. This is an important concept because it determines how much potential energy is available to move charges through a circuit, enabling devices to operate.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water pump that pushes water through a hose. The energy provided by the pump (like the EMF) causes water (representing electric charge) to flow. The more powerful the pump, the more water can be pushed out, similar to how a higher EMF allows more charge to flow and do work.
Maximum Potential Difference
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● It is the maximum potential difference between the terminals of a cell when no current is flowing.
Detailed Explanation
The EMF of a cell is specifically described as the maximum potential difference between its terminals when no current is flowing. This scenario is known as 'open circuit condition.' Under these conditions, the terminal voltage equals the EMF value, indicating the maximum energy available for work from the cell.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a fully charged battery sitting on a shelf. The voltage it can provide when not connected to any device (no current flowing) represents its EMF. It's like a fully inflated balloon that is sitting still – it has the potential to pop if you use it, but it is not doing anything until you interact with it.
Unit of EMF
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Measured in volts (V).
Detailed Explanation
Electromotive Force (EMF) is measured in volts (V), which is standard across electrical measurements. This unit provides a consistent way to express the energetic capacity of various power sources, making it easier to compare different batteries or cells.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how we measure the capacity of fuel tanks in cars in liters. Similarly, measuring EMF in volts tells us how much electrical energy a battery can potentially supply, similar to how a liter tells us how much fuel is available for driving.
Key Concepts
-
Electromotive Force (EMF): Total energy supplied by a cell per coulomb.
-
Voltage: Another term synonymous with EMF when no current flows.
-
Coulomb: Unit of electric charge that EMF references.
Examples & Applications
- A simple battery like AA provides an EMF of 1.5 V, which drives current in a flashlight.
- A car battery might provide an EMF of 12 V, enabling the vehicle to start and run electrical components.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
EMF is the energy's beat, volts measure each charge that we meet.
Stories
Imagine a battery as a well filled with energy. When it’s full, it pushes the water (charge) out strongly, representing high EMF. As it drains, the push reduces, indicating a drop in EMF.
Memory Tools
Remember EMF: E - Energy, M - Maximize, F - Force. It supplies energy per charge.
Acronyms
EMF
Energy Maximized For electric flow.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electromotive Force (EMF)
The total energy supplied by a cell or battery per coulomb of charge, measured in volts.
- Potential Difference
The work done to move a unit charge between two points in an electric field, also measured in volts.
- Coulomb
The unit of electric charge, symbolized as C.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
