Tissues in Animals
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
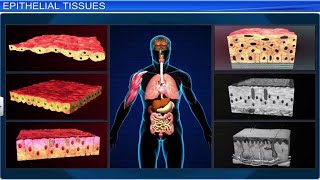
Epithelial Tissue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss epithelial tissue. Can anyone tell me what epithelial tissue is?

Isn't it the tissue that covers surfaces and lines cavities?

Exactly! Epithelial tissue acts as a protective barrier. What are some functions of this tissue?

It helps in absorption and secretion, right?

Correct! Remember the acronym 'PSA' - Protects, Secretes, Absorbs to help you recall the key functions.

Are there different types of epithelial tissue?

Yes! It can be either simple or stratified, depending on the number of cell layers. Let's move on to connective tissue.

To summarize, epithelial tissue covers surfaces, protects, absorbs, and secretes.
Connective Tissue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss connective tissue. Can anyone tell me what connective tissues do?

They support and bind other tissues!

Correct! Connective tissues include types like blood and bone. What are some differences among them?

Blood transports substances while bone provides structural support.

Great observation! Here’s a mnemonic: 'B.B.C.': Blood, Bone, Cartilage. These are examples of connective tissues.

What other types are there, specifically?

There’s adipose tissue for fat storage, and cartilage for flexibility in some joints. Allowing movement yet providing support!

In summary, connective tissue is diverse, supporting various functions like transport and protection.
Muscular Tissue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to muscular tissue! What do you think is its primary function?

To facilitate movement, I think!

Spot on! There are three types of muscular tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Can anyone describe them?

Skeletal muscle is voluntary and helps in body movements, right?

Exactly, it’s under voluntary control! What about smooth muscle?

Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in organs like the stomach!

Wonderful! Lastly, cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. Remember the phrase 'SMSC' - Skeletal, Muscular, Smooth, Cardiac for the types!

To sum up, muscular tissue is responsible for all types of movement in our bodies.
Nervous Tissue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Last but not least, let's talk about nervous tissue. What role does it play?

It's responsible for transmitting impulses, right?

Correct! Nervous tissue consists of neurons and glial cells. Can anyone explain the roles of each?

Neurons transmit impulses, while glial cells support and protect neurons.

Great job! Here’s a mnemonic: 'N.G.' - Neurons and Glial cells. This will help you remember the major players in nervous tissue.

So, nervous tissue is integral for communication within the body?

Exactly right! In summary, nervous tissue is crucial for transmitting impulses and coordinating bodily functions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Animal tissues are categorized into four main types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. Each type plays a vital role in the body, from providing coverage and support to facilitating movement and transmitting impulses.
Detailed
Tissues in Animals
This section delves into the four primary types of animal tissues, each with distinct structural characteristics and crucial roles in ensuring the proper functioning of an organism:
- Epithelial Tissue: This type covers body surfaces and lines internal cavities, providing protection, absorption, and secretion. It can be categorized as simple or stratified, depending on the number of cell layers.
- Connective Tissue: Connective tissues provide support, bind other tissues and organs together, and assist in various bodily functions. Examples include blood, bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue, each serving unique roles in the body’s architecture and metabolism.
- Muscular Tissue: Responsible for movement, muscular tissue can be further divided into three types: skeletal muscle, which facilitates voluntary movements; smooth muscle, found in walls of hollow organs and under involuntary control; and cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, facilitating its pumping action.
- Nervous Tissue: This tissue is vital for communication and coordination within the body. It consists of neurons which transmit impulses and glial cells that support and protect the neurons.
Understanding these tissues is fundamental to grasping how complex multicellular organisms function, as they provide the necessary structure and enable various physiological processes.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Animal Tissues
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There are four primary animal tissues:
Detailed Explanation
Animal tissues are classified into four primary types, each serving different functions in the body. By understanding these basic categories, we can appreciate the complexity and functionality of animal organization at the tissue level.
Examples & Analogies
Think of animal tissues like the different departments in a school. Just as each department (like science, math, arts) has its own role but works together for the school's overall education mission, animal tissues have distinct functions but collaborate to maintain the body’s health.
Epithelial Tissue
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Epithelial Tissue: Covers body surfaces and lines cavities.
Detailed Explanation
Epithelial tissue serves as a protective layer for the body. It covers the skin and lines internal organs and cavities. This tissue acts as a barrier to protect underlying structures from mechanical injuries, pathogens, and dehydration. It also has roles in absorption, secretion, and sensation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wearing a raincoat when it rains. Just like a raincoat keeps you dry and protects you from the weather, epithelial tissue protects your organs and keeps various surfaces of your body safe from external harm.
Connective Tissue
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Connective Tissue: Supports and binds other tissues; includes bone, cartilage, blood, adipose, etc.
Detailed Explanation
Connective tissue plays a critical role in supporting and binding other tissues of the body. It provides structure, stores energy, and helps transport substances, such as nutrients and waste. Various types include bone (providing support), cartilage (providing flexibility), and blood (transporting substances).
Examples & Analogies
Think of connective tissue like the framework of a house. Just as the frame supports the walls and roof, connective tissue supports organs and connects different body parts together, ensuring everything stays in place.
Muscular Tissue
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Muscular Tissue: Responsible for movement; includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
Detailed Explanation
Muscular tissue is essential for movement in the body. It is divided into three types: skeletal muscle, which is under voluntary control and moves bones; smooth muscle, which is involuntary and lines organs; and cardiac muscle, which makes up the heart. Together, they enable both voluntary and involuntary movements.
Examples & Analogies
Consider muscular tissue as the engine of a car. Just like the engine powers movement and functionality of the vehicle, muscular tissue powers movement within the body, enabling activities from walking to the beating of the heart.
Nervous Tissue
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Nervous Tissue: Transmits impulses and coordinates responses.
Detailed Explanation
Nervous tissue is responsible for communication within the body. It consists of neurons that transmit electrical signals, enabling the body to react to stimuli. This tissue is crucial for coordination, reflexes, and processing sensory information.
Examples & Analogies
Think of nervous tissue as a telephone line. Just like a telephone line carries messages back and forth, nervous tissue transmits signals throughout the body, allowing different parts of the body to communicate quickly and effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Epithelial Tissue: Covers surfaces and is involved in protection, absorption, and secretion.
-
Connective Tissue: Provides support and binds other tissues and organs.
-
Muscular Tissue: Facilitates movement within the body.
-
Nervous Tissue: Responsible for communication within the body through impulse transmission.
Examples & Applications
Epithelial tissue forms the outer layer of skin, protecting underlying structures.
Bone is a type of connective tissue that provides structural support.
Skeletal muscle enables voluntary movements like running.
Neurons in nervous tissue transmit signals quickly across the body.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Epithelial for cover and defense, connective for support, that's common sense.
Stories
Once upon a time, in the body’s kingdom, the Epithelia protected the realm while Connective provided the walls of the castle, Muscular danced around, and Nervous sent the messages through the kingdom.
Memory Tools
Remember 'E.C.M.N.' for Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous tissues.
Acronyms
'SMSC' for Skeletal, Muscular, Smooth, Cardiac—types of muscular tissue.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that covers body surfaces and lines cavities; functions in protection, absorption, and secretion.
- Connective Tissue
Tissue that supports and binds other tissues and organs, including blood, bone, and cartilage.
- Muscular Tissue
Tissue responsible for movement, divided into skeletal, smooth, and cardiac types.
- Nervous Tissue
Tissue that transmits impulses and coordinates responses, consisting of neurons and glial cells.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
