Thermal Expansion of Liquids
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thermal Expansion of Liquids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to dive into the thermal expansion of liquids. Can anyone tell me what happens to a liquid when it gets heated?

I think it gets hotter and maybe it increases in size?

Great point! When a liquid is heated, it does indeed get hotter and expands uniformly in all directions. This phenomenon is known as thermal expansion. It's something we will explore in depth today.

How do we actually measure this expansion?

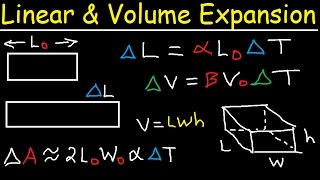
Good question! We measure the change in volume using the formula $$\Delta V = \beta V_0 \Delta T$$ where $\Delta V$ is the change in volume, $V_0$ is the original volume, and $\beta$ is a constant for the liquid called the coefficient of volumetric expansion.

What is the typical value of $\beta$ for water?

For water, the coefficient of volumetric expansion is approximately $2.1 \times 10^{-4}$ °C⁻¹. This means that for every degree Celsius increase in temperature, the volume of water increases by that fraction.

So, if we have 1 liter of water and heat it, how much does it expand?

Exactly! Let’s calculate that. If 1 liter is $10^{-3}$ m³ and we heat it from 10°C to 80°C, substituting the values into our formula, we find that the volume increases by $1.47 \times 10^{-5}$ m³.

To summarize this session: liquids expand uniformly when heated, and we use a specific formula to calculate the change in volume based on the coefficient of expansion.
Applications of Liquid Expansion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand how liquids expand, let’s talk about some real-world applications. Who can think of any example that uses the thermal expansion of liquids?

Thermometers! They use liquid to show temperature changes.

Absolutely! Liquid thermometers utilize the expansion of liquids like mercury or alcohol. As temperature increases, the liquid expands and moves up a narrow tube, which is how we read the temperature.

What if the liquid expands too much?

Great question! If the liquid expands too much, some thermometers are designed to handle this by having a reservoir where excess liquid can go. Otherwise, it could lead to inaccurate readings or even break the thermometer.

Are there other applications for this principle?

Yes! Besides thermometers, thermal expansion of liquids is also crucial in designing various engineering systems and equipment, such as pressure vessels where liquid expansion needs to be accommodated.

In conclusion, understanding thermal expansion in liquids is essential not only for thermometers but also in various industrial applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Thermal expansion of liquids occurs uniformly in all directions when heated, which is quantified using the formula for volumetric expansion. This section examines the formula, provides a practical example using water, and discusses the application of this principle in liquid thermometers.
Detailed
Thermal Expansion of Liquids
Thermal expansion refers to the increase in volume of substances when heated. In the case of liquids, this expansion occurs uniformly in all directions, causing a proportional increase in volume as temperature rises. The mathematical representation for the change in volume of a liquid is given by the formula:
$$\Delta V = \beta V_0 \Delta T$$
where:
- $\Delta V$ is the change in volume (in m³)
- $\beta$ is the coefficient of volumetric expansion of the liquid (in per °C)
- $V_0$ is the original volume of the liquid (in m³)
Example of Liquid Expansion
To illustrate this principle, consider 1 liter of water (which is equivalent to $10^{-3}$ m³) heated from 10°C to 80°C. The coefficient of volumetric expansion for water is approximately $2.1 \times 10^{-4}$ °C⁻¹. Applying the formula:
$$\Delta V = (2.1 \times 10^{-4}) \times 10^{-3} \times (80 - 10) = 1.47 \times 10^{-5} \text{ m}^3$$
Thus, the volume increases by $1.47 \times 10^{-5}$ m³.
Application of Thermal Expansion
Liquid thermometers are a practical application of this principle. They rely on the expansion of liquids like mercury or alcohol. As temperature increases, these liquids expand and move up a narrow tube, indicating the temperature effectively.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Volumetric Expansion of Liquids
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Liquids expand uniformly in all directions when heated. The formula for the change in volume of a liquid is:
ΔV=βV0ΔT
Where:
○ ΔV = Change in volume (in m³)
○ β = Coefficient of volumetric expansion of the liquid (in per °C)
○ V0 = Original volume of the liquid (in m³)
Detailed Explanation
When liquids are heated, they do not just expand in one direction; they expand equally in all directions. This uniform expansion is expressed mathematically by the formula ΔV = βV0ΔT, where ΔV represents the change in volume, β is the coefficient of volumetric expansion specific to the liquid being heated, V0 is the original volume of the liquid, and ΔT is the change in temperature. Essentially, the term β indicates how much the volume of the liquid increases for each degree the temperature rises.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a balloon filled with water. When you heat the balloon (by placing it in warm water, for instance), the water expands equally in all directions within the balloon, causing the balloon to inflate. This behavior is similar to how liquids expand uniformly when heated.
Example of Liquid Expansion
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If 1 liter of water (volume V0=10−3 m³) is heated from 10°C to 80°C, and the coefficient of volumetric expansion for water is 2.1×10−4 °C⁻¹, the change in volume is:
ΔV=(2.1×10−4)×10−3×(80−10)=1.47×10−5 m³
Hence, the volume increases by 1.47×10−5 m³.
Detailed Explanation
Let's calculate how much a specific volume of water expands when heated. We start with 1 liter of water, which is equivalent to 10−3 m³. When we heat the water from 10°C to 80°C, the change in temperature (ΔT) is 70°C. Using the coefficient of volumetric expansion for water, which is 2.1×10−4 °C⁻¹, we can apply the formula ΔV = βV0ΔT. Substituting the values, we find that the change in volume (ΔV) is 1.47×10−5 m³. This means the water's volume increases slightly due to the expansion caused by heating.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a bottle of water on a sunny day. As the sun warms the water, it expands and may rise up to the cap of the bottle. This is a real demonstration of liquid expansion, showing how even a small increase in temperature can lead to a perceptible increase in volume.
Thermometers
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Liquid thermometers rely on the expansion of liquids like mercury or alcohol. As the temperature increases, the liquid expands and moves up a narrow tube, indicating the temperature.
Detailed Explanation
Liquid thermometers are fascinating instruments that utilize the principle of thermal expansion of liquids to measure temperature. When the temperature rises, the liquid inside the thermometer, typically mercury or alcohol, expands. This expansion occurs uniformly, causing the liquid to move up a narrow tube. The height the liquid rises corresponds to a specific temperature measurement on the thermometer, enabling us to read the temperature accurately. This process exemplifies how the thermal expansion of liquids is applied in practical tools to provide important information.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a liquid thermometer like a straw in a drink. If you place a straw in a cup and then heat the drink, the liquid inside the straw rises. Similarly, in a thermometer, when the liquid heats up due to temperature increase, it rises in the tube, allowing you to measure how hot or cold something is.
Key Concepts
-
Thermal Expansion of Liquids: Liquids expand uniformly in all directions when heated, leading to an increase in volume.
-
Coefficient of Volumetric Expansion: A measure of how much a liquid expands for each degree of temperature change.
-
Liquid Thermometers: Devices that measure temperature by utilizing the expansion of liquids.
Examples & Applications
When heating 1 liter of water from 10°C to 80°C, its volume increases by approximately 1.47 x 10^-5 m³ due to thermal expansion.
Liquid thermometers work by measuring changes in the level of liquid that expands as temperature increases.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When liquids get hot, they begin to rise, expanding their volume, oh so wise!
Stories
Imagine a tiny water droplet sitting in a pan on the stove. As the heat rises, it feels warmer, and before long, it starts to jump and dance around—the droplet expands, showing us how temperature makes it grow!
Memory Tools
For thermal expansion, remember V.B.T. - Volume, Beta (β), Temperature change!
Acronyms
Remember 'VET' for Volume, Expansion, Temperature—key concepts for thermal expansion!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thermal Expansion
The increase in size or volume of a substance when its temperature increases.
- Volumetric Expansion
The change in volume of a substance as a function of temperature change.
- Coefficient of Volumetric Expansion
A constant that quantifies how much a liquid expands per degree of temperature change.
- Liquid Thermometer
A device that uses the expansion of liquid to measure temperature.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
