Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is a Solenoid?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll talk about solenoids. A solenoid is basically a long coil of wire with many turns. Can anyone tell me what happens when we pass a current through it?

I think it creates a magnetic field!

Correct! When current flows through a solenoid, it generates a strong and uniform magnetic field inside. Can anyone guess how this field compares to a bar magnet?

I believe it resembles the field of a bar magnet?

Exactly! One end of the solenoid acts as a North pole while the other serves as a South pole. Great observation!
Factors Affecting Magnetic Field Strength in a Solenoid
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's delve into what factors might affect the strength of the magnetic field inside a solenoid. Who can think of any?

The number of turns in the wire, right?

That's right! The magnetic field strength increases with the number of turns of the coil. What else?

The current passing through the solenoid?

Exactly! More current means a stronger field. And one more factor?

Using a soft iron core?

Yes! Adding a soft iron core greatly enhances the magnetic field strength due to its magnetic properties. Well done!
Applications of Solenoids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore how solenoids are utilized in real-world applications. Can anyone think of where we might find solenoids?

In electromagnets?

Absolutely! Electromagnets use solenoids to create a magnetic field. Any other uses?

Electric doorbells and latches?

Great examples! Solenoids are indeed used in these devices for their ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. Excellent contributions, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses the properties of a solenoid, including how it creates a magnetic field inside that is strong and uniform, while its exterior resembles that of a bar magnet. Key factors affecting the magnetic field strength include the number of turns of the coil, the current flowing through it, and the use of a soft iron core.
Detailed
Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
A solenoid is characterized as a long coil of wire that contains many tightly wound turns. When an electric current passes through the solenoid, an intense magnetic field is produced within it. This internal magnetic field is notable for being strong, uniform, and linear, whereas the magnetic field outside the solenoid exhibits characteristics similar to that of a bar magnet, with one end acting as the North pole and the opposite end functioning as the South pole. The strength of the magnetic field inside the solenoid can be increased by enhancing the number of wire turns, increasing the current, or inserting a soft iron core within the solenoid. Understanding these principles is crucial as it forms the basis for many practical applications, including electromagnets and various electronic devices.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Solenoid
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Solenoid: A long coil of wire with many turns placed close together.
Detailed Explanation
A solenoid is a cylindrical coil of wire designed to generate a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. The wire is wound tightly in loops, and these many turns create a concentrated magnetic field inside the coil.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a solenoid like a tightly coiled spring. Just as a spring can store energy, the solenoid can store magnetic energy when electricity runs through it.
Magnetic Field Inside the Solenoid
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● When current flows:
○ Magnetic field inside is strong, uniform, and straight.
Detailed Explanation
When current passes through a solenoid, it creates a magnetic field that is strong and uniform throughout the inside of the coil. This means that every part of the solenoid has the same strength of magnetic field, pointing in the same direction, which is why it's referred to as 'strong' and 'straight.'
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the solenoid as a straight pipe filled with water. If you pump water through it, the flow is strong and even along the entire length, similar to how the magnetic field is inside the solenoid.
Magnetic Field Outside the Solenoid
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Outside, it resembles the field of a bar magnet.
Detailed Explanation
The magnetic field outside a solenoid behaves similarly to the field of a bar magnet. This means that outside the solenoid, the magnetic field lines spread out, indicating the presence of a north and south pole, just like a typical magnet.
Examples & Analogies
Picture how a bar magnet works, with its magnetic field extending outward in a distinctive pattern. The ends of the solenoid act as the poles of this 'magnet,' creating an analogous field.
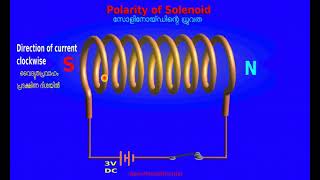
Polarity of the Solenoid
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ One end behaves like a North pole, the other as South pole.
Detailed Explanation
In a solenoid, one end will act as a north pole while the opposite end acts as a south pole. This is based on the direction of the current flowing through the coils. The acceptance of the solenoid as a magnet is crucial in many applications, where determining the north and south is essential.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the solenoid as a switch. Just as flipping the switch can turn a light on or off, changing the current direction in the solenoid can switch its magnetic polarity, changing which end is north and which is south.
Factors Affecting Magnetic Field Strength
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Magnetic field inside solenoid increases with:
○ Number of turns
○ Current
○ Use of soft iron core
Detailed Explanation
The magnetic field strength inside a solenoid is influenced by three main factors: 1) the number of turns of wire, 2) the amount of current flowing through the wire, and 3) the presence of a soft iron core inside the solenoid. More turns and higher current result in a stronger magnetic field, while adding an iron core helps concentrate the field even more.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water hose. If you want more water to flow out, you can increase the water pressure, add more hoses, or use a larger pipe to funnel the water. Similarly, to enhance the magnetic field in a solenoid, you can adjust these factors.
Key Concepts
-
Solenoid: A coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when current flows through it.
-
Magnetic Poles: The ends of a solenoid act like the North and South poles of a magnet.
-
Factors Affecting Magnetic Field: The strength of a solenoid's magnetic field depends on the number of turns, the current flowing through it, and the use of a soft iron core.
Examples & Applications
A solenoid can be used in an electric door lock to create a magnetic field to pull a bolt into the locked position.
In MRI machines, solenoids are used to create the strong magnetic fields required for imaging.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a coil we see, magnetic fields agree, Solenoid’s strength is from turns and current, that’s the key!
Stories
Imagine a wire coiled tightly in a magical way—when current passes, it becomes a magnet, working night and day!
Memory Tools
To remember solenoid strengths, think C for Current, T for Turns, I for Iron core—strong magnetic fields are what we implore!
Acronyms
STIC
Strength
Turns
Iron Core - all key for solenoid's magnetic score!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Solenoid
A long coil of wire with many turns, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it.
- Magnetic Field
The region around a magnet or electric current where magnetic forces can be experienced.
- North/South Pole
The ends of the solenoid where the magnetic field is strongest, resembling the poles of a bar magnet.
- Soft Iron Core
A core made of soft iron used in solenoids to enhance the strength of the magnetic field.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
