Introduction to Final Accounts
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What are Final Accounts?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss Final Accounts. Can anyone tell me what they think final accounts are?

Are they the reports that businesses prepare to show their financial status?

That's right! Final accounts are financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period. They help assess the profitability and financial position of a business. Can anyone name the three main components?

Is it the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet?

Exactly! Those three are essential for understanding a business's financial performance. Let's remember: T for Trading, P for Profit and L for Loss, and B for Balance Sheet - TPLB!

What do we use these final accounts for?

Great question! They help stakeholders like owners and investors make informed decisions. So why do you think it's important for businesses to have accurate final accounts?

To make sure they are making profits and managing resources wisely!

Exactly! Accurate final accounts lead to better financial decision-making.
Purpose of Final Accounts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Building on our previous discussion, let's focus on the purpose of final accounts. Why do stakeholders need these accounts?

Maybe to see if the business is profitable?

That's one reason! Final accounts help evaluate profitability and financial position. Can anyone name other stakeholders involved?

Creditors and investors are also stakeholders!

Good! They use this information to decide whether to lend money or invest in the business. Remember, final accounts are crucial for making informed business decisions. To summarize, who can tell me the purposes of final accounts?

They evaluate performance and assist in decision-making!

Perfect! You're catching on well!
Accounting Equation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into the Balance Sheet. Can someone tell me the basic accounting equation?

Is it Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity?

Excellent! This equation is fundamental to understanding how the Balance Sheet is structured. It shows how a business's resources are financed through debts and equity. Why do you think this equation is important?

It helps ensure the Balance Sheet balances!

Exactly right. Let’s remember: A for Assets, L for Liabilities, and E for Equity - ALE! If a business does not keep the equation balanced, what might happen?

It could mislead investors and creditors!

Fantastic! This is why accurate final accounts are vital.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Final accounts consist of the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, and serve to evaluate a business's financial performance and position. These statements are essential for stakeholders in decision-making processes.
Detailed
Introduction to Final Accounts
Final accounts are critical financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period, providing insight into the profitability and financial position of a business. They consist of three primary components:
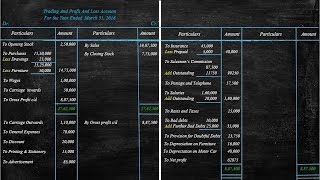
- Trading Account: This account determines the gross profit or gross loss by showcasing the direct income and expenses related to the sale of goods.
- Profit and Loss Account: This account assesses net profit or net loss by including indirect income and expenses, such as rent and salaries.
- Balance Sheet: This statement displays the business's financial position on a specific date, listing assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity, following the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity.
The purpose of preparing these final accounts is to evaluate the financial performance and position of the business effectively. Stakeholders like owners, managers, creditors, and investors utilize this information for informed decision-making, which underscores the importance of accurate financial reporting in business operations.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What are Final Accounts?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Final accounts are the financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period to determine the profitability and financial position of a business. These accounts include:
1. Trading Account
2. Profit and Loss Account
3. Balance Sheet
Detailed Explanation
Final accounts are essential financial statements produced after an accounting period ends. Their primary purpose is to analyze how well a business has performed financially and to understand its overall financial health. The three main components of final accounts are:
1. Trading Account: This account focuses specifically on the revenue from sales and the costs incurred from producing goods, helping to identify gross profit or loss.
2. Profit and Loss Account: This statement takes it a step further, including indirect expenses and incomes, to calculate the net profit or loss.
3. Balance Sheet: This presents a snapshot of what the business owns (assets) and what it owes (liabilities) at a specific point in time.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a student's report card at the end of the school year. It reveals the student's achievements (final accounts), showing grades for each subject (trading account), overall performance (profit and loss account), and the total units completed (balance sheet). Just like the report card helps students and parents understand educational performance, final accounts help a business understand financial performance.
Purpose of Final Accounts
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Final accounts help to evaluate the financial performance (profitability) and the financial position (assets, liabilities, and equity) of a business. They are crucial for stakeholders such as owners, managers, creditors, and investors for making informed decisions.
Detailed Explanation
The purpose of final accounts is multi-faceted:
- Evaluating Financial Performance: By detailing expenses and incomes, these accounts help assess whether the business is making profits or incurring losses.
- Understanding Financial Position: Final accounts clearly show the assets the business possesses and the liabilities it owes, allowing stakeholders to gauge financial stability and solvency.
- Informed Decision-Making: Business owners, managers, and investors depend on these accounts to guide their decisions, such as whether to invest more, cut costs, or expand operations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of final accounts like an annual health check-up for an individual. Just as a doctor evaluates vital signs, weight, and medical history to assess health, final accounts provide a comprehensive view of a business's financial health. Stakeholders, like doctors, use this information to recommend actions—whether that’s scaling up business activities or taking preventive measures against financial stress.
Key Concepts
-
Final Accounts: Financial statements that provide a summary of a business's financial health.
-
Trading Account: An account showing direct income and expenses related to goods sold.
-
Profit and Loss Account: A summary of net profit or loss from operations after accounting for indirect expenses.
-
Balance Sheet: A statement that represents a company's financial position on a specific date.
-
Accounting Equation: A fundamental equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity.
Examples & Applications
A retail store prepares final accounts at the end of the year to determine its profitability and financial position.
A start-up business uses its final accounts to attract potential investors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Final accounts are three in line, T, P, B, all shine!
Stories
Imagine a business preparing for the end of the year. They gather their Trading Account to understand their gross profit, check their Profit and Loss for net results, and finally, prepare the Balance Sheet to show their financial health. It's a story of numbers and decisions, neatly tied at year’s end.
Memory Tools
Remember 'TPLB' for Trading, Profit and Loss, and Balance. Each is vital in creating a complete picture of financial health.
Acronyms
Use 'FAP' for Financial Assessments of Profitability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Final Accounts
Financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period to assess profitability and financial position.
- Trading Account
Account that determines gross profit or loss based on direct income and expenses from sales.
- Profit and Loss Account
Account that determines net profit or loss, incorporating indirect incomes and expenses.
- Balance Sheet
Statement showing a business's financial position, listing assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Stakeholders
Individuals or groups concerned with or affected by a business’s financial performance.
- Accounting Equation
The formula Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity, representing the financial structure of a company.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
