Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Levels of Organisation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the levels of biological organization. Can anyone tell me what the basic unit of life is?

Is it the cell?

Correct! Cells are indeed the basic unit of life. Now, who can explain what happens when multiple cells work together?

They form tissues?

Exactly! Tissues are groups of similar cells fulfilling a specific function. So, what do we call groups of different tissues that work together for a specific task?

Those are organs, right?

Right again! Organs are made from different tissue types. Finally, when several organs collaborate, they form an organ system. We'll remember this using the acronym C-T-O-O: Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ systems. Can anyone recap this for us?

C-T-O-O stands for Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems!

Great job! Understanding this hierarchy helps us grasp how complex organisms can perform essential functions.
Tissues in Animals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's focus on animal tissues. Can anyone name the four primary types of animal tissues?

Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, and Nervous tissues.

Correct! Let’s break these down. What do epithelial tissues do?

They cover body surfaces and line cavities.

Right! And what about connective tissue? What are some examples?

It supports and binds other tissues, like bone, blood, and adipose.

Exactly! And what's the role of muscular tissue?

It enables movement.

Awesome! It includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Now, can anyone describe nervous tissue?

It transmits impulses and coordinates responses!

Well done! Remembering the roles of these tissues is fundamental for understanding how animals function.
Tissues in Plants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to plant tissues, what are the two major classifications of plant tissues?

Meristematic and Permanent tissues.

Great! Let's dive deeper. What are meristematic tissues responsible for?

They are regions of active cell division and help with growth.

Correct! How about permanent tissues?

They are specialized for different functions.

Exactly! There are two types of permanent tissues: simple and complex. Can anyone name examples of simple permanent tissues?

Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma.

Excellent! And what are the complex permanent tissues?

Xylem and Phloem.

Perfect! Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem carries food. Understanding these tissues is crucial for grasping how plants function and thrive!
Functions of Tissues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s review the functions of different tissues. Can anyone tell me what parenchyma does?

It is involved in storage, photosynthesis, and wound healing.

Right! And what role does collenchyma play?

It provides flexible support.

Exactly! Now, sclerenchyma provides what?

Mechanical strength to the plant.

Very good! Now let's switch gears to vascular tissues. What does xylem do?

It transports water and minerals from roots to other plant parts.

Correct! And phloem?

It transports food.

That's right! All these functions are critical for both plants and animals to operate effectively in their environments.
Differences Between Animal and Plant Tissues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s compare animal and plant tissues. How do they differ?

Animal tissues are more varied in function.

Exactly! Can anyone explain why this is the case?

Because animals need various tissues for movement, coordination, and other functions.

Great point! And what about plant tissues? What is their primary role?

They mainly support and transport substances, focusing less on movement.

That's right! So, overall, understanding these differences helps us appreciate how plants and animals adapt to their environments. Let's summarize: animal tissues are diverse and specialized for movement, while plant tissues focus on support and transport.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section delves into the different levels of biological organization, from cells to organ systems, and classifies animal and plant tissues based on their structure and function. It highlights the significance of each type of tissue in supporting the organism's overall activities.
Detailed
Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
Living organisms exhibit complex organization ranging from microscopic cells to extensive organ systems. This structural hierarchy is crucial for understanding how organisms perform various vital functions. The organization levels include:
- Cells - The basic unit of life.
- Tissues - Groups of similar cells working together for a common function.
- Organs - Different tissues harmonizing to execute specific functions.
- Organ Systems - Collaborations of groups of organs to perform larger bodily tasks.
Animal Tissues
Four primary types of animal tissues are identified:
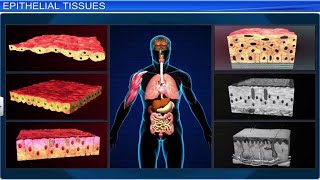
- Epithelial Tissue: Serves as a protective layer covering body surfaces.
- Connective Tissue: Binds and supports other tissues; includes blood, bone, and adipose.
- Muscular Tissue: Facilitates bodily movement, categorized into skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
- Nervous Tissue: Responsible for transmitting impulses and coordinating functions.
Plant Tissues
In contrast, plant tissues are categorized into:
- Meristematic Tissues: Actively undergoing cell division contributing to growth.
- Permanent Tissues: Specialized for various functions and categorized into:
- Simple Permanent Tissues (similar cells: parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma).
- Complex Permanent Tissues (various cell types: xylem and phloem).
Overall, understanding these tissue types aids in comprehending the functional variations between plants and animals.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Structural Organisation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Living organisms exhibit complex organization starting from microscopic cells to large organ systems. Understanding this structural hierarchy helps explain how organisms perform vital functions.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the fundamental concept of structural organization in living organisms. It explains that all living beings, regardless of their size, are made up of small building blocks called cells. These cells group together to form tissues, which then combine into organs, and ultimately create systems that carry out various functions necessary for survival. Understanding this hierarchy allows scientists and students alike to comprehend how different parts of a living organism work together to maintain life.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a city. At the smallest level, it has individual houses (cells). Many houses grouped together form a neighborhood (tissues). Different neighborhoods create sections of the city (organs), and all the sections work together to create the city as a whole (organ systems). Just like a city functions efficiently when all parts are connected, so do living organisms.
Levels of Organisation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Biological structures are organized in a hierarchical manner:
● Cells: The basic unit of life.
● Tissues: Groups of similar cells performing a common function.
● Organs: Different tissues working together for specific functions.
● Organ Systems: Groups of organs coordinating to perform bodily functions.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk lists the levels of biological organization, which include:
1. Cells - The smallest unit of life that can function independently. They perform all necessary life processes.
2. Tissues - Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function, like muscle tissue responsible for movement.
3. Organs - Structures composed of multiple tissue types that work together to fulfill a complex function, such as the heart pumping blood.
4. Organ Systems - Combinations of various organs that work together to carry out major functions; for example, the digestive system processes food.
This hierarchical organization is critical for understanding how living organisms grow, develop, and function.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake. The individual ingredients (cells) like flour, sugar, and eggs mix to create a batter (tissues). Once baked, the cake itself becomes the final product (organ), and when served to people enjoying a meal together, it represents the celebration and joy (organ system). Each part is essential for the success of the cake as a whole.
Key Concepts
-
Cells: The basic structural and functional units of life.
-
Tissues: Groups of similar cells that perform a specific function.
-
Organs: Structures consisting of different tissues working together.
-
Organ Systems: Groups of organs that collaborate to perform vital functions.
-
Epithelial Tissue: Protective layer covering surfaces.
-
Muscular Tissue: Facilitates movement in organisms.
-
Connective Tissue: Binds and supports other tissues.
-
Nervous Tissue: Responsible for transmitting signals.
-
Meristematic Tissues: Regions of active cell division in plants.
-
Permanent Tissues: Specialized tissues derived from meristematic tissues.
Examples & Applications
Epithelial tissue covering the skin and lining the intestines is crucial for protection and absorption.
Muscular tissue, exemplified by cardiac muscle, is essential for pumping blood in the heart.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Epithelial for a cover, connective binds like a lover. Muscles move, nerves communicate — this is how we all relate!
Stories
Once upon a time in a forest, a tiny cell wanted to grow. It met other cells and formed tissues. Together they became organs, like a heart that pumped and a leaf that absorbed sunlight!
Memory Tools
Remember: E-C-M-N for Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous tissues.
Acronyms
T-O-C for Tissues, Organs, and Cells.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cells
The basic unit of life in organisms.
- Tissues
Groups of similar cells working together to perform a particular function.
- Organs
Structures composed of different tissues performing a specific function.
- Organ Systems
Groups of organs working together to perform complex functions.
- Epithelial Tissue
A type of tissue that covers body surfaces and lines cavities.
- Connective Tissue
Tissue that supports and binds other tissues.
- Muscular Tissue
Tissue responsible for movement, consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle types.
- Nervous Tissue
Tissue responsible for transmitting impulses and coordinating activities.
- Meristematic Tissues
Tissues with cells that are actively dividing, contributing to plant growth.
- Permanent Tissues
Tissues that are differentiated from meristematic tissues and specialized for specific functions.
- Parenchyma
A type of simple permanent tissue involved in the storage, photosynthesis, and healing.
- Collenchyma
A type of simple permanent tissue providing flexible support.
- Sclerenchyma
A type of simple permanent tissue providing mechanical strength.
- Xylem
Complex tissue responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants.
- Phloem
Complex tissue responsible for the transport of food in plants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
