Conditionals (Decision Making Statements)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Conditionals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll dive into conditionals, which are essential decision-making statements in programming. Can anyone tell me what they think a conditional does?

I think it decides whether to run a piece of code or not.

Exactly! Conditionals execute a block of code only when a specific condition is true. For example, if a student gets a certain number of marks, we can display 'Pass' or 'Fail'.

What if there are multiple conditions to check?

Great question! That's where `if-elif-else` statements come in. They allow us to check multiple conditions in sequence.

So, it's like making choices based on different situations?

Precisely! Let’s summarize: Conditionals help our program make decisions based on specific conditions.
Structure of Conditional Statements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at different types of conditional statements. The first is the `if` statement. Can someone give me a simple example?

Like checking if a number is positive?

Exactly! We might write: `if number > 0: print('Positive')`. This checks if the number is greater than zero and prints a message accordingly.

What about `if-else` statements?

"An `if-else` statement executes one block of code if the condition is true and another if it's false. For instance:
Common Use Cases for Conditionals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the types of conditionals, let’s discuss some common use cases. Can someone think of a scenario where conditionals could be used?

We could use them for grading in school!

Exactly! Conditionals check pass/fail status based on the grades. What are other scenarios?

Repeating tasks, like printing numbers?

Correct! Conditionals can even be combined with loops for more complex tasks, such as generating a list of all even numbers within a range.

How about calculating the average?

Yes! You can use conditionals to check how many numbers to divide by in average calculations. Let’s summarize: conditional statements are versatile and used in various programming tasks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces conditionals as fundamental programming tools that allow for decision-making within code. It explains the different types of conditional statements and their applications, emphasizing their role in controlling program flow.
Detailed
Conditionals (Decision Making Statements)
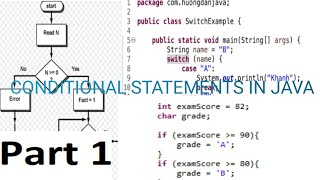
Conditionals are a crucial part of programming that facilitate decision-making by executing certain blocks of code based on whether specific conditions are true or false. In programming languages like Python, the common conditional statements include if, if-else, and if-elif-else.
- if: Executes a block of code if the condition evaluates to true.
- if-else: Provides two pathways - one block is executed if the condition is true, while a different block is executed if the condition is false.
- if-elif-else: A structure that checks multiple conditions in sequence, allowing for more complex decision-making.
For instance, in pseudocode:
This code exemplifies a straightforward application of conditionals in evaluating whether a student's marks indicate a pass or failure status. Mastery of these statements is essential for developers as they dictate the program's flow based on user input or other variables.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Conditionals
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Conditionals execute a block of code only when a specific condition is true.
Detailed Explanation
Conditionals are fundamental in programming as they help the program to make decisions based on certain conditions. If a specific condition evaluates to true, the corresponding block of code will run. If the condition is false, that block will be skipped, and the program will continue to the next part. This allows for more dynamic and interactive programming.
Examples & Analogies
Think of conditionals like a traffic light. When the light is green, cars can go (the block of code executes), but when it's red, cars must stop (the block of code does not execute). Similarly, in programming, conditionals control the flow based on 'traffic rules.'
Common Conditional Statements
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Common conditional statements:
- if: Executes a block if the condition is true
- if-else: Executes one block if condition is true, another if false
- if-elif-else: Checks multiple conditions in sequence
Detailed Explanation
There are three common forms of conditional statements in programming. The 'if' statement checks a single condition and executes code if that condition is true. The 'if-else' statement provides an alternative action if the condition is false. The 'if-elif-else' statement allows checking multiple conditions in a sequence, executing the corresponding block as soon as a true condition is encountered.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a road trip. You might check the weather before leaving. If it's sunny (if condition), you pack sunglasses (execute code). If it's raining (else condition), you pack an umbrella instead. If you check multiple locations (if-elif), you might end up packing differently based on which weather report is true.
Example of Conditionals in Coding
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example (Python-like pseudocode):
if marks >= 35:
print("Pass")
else:
print("Fail")
Detailed Explanation
In this example, a simple conditional structure is shown using pseudocode similar to Python. It checks if a student's marks are greater than or equal to 35. If true, it will print 'Pass'. If false, it defaults to the else clause and prints 'Fail'. This demonstrates how conditionals can implement logic to evaluate outcomes based on conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this as a teacher grading exams. If a student scores 35 or more marks, the teacher tells them they passed. If they scored less than 35, the teacher informs them they failed. This decision-making process mirrors how conditionals operate in programming.
Key Concepts
-
If Statement: Executes a code block if a condition is true.
-
If-Else Statement: Executes one block if true and another if false.
-
If-Elif-Else statement: Allows checking multiple conditions in sequence.
Examples & Applications
Example of an if statement: if grade >= 60: print('Pass'). This checks if a student's grade is 60 or more to determine if they pass.
Example of if-else: if temperature < 0: print('Freezing'); else: print('Not Freezing'). This determines if the temperature indicates freezing conditions or not.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If it's true, the block goes through; If not, the else takes its cue.
Stories
Imagine a student who checks grades; if they pass, they shout hooray! If they fail, they study all day, aiming to pass the next exam play.
Memory Tools
Remember: ICE - If condition, evaluate; else condition, take alternate path.
Acronyms
WHEN - Write condition, Handle else, Evaluate other conditions, Navigate flow.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Conditionals
Statements in programming that control the flow of execution based on certain conditions being true or false.
- if statement
A conditional statement that executes a block of code if a specified condition is true.
- ifelse statement
A conditional statement that executes one block if the condition is true and another block if it is false.
- ifelifelse statement
A structure used to check multiple conditions in a sequence.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
