Volumetric Expansion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Volumetric Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about volumetric expansion, which describes how materials change their volume when heated. Can anyone tell me why this happens?

Is it because the particles move faster when heated?

Exactly! As temperature increases, particles gain thermal energy and move apart, leading to an increase in volume. Now, the formula we use to calculate this change in volume is ΔV equals βV₀ΔT. Who can tell me what each symbol stands for?

ΔV is the change in volume, V₀ is the original volume, and ΔT is the change in temperature, but what about β?

Great question! β is the coefficient of volumetric expansion, a property of the material that tells us how much it will expand with each degree change in temperature.
Application of Volumetric Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone think of where we might encounter volumetric expansion in real life?

I think thermometers use this idea, right? The liquid expands when heated.

Exactly! Liquid thermometers, like those containing mercury or alcohol, work based on volumetric expansion. As temperature rises, the liquid expands and moves up a tube to give us a reading.

So what happens if it's too hot? Could it break the thermometer?

That's a good point! If the temperature gets too high, it may exceed the limits of the thermometer's design, which is why they must be calibrated carefully.
Relating Volumetric and Linear Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss how volumetric expansion relates to linear expansion. Who can tell me how these two concepts are connected?

I've heard that volumetric expansion is related to linear expansion. But how?

That's right! The coefficient of volumetric expansion is approximately three times the coefficient of linear expansion. So, if you know how much a material expands in length, you can estimate how much it expands in volume.

Does that mean if we know one, we can predict the other?

Exactly! This relationship is essential for engineers when designing structures that need to withstand temperature changes.
Coefficients of Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk a bit more about the coefficients. Why is it important to know the coefficient of volumetric expansion for a substance?

I guess it helps in predicting how much a material will expand, right?

Exactly! For example, materials with a high coefficient will expand significantly more than those with a low coefficient when subjected to the same temperature change.

Are there materials that don’t expand much at all?

Yes! For instance, metals such as lead or gold expand less compared to gases. Understanding these differences helps us make critical choices in engineering and design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we delve into volumetric expansion, defining it in terms of its mathematical formulation and explaining how it differs across various states of matter. We also discuss the coefficient of volumetric expansion, which significantly influences how materials expand when subjected to temperature changes.
Detailed
Volumetric Expansion
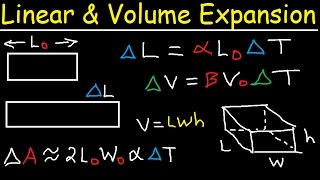
Volumetric expansion is the change in volume of a substance as its temperature changes. This phenomenon occurs due to the increased kinetic energy of particles, causing them to move further apart as the temperature rises. The formula for calculating volumetric expansion is given by:
$$ \Delta V = \beta V_0 \Delta T $$
where:
- $ \Delta V $ = change in volume (in m³)
- $ \beta $ = coefficient of volumetric expansion (in per °C)
- $ V_0 $ = original volume (in m³)
- $ \Delta T $ = change in temperature (in °C)
For most materials, the coefficient of volumetric expansion is approximately three times the coefficient of linear expansion. This concept is crucial in various applications, including thermometers and the engineering of structures, as it helps predict how materials will behave under different temperature conditions.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Volumetric Expansion
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The change in volume of a solid when its temperature changes is given by:
ΔV=βV0ΔT
Where:
○ ΔV = Change in volume (in m³)
○ β = Coefficient of volumetric expansion (in per °C)
○ V0 = Original volume (in m³)
Detailed Explanation
Volumetric expansion refers to how the volume of a substance changes when its temperature changes. When a solid is heated, its particles gain energy and move apart, resulting in an increase in volume. The formula for calculating this expansion is ΔV = βV0ΔT, where ΔV is the change in volume, β is the material's coefficient of volumetric expansion, V0 is the initial volume, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a balloon filled with air. When you heat the balloon by holding it near a warm surface, the air inside expands because its particles are moving faster. As a result, the balloon increases in size. This is similar to how solids expand when heated.
Coefficient of Volumetric Expansion
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The coefficient of volumetric expansion is approximately three times the coefficient of linear expansion for most materials.
Detailed Explanation
The coefficient of volumetric expansion (β) indicates how much the volume of a material will expand per degree Celsius increase in temperature. It's important to note that for many materials, this value is roughly three times greater than the coefficient of linear expansion (α), which measures how much a material expands in one dimension (length). This relationship helps in predicting and understanding the behavior of materials when they undergo temperature changes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pot of water heating on a stove. While the water level will rise as it heats due to volumetric expansion, any solid components, like a spoon, will expand in length as well. The spoon's tip hardly feels a change, but the entire material responds to the heat more significantly in volume.
Key Concepts
-
Volumetric Expansion: The process by which a substance expands in volume as its temperature increases.
-
Coefficient of Volumetric Expansion: Key parameter that indicates how much a material will expand for each degree of temperature increase.
Examples & Applications
If you heat a balloon, the air inside expands, causing the balloon to inflate.
Mercury expands in a thermometer, rising to indicate temperature.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When temperatures climb, expansions are prime; liquids and gas expand, solid's a little less grand.
Stories
Imagine a shape-shifting balloon that inflates with warmth, demonstrating how air molecules spread apart as they gain energy.
Memory Tools
Remember V-Bot: V = βV₀ΔT, to recall the volumetric expansion formula easily.
Acronyms
For expansion remember ABC – A is Area, B is Bulk (Volumetric), and C is Coefficient.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Volumetric Expansion
The change in volume of a substance due to an increase in temperature.
- Coefficient of Volumetric Expansion
A material-specific value that represents the fractional change in volume per degree change in temperature.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
