Final Accounts without Adjustments
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Final Accounts Without Adjustments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss final accounts prepared without any adjustments. Can anyone tell me why final accounts are important?

They show how much profit a company made, right?

Exactly! Final accounts help in revealing a company's profitability and financial health. Let's start with the Trading Account. Who can define what a Trading Account is?

It's where we calculate gross profit or loss from sales.

Well done! How do we calculate gross profit in the Trading Account?

Gross profit is calculated by subtracting cost of goods sold from net sales.

Great! Remember the formula: Gross Profit = Sales - Cost of Goods Sold. So what comes next after the Trading Account?

The Profit and Loss Account!

Correct! In the Profit and Loss Account, we calculate net profit by accounting for indirect incomes and expenses. Can anyone name an example of an indirect expense?

Salaries, right?

Yes, salaries are an indirect expense. Now, what do we prepare after calculating net profit?

The Balance Sheet!

Exactly! The Balance Sheet gives us the financial position of the business by listing the assets and liabilities. Let’s summarize: we prepare three accounts: Trading, Profit and Loss, and Balance Sheet. These allow us to analyze profitability and financial stability.
Detailed Analysis of the Trading Account
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let’s take a closer look at the Trading Account. Can anyone tell me what goes on the debit side?

Opening stock, purchases, and direct expenses.

Correct! And what about the credit side?

Sales and gross profit.

That’s right! We list income on the credit side and expenses on the debit side. Does anyone know how we derive gross profit from this account?

We subtract the total costs from the sales revenue.

Exactly! Remember, Gross Profit = Sales - (Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses - Closing Stock). Now, let’s discuss the impact of the gross profit on the Profit and Loss Account. Can gross profit impact what?

It impacts the net profit!

Well said! Gross profit is essential as it flows into the Profit and Loss Account. Next, let’s wrap up by discussing its effects and importance. Why do we care about knowing Gross Profit?

It helps assess the efficiency of production and sales.

Exactly right! Understanding gross profit allows businesses to make strategic decisions. Let’s summarize today's key points on the Trading Account.
Exploring the Profit and Loss Account
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move on to the Profit and Loss Account. Who can remind me of its primary purpose?

To calculate net profit or loss by considering indirect incomes and expenses.

Exactly! We assess indirect expenses like rent and indirect income such as interest earned. How do we determine the net profit?

We take gross profit and subtract total indirect expenses.

Correct! So what could impact our net profit besides indirect expenses?

Indirect income would also impact it positively.

Right! It’s essential to track both expenses and income. Now, let’s summarize the Profit and Loss Account’s role in finalizing our financial statements.
Finalizing with the Balance Sheet
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've calculated net profit, we’ll examine the Balance Sheet. What is the primary purpose of the Balance Sheet?

To show the financial position of a business at a specific date.

Exactly! It showcases assets, liabilities, and equity. Can anyone state the accounting equation that the Balance Sheet is based on?

Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity.

Well done! What types of assets do we typically see on a Balance Sheet?

Fixed assets and current assets.

Correct! And what about liabilities? What do we classify them as?

Long-term and short-term liabilities.

Exactly. Understanding the Balance Sheet is critical for assessing a company's health. Let’s summarize its purpose and importance in decision-making.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the procedure for preparing final accounts without adjustments. We begin with the Trading Account to determine gross profit, move on to the Profit and Loss Account to calculate net profit, and conclude with the Balance Sheet to assess the financial position of the business.
Detailed
Final Accounts Without Adjustments
In this section of Chapter 7, we will focus on the preparation of final accounts in the absence of any adjustments. Final accounts refer to the financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period, and they play a pivotal role in assessing a business's profitability and financial position.
Procedure for Preparing Final Accounts Without Adjustments
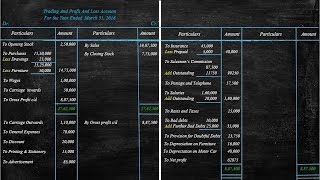
- Trading Account: This is the first step in the preparation, where we determine the gross profit or loss. The Trading Account summarizes the direct income from sales and the direct expenses incurred, ultimately leading to the calculation of gross profit.
- Profit and Loss Account: After calculating the gross profit, the next step involves preparing the Profit and Loss Account. This account reflects the net profit or loss by considering all indirect incomes and expenses.
- Balance Sheet: Finally, the Balance Sheet is prepared to present the overall financial position of the business, showing assets, liabilities, and owner's equity.
The importance of this section lies in the fact that even without adjustments, the foundational concepts in financial accounting remain the same, demonstrating the sequential nature of preparing final accounts.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Preparation of Final Accounts
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When no adjustments are necessary, the trading account is prepared to determine the gross profit, followed by the profit and loss account to calculate the net profit.
Detailed Explanation
In this step, we focus on preparing the trading account first to find out how much gross profit a business has made. The trading account summarizes all revenues from sales and the direct expenses incurred to generate those sales. Once the gross profit is known, we then move to the profit and loss account to consider any indirect expenses and incomes to finally determine the net profit. The absence of adjustments simplifies this process as all revenues and expenses are known and recorded accurately.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the trading account like a chef preparing a classic dish. The chef first gathers all ingredients (sales and direct costs) to figure out if the dish is a success (gross profit). Once they have the main dish ready, they might add seasoning or garnishes (indirect costs and income) before presenting it as a complete meal to the diners (the net profit).
Compiling the Balance Sheet
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The balance sheet is prepared after calculating net profit or loss, showing the business’s financial position.
Detailed Explanation
After we have calculated the net profit from the profit and loss account, it's time to prepare the balance sheet. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a business’s financial situation at a specific point in time. It lists all the business's assets, what it owes (liabilities), and the owner's equity. This part is critical as it helps stakeholders understand everything the business owns versus what it owes, hence the overall health of the business.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a personal net worth statement. If you list all your valuables like your car and house (assets) and subtract your debts such as loans or credit card bills (liabilities), you'll arrive at your net worth (owner's equity). Similarly, the balance sheet gives business owners and investors clarity about the total worth of the business at that moment.
Key Concepts
-
Final Accounts: Financial statements prepared to evaluate the profitability and financial position of the business.
-
Trading Account: Determines gross profit or loss from sales.
-
Profit and Loss Account: Calculates net profit by accounting for indirect income and expenses.
-
Balance Sheet: Presents the financial position of a business at a specific date.
Examples & Applications
A company sold goods totaling ₹100,000, with a cost of goods sold amounting to ₹60,000. The gross profit calculated in the Trading Account would be ₹40,000.
If the total indirect expenses amount to ₹20,000 and the gross profit was ₹40,000, the net profit reflected in the Profit and Loss Account would be ₹20,000.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To profit and loss we add and subtract, Balance Sheet shows all, that's a fact!
Stories
Imagine a baker who sells cakes. She calculates her sales and expenses. First, she notes what she sold (the Trading Account), then counts the bills (the Profit and Loss Account), and finally checks her savings (the Balance Sheet)!
Memory Tools
Remember: T P B (Trading, Profit&Loss, Balance) to prepare financials on your way!
Acronyms
TPB for Trading, Profit and Loss, and Balance - guiding your accounting path!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Trading Account
A financial statement that shows the gross profit or loss by summarizing sales and costs related to goods sold.
- Profit and Loss Account
A statement that determines the net profit or loss by accounting for indirect incomes and expenses.
- Balance Sheet
A financial statement representing a business's financial position by listing its assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at a specific date.
- Gross Profit
The profit calculated from gross sales minus cost of goods sold.
- Net Profit
The profit remaining after all expenses, including indirect expenses, have been deducted from gross profit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
