Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Importance of Final Accounts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Final accounts play a vital role in evaluating a business's financial health. Can anyone tell me why we need these accounts?

They help in tracking profits, right?

Exactly! They show us the profitability through the Trading Account and the overall financial position through the Balance Sheet. Why do you think stakeholders care about these reports?

Because they need to make informed decisions based on financial data!

Great point! Stakeholders, including owners and investors, rely on this data to plan and make impactful decisions.

Can you sum that up for us?

Sure! Final accounts are essential for assessing profitability, guiding stakeholder decisions, and ensuring compliance.
Adjustments and Their Role in Final Accounts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about adjustments. Why do we need to make adjustments in our final accounts?

To make sure all income and expenses are accounted for, right?

Exactly! Adjustments like accrued income and outstanding expenses help reflect the actual financial position. Can someone give an example of one?

Accrued income, like receiving payment after the accounting period ends?

Correct! This ensures that our financial reports are precise and reflective of all transactions. What do you think happens if we skip these adjustments?

The reports might be misleading!

Absolutely! Adjustments maintain the integrity of financial reporting.
Marshalling of the Balance Sheet
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the concept of marshalling the Balance Sheet. Can anyone explain what that means?

Is it about organizing the balance sheet better?

Exactly right! Marshalling arranges assets and liabilities in a systematic way. Why could this be important for someone reviewing the balance sheet?

It makes it easier to understand the financial health quickly!

Precisely! Clarity is key in financial documents. Can you name the common orders used in marshalling?

Order of liquidity for assets and order of maturity for liabilities!

Well done! That structure enhances comprehension and allows for better decision-making.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The conclusion emphasizes the significance of final accounts in determining a business's profitability and financial status. By summarizing key components like the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, along with the importance of adjustments and marshalling, this section highlights the overall framework for proper financial reporting.
Detailed
Conclusion of Final Accounts
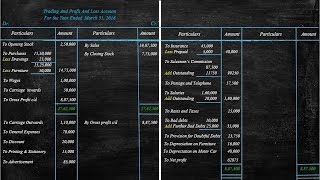
Final accounts are critical financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period. They encompass the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, each serving a unique purpose in determining a business's profitability and financial position. The Trading Account calculates gross profit or loss, whereas the Profit and Loss Account assesses net profit or loss. The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of the financial position, ensuring all assets and liabilities are accurately represented.
Adjustments, which account for accrued income, outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, and depreciation, are essential for maintaining accuracy in financial reporting. Furthermore, the marshalling of the balance sheet enhances clarity and comprehensibility by arranging assets and liabilities in a systematic order.
In conclusion, final accounts not only support regulatory compliance but also empower stakeholders—owners, managers, and investors—to make informed decisions regarding financial performance and planning.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Summary of Key Points
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Final accounts provide crucial information about the profitability and financial position of a business.
The Trading Account calculates gross profit, the Profit and Loss Account determines net profit, and the Balance Sheet shows the financial position.
Adjustments are necessary for accurate financial reporting, and Marshalling helps organize the balance sheet for clarity.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we summarize the primary roles of final accounts in a business setting. Final accounts, consisting of the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, collectively offer insights into a company's profitability and financial standing. The Trading Account calculates the gross profit by evaluating sales and direct costs, while the Profit and Loss Account assesses the net profit by considering indirect expenses and incomes. The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position on a specific date. Additionally, adjustments are important to ensure that the financial data accurately reflects the business's economic activities, and marshalling is the process of organizing this information for better clarity and usability.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine running a lemonade stand over the summer. At the end of the season, you need to know how much profit you made. Your Trading Account would help you calculate how much money you earned from selling lemonade versus how much you spent on lemons and sugar. Next, your Profit and Loss Account would factor in other costs like the price of the stand and permits, helping you understand your net earnings. Finally, your Balance Sheet would list all the resources you have, like the cash in your hand and any debts, giving you a complete picture of your lemonade business's financial health at that moment.
The Importance of Final Accounts
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Final accounts play a vital role in business decision-making, financial planning, and regulatory compliance. They help in evaluating business performance and assessing financial health.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the significance of final accounts in various business functions. Final accounts are not merely numbers; they are critical tools for making informed decisions. Business owners rely on these accounts to plan future investments, manage expenses, and ensure they comply with regulations. Effective financial reporting helps managers understand where the business stands and where adjustments might be needed. Overall, final accounts serve as a foundation upon which businesses assess performance and strategize for the future.
Examples & Analogies
Think of final accounts like a GPS system for a road trip. Just as a GPS helps you determine your current location and suggest the best route to your destination, final accounts provide essential information on where the business currently stands and help identify the necessary steps to achieve future goals. Without proper guidance from these financial documents, navigating the business landscape can become challenging and may lead to detours or miscalculations.
Key Concepts
-
Final Accounts: Essential financial statements assessing profitability and position.
-
Trading Account: Focuses on direct incomes and expenses to determine gross profit.
-
Profit and Loss Account: Tackles indirect incomes and expenses for net profit.
-
Balance Sheet: Displays the financial position regarding assets, liabilities, and equity.
-
Adjustments: Necessary for accurate financial statements and reports.
-
Marshalling: Enhances clarity and logical structure in balance sheets.
Examples & Applications
A Trading Account shows that in April, a company had sales of $10,000 and costs of goods sold were $7,000, resulting in a gross profit of $3,000.
In a Profit and Loss Account, a business adds indirect income of $2,000 and has total indirect expenses of $1,500, leading to a net profit of $3,500.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To report it right, we need to adjust, or the numbers we trust will turn into dust.
Stories
Imagine a baker, Joe, who tracks all his sales. Without his profit reports, he would miss the trails of what’s working or what’s stale in his bakery!
Memory Tools
Remember 'FAT' for final accounts: F for Financial health, A for Adjustments, and T for Trading insights.
Acronyms
Acronym 'BAL' for Balance Sheet
for Balance
for Assets
for Liabilities.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Final Accounts
Financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period to assess profitability and financial position.
- Trading Account
An account that calculates gross profit or loss based on direct incomes and expenses.
- Profit and Loss Account
An account that determines net profit or loss by considering indirect incomes and expenses.
- Balance Sheet
A statement that presents a company's financial position, listing assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity.
- Adjustments
Entries made to align financial statements with actual incomes and expenses not recorded during the accounting period.
- Marshalling
The systematic arrangement of items in a balance sheet for clarity and consistency.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
