Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Fundamentals of Thermal Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss thermal expansion. Who can tell me what happens to a substance when its temperature increases?

It gets bigger, right?

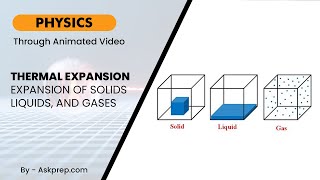
Exactly! This is called thermal expansion. Can anyone explain how thermal expansion differs between solids, liquids, and gases?

I think solids expand in a particular direction, while liquids expand equally in all directions.

And gases can expand and also affect pressure.

Great observations! Remember: solids expand linearly, liquids volumetrically, and gases can change both pressure and volume.

To help remember this, think of the acronym 'SVG': Solids, Volumetric, Gases.

That's helpful!

Let's recap: thermal expansion entails size increase due to temperature changes. Ready to move on?
Coefficients of Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into coefficients of thermal expansion. Who can explain what a coefficient is?

Is it how much something expands per degree of temperature change?

Well put! For solids, it’s denoted by alpha (α), and it varies by material. What happens with liquids?

They have a volumetric expansion coefficient, right?

Exactly! And for gases, we see this in laws like Charles' Law. So why is this important in engineering?

To design structures that can withstand temperature changes without breaking!

Precisely! Remember, knowing these coefficients ensures we can predict how materials will react to temperature fluctuations. Let's summarize what we've learned: the coefficient is crucial for predicting expansion.
Real-Life Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about real-world applications of thermal expansion. Can anyone share an example?

Bridges use expansion joints to allow for changes in temperature!

Correct! Expansion joints are critical for preventing structural damage. What about thermometers?

They use liquids that expand to indicate temperature!

Spot on! We also have pressure cookers that utilize vapor expansion. Let’s summarize today: thermal expansion is present in everyday structures and devices. Why do we need to understand this?

To ensure safety and efficiency!

Exactly! It all connects back to ensuring reliable designs and functioning products.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The conclusion reiterates that thermal expansion affects the size and volume of materials when heated and distinguishes between expansions in solids, liquids, and gases. It also highlights the relevance of understanding these principles across various applications in daily life and engineering.
Detailed
Conclusion
Thermal expansion is a crucial concept in physics, describing how the size or volume of a substance increases with temperature. In this chapter, we explored:
- Mechanisms of Expansion:
- Solids expand linearly in one, two, or three dimensions depending on their structure.
- Liquids expand uniformly in all directions, which is vital for predictable behaviors in thermometers and other applications.
- Gases undergo volumetric expansion, with pressure and volume intricately related by temperature variations.
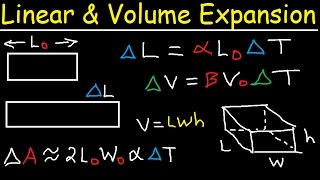
- Coefficients of Expansion: Each material has a unique coefficient of thermal expansion, influencing how much it will expand when heated. This knowledge is essential for engineers when designing structures or components that will experience temperature changes.
- Applications in Real Life: Understanding thermal expansion is essential in fields like construction, thermodynamics, and everyday utilities, including the design of bridges, railways, and pressure vessels, to ensure safety and functionality under varying temperatures.
Overall, mastering thermal expansion is fundamental for both practical applications and theoretical studies in the sciences.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Summary of Thermal Expansion
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Thermal expansion is the increase in size or volume of a substance when its temperature increases.
Detailed Explanation
Thermal expansion refers to the physical phenomenon that occurs when a substance's temperature rises, causing its particles to gain energy and move more vigorously. This increase in particle motion results in the substance expanding in size or volume. This concept is fundamental in understanding how materials behave under temperature changes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a balloon filled with air. When you heat the balloon by placing it in a warm room, the air molecules inside move faster, causing the balloon to expand. This illustrates thermal expansion in gases.
Different Forms of Expansion
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Solids expand linearly, liquids expand volumetrically, and gases expand in both volume and pressure.
Detailed Explanation
Different states of matter exhibit distinct patterns of thermal expansion. Solids generally expand in a linear fashion, meaning a specific length increase per temperature increase. Liquids, on the other hand, expand uniformly in all directions, which is termed volumetric expansion. Gases demonstrate a more complex behavior, as they can expand both in volume and feel changes in pressure, governed by laws like Charles' Law.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a metal rod placed in the sun. It will become slightly longer as it heats up (linear expansion). Conversely, if you warm water in a pot, the entire volume of water expands as its temperature increases (volumetric expansion). Lastly, consider a sealed balloon filled with air; when heated, both the volume of the air increases and the pressure inside the balloon rises (gaseous expansion).
Coefficients of Thermal Expansion
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ The coefficients of thermal expansion are material-dependent and determine the extent of expansion.
Detailed Explanation
Materials have specific coefficients of thermal expansion, which quantify how much a material will expand per degree of temperature increase. These coefficients vary greatly among different materials, meaning that some materials will expand more than others for the same temperature change. Understanding these coefficients is crucial in applications where precise dimensional changes are necessary.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine two different metals: steel and aluminum. If both are heated to the same temperature increase, aluminum will expand more than steel. This is why engineers must carefully choose materials in construction; using materials with suitable expansion coefficients ensures stability and integrity in structures.
Applications of Thermal Expansion
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Thermal expansion is vital in applications like construction, thermometers, and pressure-based devices.
Detailed Explanation
The principles of thermal expansion are applied in various fields such as construction, where engineers design structures like bridges and buildings to accommodate expansion and contraction from temperature changes. In thermometers, the expansion of liquids provides a direct reading of temperature changes. Pressure-based devices, like pressure cookers, rely on thermal expansion to increase pressure and speed up cooking.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bridge; during hot weather, the materials expand and could lead to buckling if not designed with expansion joints that allow for this movement. In everyday life, think of a glass thermometer—when you dip it in warm water, the liquid inside expands and rises, showing a higher temperature. In the kitchen, when cooking with a pressure cooker, the steam expands due to heat, increasing the pressure and allowing food to cook faster.
Key Concepts
-
Thermal Expansion: The increase in size or volume of a substance due to temperature rise.
-
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: A material-dependent value indicating how much a substance expands.
-
Linear Expansion: The increase in length of a solid as temperature varies.
-
Volumetric Expansion: Change in volume of a liquid or gas due to temperature increase.
-
Real-World Applications: Understanding thermal expansion is crucial for constructing safe and effective tools and structures.
Examples & Applications
A metal rod expands 3.6 mm when heated from 20°C to 100°C due to its linear expansion.
A thermometer filled with mercury rises in the tube as temperature increases due to liquid expansion.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hotter gets bigger, that's the sway; solids, liquids, gases in their play.
Stories
Imagine a metal bridge on a hot day, its joints widen and sway. Liquid thermometers rise high, while gas fills balloons up to the sky! All expand when temperatures fly!
Memory Tools
GLS for 'Gases, Liquids, Solids' - Remember the order of expansion types.
Acronyms
Remember 'TESS' - Thermal Expansion Safety Solutions for engineering design.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thermal Expansion
The increase in size or volume of a substance due to a rise in temperature.
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
A measure of how much a material expands per degree of temperature change.
- Linear Expansion
The change in length of a material due to temperature change.
- Volumetric Expansion
The change in volume of a material as its temperature changes.
- Expansion Joints
Structural devices used to allow movement due to thermal expansion.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
