Summary of Differences Between Animal and Plant Tissues
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Animal Tissues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the four primary types of animal tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues. Each of these tissues has a unique structure and function.

What does epithelial tissue do?

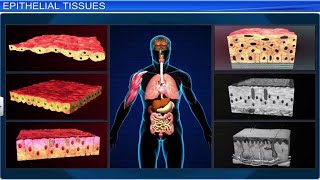
Great question! Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces and lines cavities. Think of it as the protective layer of our body. To remember it, just keep in mind the 'E' for 'Enclosing'.

And what about connective tissue?

Connective tissue supports and binds other tissues. It includes types like bone, cartilage, and blood. Just remember 'Connective = Connecting the dots between body parts!'

What does muscular tissue do?

Muscular tissue helps in movement; we have skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Remember, 'Muscles Move!'

What about nervous tissue?

Nervous tissue transmits impulses and coordinates responses. Think 'Nerves Relay Messages!'.

In summary, animal tissues vary in structure and function—each type tailored for specific roles essential for survival.
Introduction to Plant Tissues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s switch gears and look at plant tissues! Plant tissues are classified into meristematic and permanent tissues. Can anyone tell me what meristematic tissues do?

They help in growth, right?

Exactly! Meristematic tissues are responsible for active cell division. Think of 'Meristem = More Cells' for growth!

What about permanent tissues?

Permanent tissues, which come from meristematic ones, are specialized for specific functions. They can be simple, like parenchyma, or complex, like xylem and phloem.

What do xylem and phloem do?

Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports food. A good mnemonic would be 'Xylem = Water Up, Phloem = Food Around'.

So, plant tissues mainly help in support and transport?

Correct! Plant tissues are critical for photosynthesis, growth, and structural integrity.
Comparative Analysis of Both Tissues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have covered both types of tissues, let’s discuss their differences. Who can summarize what we have learned?

Animal tissues are diverse in function while plant tissues are more specialized?

Exactly! Animal tissues facilitate movement and coordination, while plant tissues mainly focus on support, transport, and growth.

What about adaptability?

Good point! Animal tissues adapt quickly to changes, whereas plant tissues are primarily adapted to efficiently use their nutrients and resources.

So in terms of complexity, animals have a richer diversity of functions?

Correct! Animals can respond to stimuli in more varied ways than plants due to their more complex nervous and muscular tissues.

Is that why animals can move around and react to danger?

Absolutely! In summary, animal tissues are more varied and complex, while plant tissues are more specialized and focused on growth and support.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The differences between animal and plant tissues are characterized by their functions and complexity. Animal tissues are more diverse in roles, including movement and coordination, while plant tissues mainly focus on supporting growth and transport processes. This section highlights the fundamental contrasts in structure and function, crucial for understanding overall biological organization.
Detailed
Summary of Differences Between Animal and Plant Tissues
This section outlines the essential differences between animal and plant tissues, which consist of specialized cells organized to perform specific functions. Understanding these differences is vital for comprehending how multicellular organisms operate.
Key Differences:
- Functionality: Animal tissues are diverse, contributing to various functions including movement (muscular tissue), protection (epithelial tissue), and messaging (nervous tissue). In contrast, plant tissues primarily focus on growth (meristematic tissues), support (sclerenchyma), and transport of water and nutrients (xylem and phloem).
- Complexity: Animal tissues often show more functional diversity, such as the ability to respond to external stimuli and perform voluntary movements, while plant tissues tend to have well-defined functions related to their structural roles.
- Adaptation: Animal tissues are more adaptable to changing conditions, while plant tissues have evolved to effectively utilize available resources like sunlight, water, and minerals for growth.
Importance
The differences between these two types of tissues illustrate the evolutionary adaptations that separate the plant and animal kingdoms, explaining their respective survival strategies in various environments.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Variation in Function of Tissues
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Animal tissues are generally more varied in function, including movement and coordination.
Detailed Explanation
Animal tissues serve multiple roles that are crucial for the survival and functioning of the organism. For example, tissues such as muscular tissue allow animals to move, while nervous tissue enables coordination and response to stimuli. This variation means that different types of animal tissues can perform unique functions, adapting to the needs of the organism.
Examples & Analogies
Think of animal tissues like a well-coordinated team in a sports game. Each player has a different role—some are responsible for scoring (muscular tissue), while others support with strategy (nervous tissue). Without this variety, the team wouldn’t perform well.
Support and Growth in Plant Tissues
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Whereas plant tissues are mainly involved in support, transport, and growth.
Detailed Explanation
In contrast to animals, plant tissues have more specialized roles focusing primarily on support, transportation of nutrients and water, and growth. For example, xylem is responsible for transporting water, while phloem carries food. Tissues like parenchyma support growth through storage and functions like photosynthesis. This specialization helps plants thrive in their environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a plant as a factory where each section has a specific responsibility. The xylem is like the delivery trucks that bring in water, the phloem is the conveyor belt transporting food to different parts, and the supportive tissues are the structural beams holding the factory up. Without each part doing its job, the factory wouldn’t function properly.
Key Concepts
-
Epithelial Tissue: Covers body surfaces.
-
Connective Tissue: Binds and supports organs.
-
Muscular Tissue: Facilitates movement.
-
Nervous Tissue: Coordinates body functions.
-
Meristematic Tissue: Involved in plant growth.
-
Permanent Tissue: Specialized plant tissues.
Examples & Applications
Epithelial tissue acts as a barrier against pathogens.
Xylem transports water necessary for photosynthesis.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Epithelial lines, connective intertwines; muscular moves, while nervous grooves.
Stories
Once upon a time, in the kingdom of Biology, there were four friends, Epi, Connecti, Muscles, and Nerves. Epi protected everyone, Connecti held the community together, Muscles helped them run and play, while Nerves communicated all their feelings.
Memory Tools
E.C.M.N - Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous.
Acronyms
PLANTS for Permanent Tissues
Photosynthesis
Locomotion
Absorption
Nutrient Transport
Structural Support.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Epithelial Tissue
A type of tissue that covers outer surfaces and lines cavities in the body.
- Connective Tissue
Tissue that supports and binds other tissues, including types like bone and blood.
- Muscular Tissue
Tissue responsible for movement, consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
- Nervous Tissue
Tissue that transmits impulses and coordinates responses in the body.
- Meristematic Tissue
Plant tissue that consists of actively dividing cells, contributing to growth.
- Permanent Tissue
Plant tissue derived from meristematic tissue, specialized for distinct functions.
- Xylem
Plant tissue responsible for the transport of water and minerals from roots to leaves.
- Phloem
Plant tissue that transports food produced by photosynthesis throughout the plant.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
