Electric Motor
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Electric Motors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore electric motors. Can anyone tell me what an electric motor does?

It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy!

That's correct! An electric motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy by using the principle of electromagnetism. Can anyone think of where we might see electric motors in real life?

In washing machines?

Also in fans and electric cars!

Exactly! They are everywhere, powering many devices. Now, let's dive into how they work!
Components of an Electric Motor
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Electric motors consist of several main parts. First, we have the armature coil. Can anyone tell me what it does?

It’s the part that rotates, right?

Exactly! The armature coil is a rectangular loop of wire. Now, what helps create the magnetic field?

The permanent magnets?

Yes, great! The permanent magnets provide a consistent magnetic field. There's also a split-ring commutator. Does anyone know its function?

It reverses the current direction every half rotation!

Correct! It ensures that the coil continues to rotate. Remember, without this commutator, the motion would stop. Let's summarize what we've learned so far.
Operation of Electric Motors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know the components, let’s see how they work together. When the battery provides current to the armature coil, what happens next?

A magnetic field is created around the coil!

And it interacts with the magnetic field from the permanent magnets!

Absolutely! This interaction creates a force that causes the coil to rotate continuously because of the way the commutator reorients the current. Why is this circular motion essential?

It allows for ongoing mechanical work, like turning a fan or a wheel!

Fantastic! Continuous rotation means that electric motors can keep performing work effectively. Let’s summarize these interactions.
Applications of Electric Motors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about where electric motors are commonly used. Can anyone name a few applications?

Vacuum cleaners!

How about elevators?

Great examples! Electric motors are pivotal in everyday appliances. Understanding how they operate helps us appreciate their design and functionality. Can anyone think of an inventive use for electric motors?

Maybe in robotics, for automated movement?

Exactly! They're crucial in robotics and automation. Let’s finalize our overview with the key roles electric motors play in technology.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Electric motors operate on the principle that a current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. Key components of an electric motor include the armature coil, permanent magnets, a split-ring commutator, brushes, and a battery, all working together to produce continuous mechanical rotation.
Detailed
Electric Motor
Electric motors are essential devices that transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. This transformation is driven by the interaction between the magnetic field and a current-carrying conductor. Understanding the functioning and components of electric motors allows us to appreciate their applications in everyday life.
Key Components of an Electric Motor
- Armature Coil: A rectangular loop of wire that rotates within the magnetic field.
- Permanent Magnets: These provide the stationary magnetic field necessary for the motor's operation.
- Split-Ring Commutator: This device serves to reverse the direction of the current every half rotation, ensuring continuous motion.
- Brushes: They deliver current to the commutator from the power source.
- Battery: Supplies the electrical current needed for the motor's operation.
When current flows through the armature coil, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the fixed magnetic field of the permanent magnets, resulting in a force that causes the coil to rotate. This rotational movement is maintained as the split-ring commutator continuously reverses the current direction, allowing for uninterrupted mechanical energy output.
Youtube Videos



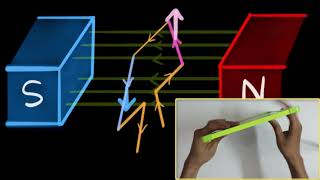

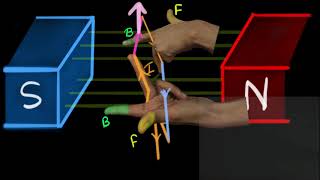
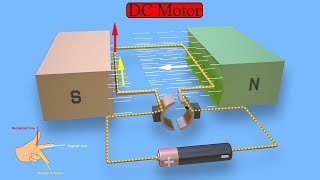


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Electric Motors
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Detailed Explanation
An electric motor is primarily designed to transform electrical energy, which comes from a power source like a battery, into mechanical energy—energy that can do work, such as turning a fan or moving a car. This conversion of energy is essential in countless applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of an electric motor like a performer on a stage. The electrical energy is like the music playing, energizing the performer (the motor) to dance and move, creating a lively performance (mechanical energy) that engages the audience.
Principle of Operation
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a force.
Detailed Explanation
The working principle of an electric motor is based on the interaction between electricity and magnetism. When an electric current flows through a conductor (like a wire), and this conductor is placed within a magnetic field, the conductor experiences a force. This force causes the conductor to move, resulting in rotation or linear motion, which is what we want from a motor.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to push a shopping cart across a parking lot while someone holds a magnet next to it. The magnet's attraction (the magnetic field) combined with your push (the current) can make the cart roll. Just as the cart moves, the motor moves thanks to this principle.
Main Parts of an Electric Motor
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Main Parts:
● Armature coil: Rectangular loop of wire
● Permanent magnets: Provide magnetic field
● Split-ring commutator: Reverses current direction every half rotation
● Brushes: Conduct current to the commutator
● Battery: Provides current
Detailed Explanation
An electric motor consists of several key components:
- Armature Coil: This is the rotating part of the motor, usually shaped like a rectangular loop, through which the current flows.
- Permanent Magnets: These are fixed in place and create a constant magnetic field, necessary for the operation of the motor.
- Split-Ring Commutator: This component ensures that the current direction through the armature coil changes every half rotation, allowing continuous rotation.
- Brushes: These conduct current to the split-ring commutator from an external power source.
- Battery: It supplies the electric current needed for the motor to operate. Each part works together to achieve the desired motion.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the electric motor like a bicycle: the armature coil is like the bike itself, driven forward by the pedals (current). The permanent magnets are like the road that keeps the bike stable, while the split-ring commutator acts like the gears that change the direction when you switch from going forward to backward. The battery is like your legs supplying the energy to pedal.
How Motion Is Achieved
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● When current flows, the coil rotates due to force on its sides, producing continuous rotation.
Detailed Explanation
The flow of electric current through the armature coil creates magnetic fields around it. When this interacts with the magnetic field from the permanent magnets, forces arise on either side of the coil, causing it to rotate. Due to the split-ring commutator, the direction of current is reversed at just the right moment, ensuring that the coil continues to spin without stopping. This leads to the continuous rotation necessary for the application of mechanical energy.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine riding a merry-go-round. As you push on one side, it begins to rotate. If you keep pushing at intervals, it will keep going around. Similarly, the motor keeps 'pushing' the coil to ensure it continues spinning.
Key Concepts
-
Electric Motor: A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy via the interaction of a magnetic field and a current-carrying conductor.
-
Armature Coil: The key component that rotates within a magnetic field in an electric motor.
-
Commutator: A crucial part that reverses the current to allow continuous rotation of the armature.
Examples & Applications
A blender uses an electric motor to rotate its blades, effectively mixing ingredients.
Electric cars utilize electric motors to power their wheels, promoting energy efficiency and reducing emissions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Electric motors spin and whirl, converting energy, making things twirl.
Stories
Once there was a magic motor that loved turning currents into magic moves, with its helper, the commutator, doing flips to keep it grooving all day long!
Memory Tools
Remember 'A PBC' for the parts: Armature, Permanent magnets, Brushes, Commutator.
Acronyms
M.E.C. for Motor, Energy, Conversion.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Armature Coil
The rectangular loop of wire that rotates within the electric motor due to electromagnetic interaction.
- Permanent Magnets
Magnets that create a constant magnetic field in which the armature coil operates.
- SplitRing Commutator
A device that reverses the direction of current through the coil every half rotation to ensure continuous motion.
- Brushes
Conductors that transfer current to the commutator from the power source.
- Battery
The source of electrical energy that powers the electric motor.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
