Applications of Thermal Expansion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Bridges and Railways
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore how engineers account for thermal expansion in bridges and railways. Can anyone tell me what might happen if we don't consider thermal expansion in these structures?

They might crack or break if it gets too hot or cold!

Exactly! That's why engineers use expansion joints. Does anyone know what an expansion joint is?

It’s a gap that allows parts to move without damaging the structure.

Correct! And they help prevent structural failures. Can anyone think of other structures where thermal expansion might be significant?

What about buildings?

Absolutely right! Let's remember: bridges, railways, and buildings all need to be designed with thermal expansion in mind.
Thermometers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss thermometers. Who can explain how they work?

They measure temperature by looking at the expansion of liquids or gases.

Great! So, what liquids are commonly used in thermometers?

Mercury and alcohol!

Exactly! As the temperature rises, the liquid expands and moves up the tube. Remember, the expansion of the liquid is what allows us to measure temperature accurately.

Are there thermometers that use gases too?

Yes, there are! Gaseous thermometers also rely on thermal expansion. So remember: thermometers work by measuring thermal expansion of liquids or gases!
Pressure Cookers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's look at pressure cookers. Who knows how they utilize the concept of thermal expansion?

They cook food faster by increasing the pressure inside!

Exactly! Can anyone tell me how thermal expansion helps with that?

The steam and air expand, which raises the pressure, allowing the cooker to reach higher temperatures.

Well said! So, the takeaway is that the expansion of gases — air and steam — is essential for increasing cooking efficiency.
Bimetallic Strips
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss bimetallic strips. Who can tell me what they are used for?

They're used in thermostats to control temperature!

Correct! How do they work, though?

They bend when heated because the two metals have different rates of expansion.

Exactly right! This bending action can open or close electrical circuits, controlling heating or cooling systems. A good way to remember this is to think of 'bending for balance'!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
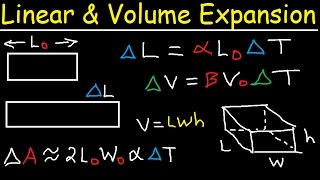
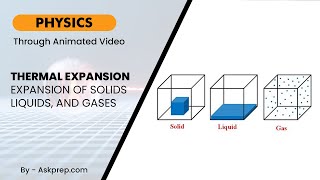
Applications of thermal expansion are crucial in several fields, including engineering and everyday items. This section covers how thermal expansion is utilized in bridges, thermometers, pressure cookers, and bimetallic strips, emphasizing their importance in accommodating temperature changes without causing structural failures.
Detailed
Applications of Thermal Expansion
This section highlights the practical uses of thermal expansion across various fields, essential for ensuring safety and functionality. These applications include:
- Bridges and Railways: Engineers design expansion joints in bridges and railways that absorb thermal expansion and contraction, preventing structural damage over time.
- Thermometers: Utilizing the thermal expansion of liquids (like mercury or alcohol) or gases, thermometers rely on the expansion of these substances with temperature changes to provide accurate readings.
- Pressure Cookers: Pressure cookers increase internal pressure using the thermal expansion of air and steam, which allows food to cook at higher temperatures and faster times.
- Bimetallic Strips: In devices like thermostats, bimetallic strips made of two different metals with distinct coefficients of expansion bend with temperature changes, helping control electrical circuits to maintain desired temperatures.
Each of these applications demonstrates the significance of understanding thermal expansion to engineer solutions that improve the safety and efficiency of various systems and everyday products.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Bridges and Railways
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Expansion joints are included in the design of bridges, railways, and buildings to allow materials to expand and contract with temperature changes without causing damage.
Detailed Explanation
Expansion joints are gaps designed into structures like bridges and railways. These gaps allow materials to expand when temperatures rise without putting stress on the structure. If structures were solidly built without these joints, the expanding materials could cause cracks or even structural failures, making it essential to incorporate them for safety and longevity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a bridge as a long, flexible piece of spaghetti. If you heat it up, it will start to bend and expand. Now, imagine that if you didn’t leave some space (like a tiny gap) for it to wiggle, it might snap or crack. Expansion joints work like those little gaps, allowing the structure to 'wiggle' safely.
Thermometers
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Thermometers work by measuring the expansion of liquids (such as mercury or alcohol) or gases with temperature changes.
Detailed Explanation
Thermometers can use liquids or gases to measure temperature. As temperature increases, the liquid or gas expands and moves up in a narrow tube, providing a reading on a calibrated scale. This principle of thermal expansion allows for precise temperature readings in everyday life.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine filling a balloon with air. As you blow more air in (which is like increasing temperature), the balloon stretches and gets larger. Thermometers operate on this principle, except instead of balloon stretching, it’s the liquid inside the thermometer expanding to show temperature changes.
Pressure Cookers
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pressure cookers rely on the expansion of air and steam to increase the pressure inside the vessel, cooking food faster.
Detailed Explanation
In a pressure cooker, when heat is applied, the water inside turns into steam, which occupies more space than the liquid. This increase in steam volume creates higher pressure inside the cooker, allowing it to cook food faster due to the higher temperature at which water boils under pressure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pressure cooker as a tightly sealed jar that you heat. Just like how steam builds up and increases the pressure in that jar, making it hard to open quickly, the pressure cooker uses this principle to cook meals in a fraction of the time it would normally take!
Bimetallic Strips
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bimetallic strips, made from two metals with different coefficients of expansion, are used in thermostats. The strip bends when heated, opening or closing electrical circuits to control temperature.
Detailed Explanation
A bimetallic strip consists of two layers of different metals. When the strip is heated, one metal expands more than the other, causing the strip to bend. This bending can be used to trigger an electrical switch, which is critical in devices like thermostats that regulate temperature in heating and cooling systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have two different kinds of dough. When you bake them, one rises faster than the other. If you put these dough pieces next to each other, the one that rises faster will push up the other. In bimetallic strips, similar action occurs when metals respond to heat at different rates, making it a clever way to control everyday temperature devices.
Key Concepts
-
Expansion Joint: A structure that allows for thermal expansion in bridges and railways.
-
Thermometer: An instrument that measures temperature based on liquid or gas expansion.
-
Pressure Cooker: A vessel that uses thermal expansion to cook food faster by increasing internal pressure.
-
Bimetallic Strip: A device made of two metals that expand at different rates, enabling temperature control in thermostats.
Examples & Applications
Bridges and railways incorporate expansion joints to prevent damage from thermal expansion.
Thermometers use the expansion of mercury or alcohol to accurately measure temperature.
Pressure cookers utilize steam and air expansion to increase cooking speed and efficiency.
Bimetallic strips in thermostats control heating and cooling systems by bending in response to temperature changes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If the temp goes up or down, thermal expansion is all around!
Stories
Once, there was a bridge that learned to breathe. Whenever it got hot outside, it would expand its joints and flex to avoid breaking—a smart bridge indeed!
Memory Tools
Think of 'T.E.P.B.' to remember: Thermal Expansion, Pressure cookers, Bimetallic strips, and Bridges!
Acronyms
Remember 'T.E.P.B.' stands for
Thermal Expansion
Expansion joints in buildings
Pressure cookers
and Bimetallic strips!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thermal Expansion
The increase in size or volume of a substance due to a rise in temperature.
- Expansion Joint
A structure that allows for movement and expansion due to thermal changes without causing damage.
- Bimetallic Strip
A strip made of two different metals that expand at different rates, used in temperature regulation devices.
- Thermometer
An instrument used to measure temperature through the expansion of liquids or gases.
- Pressure Cooker
A sealed cooking pot that uses steam pressure to increase the temperature and speed up cooking.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
