Levels of Organisation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today we're going to discuss the first level of biological organization: cells. Can anyone tell me why cells are considered the basic unit of life?

Because they make up all living organisms!

Exactly! Cells perform essential functions necessary for an organism's survival. Here’s a mnemonic to help you remember: 'C for Cell, the building block of life.' Now, what are some functions that cells perform?

Cells can produce energy and help in growth!

Right! They also help in repairing tissues. Let’s move to the next level of organization.
Understanding Tissues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve covered cells, let’s talk about tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that perform a shared function. Who can name a type of tissue?

Muscle tissue!

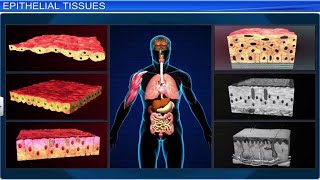
Correct! Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. Remember the acronym 'EMP' for Epithelial, Muscular, Connective, and Nervous tissues. Can anyone explain the function of epithelial tissue?

It covers body surfaces and lines cavities!

Well done! Epithelial tissue plays a key role in protection. Let’s shift our focus to how tissues combine to form organs.
Exploring Organs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We have learned about cells and tissues. Now let's examine organs, which are structures made of multiple tissue types. Can anyone provide an example of an organ?

The heart?

Yes! The heart is an excellent example. It consists of muscle tissue for contraction, connective tissue for structure, and nervous tissue for coordinating the heartbeat. Why do you think it is important for organs to work together?

To perform specific functions efficiently!

Exactly! Now, let’s discuss how these organs come together to form systems.
Introduction to Organ Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, we have organ systems, which are groups of organs that work together. What is an example of an organ system, and what does it do?

The circulatory system, which moves blood around the body!

Correct! The circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. An easy way to remember it is by thinking of how highways (blood vessels) transport cars (blood) in a city (our body). Can anyone tell me another function of organ systems?

They help maintain homeostasis!

Great job! Homeostasis is crucial for maintaining a stable internal environment. Let’s summarize today’s lesson.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Biological structures are arranged in a hierarchical manner, starting from cells, which are the basic units of life, to tissues made of cells, organs composed of different tissues, and ultimately to organ systems that coordinate bodily functions.
Detailed
Levels of Organisation
In biology, structures are organized in a hierarchy that is essential for understanding how living organisms function. This organization comprises four primary levels:
- Cells: The basic unit of life, responsible for performing various functions necessary for survival.
- Tissues: Groups of similar cells that work together to carry out a specific function. For example, muscle tissue enables movement through the contraction of muscle fibers.
- Organs: Structures made up of different types of tissues working collaboratively to perform specific functions, such as the heart, which pumps blood throughout the body.
- Organ Systems: Groups of organs that coordinate their functions to support complex life processes. An example is the digestive system, which includes the stomach, intestines, and other organs that break down food.
This hierarchical organization is fundamental in biology as it illustrates how different components come together to form a functional organism.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Cells: The basic unit of life.
Detailed Explanation
Cells are the smallest units of life that can carry out all the essential functions necessary for living organisms. They are often referred to as the building blocks of life. Each cell can survive and function independently, performing tasks such as taking in nutrients, generating energy, and excreting waste. Understanding cells is fundamental to biology because they form the foundation for larger structures in the organisation of living beings.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a cell like a single brick in a building. Just like bricks come together to form walls, rooms, and eventually a house, cells come together to create tissues and organs in a living organism.
Tissues: Groups of Similar Cells
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Tissues: Groups of similar cells performing a common function.
Detailed Explanation
Tissues are formed when groups of similar cells work together to perform a particular function. For instance, muscle tissue is made of muscle cells that contract to enable movement. There are different types of tissues, each serving specific roles in an organism. Understanding tissues helps us appreciate how various cell types work collaboratively to maintain the body's health and functionality.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sports team where each player has a specific role, but they all work together to win a game. Similarly, in our bodies, different types of cells form tissues that collaborate to accomplish particular tasks, just like a team working towards a common goal.
Organs: Different Tissues at Work
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Organs: Different tissues working together for specific functions.
Detailed Explanation
An organ is a structure composed of two or more types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. For instance, the heart is an organ that contains muscle tissue to pump blood, connective tissue to provide support, and epithelial tissue to line its inner chambers. The interaction of different tissues allows organs to perform complex functions efficiently, which is vital for the organism's survival.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a car as an analogy for an organ. Just like different parts of a car (engine, wheels, body) need to work together for the car to run smoothly, various tissues in an organ need to cooperate to ensure it functions effectively.
Organ Systems: Grouping for Bodily Functions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Organ Systems: Groups of organs coordinating to perform bodily functions.
Detailed Explanation
Organ systems are groups of organs that work together to perform complex bodily functions. For example, the circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood, all coordinating to circulate nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. Each organ system plays a crucial role, and they work interdependently, ensuring the organism remains healthy and operates efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an organ system like a department in a large company. Just as various departments (like sales, marketing, and production) collaborate to achieve business objectives, different organ systems in the body work together to sustain life and perform essential functions.
Key Concepts
-
Cells: The basic unit of life crucial for all biological processes.
-
Tissues: Groups of similar cells that perform specific functions together.
-
Organs: Composed of multiple tissue types working in harmony.
-
Organ Systems: Groups of organs that coordinate to fulfill complex functions.
Examples & Applications
Example of a tissue is muscle tissue, which allows movement.
The heart is an organ made of muscle, connective, and nervous tissues working together.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cells, tissues, organs too; organ systems help us through.
Stories
Imagine a city: Cells are the houses, Tissues are the teams that work there, Organs are the buildings where teams gather, and Organ Systems are the entire city working smoothly.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CTOS' (Cells, Tissues, Organs, Systems) for the hierarchy of organization.
Acronyms
Use 'MCT' for Muscle, Connective, and Tissue types in organs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cells
The basic unit of life that performs essential functions necessary for an organism's survival.
- Tissues
Groups of similar cells that work together to carry out a specific function.
- Organs
Structures made up of different types of tissues working collaboratively to perform specific functions.
- Organ Systems
Groups of organs that coordinate their functions to support complex life processes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
