Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Values
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the concept of values in programming. Values are the actual data stored in variables or constants, like the number 10 or the text 'Hello'.

So, are values just numbers and words?

Exactly! Values can be numbers like 10 or strings like 'Hello'. They represent the information we want to store.

What happens if I try to store different data types in one variable?

Good question! That leads us to data types, which we'll discuss next.
Understanding Data Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

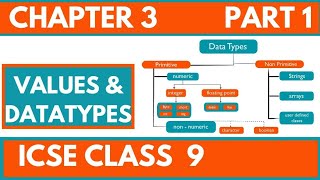
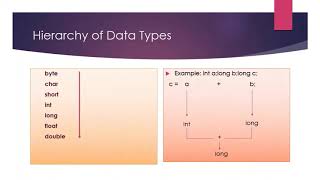
Now that we understand values, let's talk about data types. Data types specify the kind of information we can store. For example, integers are whole numbers like 10, while strings are sequences of characters like 'Hello'.

Can you give us more examples of data types?

"Sure! We have:

Is it important to use the correct data type?

Absolutely! Using the correct data type ensures our program runs without errors.
Variables and Constants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at variables and constants. A variable is a named storage location that can hold values that may change, while a constant is a storage location with a fixed value that does not change.

Can you give an example of a variable?

Of course! If you have a variable called `score`, it can change during your program. If you score 10 points, it changes to 10, and if you score 5 more, it changes to 15.

And what about constants?

A constant could be something like `PI`, which we often use as 3.14. Its value doesn’t change in the context of our program.
Type Compatibility and Conversion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss type compatibility. Values must match the data type of the variable where they're stored. For instance, you can't store a string in an integer variable without converting it.

What if I need to convert a number to text?

That's called type conversion. It allows us to convert one data type to another, ensuring compatibility in operations.

Why is data typing important?

Data types ensure efficient storage, prevent errors, and guide the interpretation of data by the computer.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Values represent the actual data stored in variables or constants, while types define the nature of this data. Understanding these concepts is crucial for writing effective and error-free code.
Detailed
Introduction to Values and Types in Programming
In programming, values represent the actual data that is stored and manipulated, while data types define the kind of data that can be processed. Values include various forms of data, such as integers, strings, and booleans. The definition of the correct data type is essential to ensure that the program runs correctly and efficiently.
Key areas covered in this section include:
- Values: The actual data, such as numbers or strings.
- Data Types: Classifications of data such as integers, floats, characters, strings, and booleans that inform how the data can be used.
Understanding the distinction between these concepts is fundamental in programming to avoid errors and to facilitate effective data manipulation.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Values and Types in Programming
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In programming, values represent data, and types define the kind of data stored or manipulated by a program.
Detailed Explanation
In programming, a 'value' refers to the specific data that we work with. For instance, it can be a number, a piece of text, or even a logical true/false outcome. Meanwhile, a 'type' is a classification that specifies what kind of value it is. The type informs the programming language how to handle that value. For example, if you have the number 10, that's a value, but its type could be an integer because it's a whole number.
Examples & Analogies
Think of values as different types of fruits: an apple, a banana, and an orange. Each fruit (value) can be classified into types, like 'citrus' or 'berry'. Just like you wouldn't put apples in a bag meant for oranges, you wouldn't mix data types in programming without proper handling!
The Importance of Understanding Values and Types
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding values and types is essential for writing correct and efficient code.
Detailed Explanation
When programmers understand the distinction between values and types, they can write code that runs smoothly and does what it's supposed to do. For instance, using the right type means avoiding errors during execution, ensuring that the program processes data correctly and efficiently. If you attempt to add a number to a string without converting, the program may crash or yield unexpected results, leading to bugs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef who needs specific ingredients for recipes. If a recipe calls for 'sugar' (a type) and the chef uses 'salt' instead (another type), the final dish could turn out disastrously wrong. Likewise, understanding the correct values and types in programming ensures that our code is like a well-prepared dish, where every ingredient is used appropriately.
Key Concepts
-
Values: Data that is stored in variables or constants.
-
Data Types: Classification of various forms of data like integers, strings, and booleans.
-
Variables: Storage locations that can change value.
-
Constants: Storage locations that cannot change value.
-
Type Compatibility: Ensures that values match variable types.
-
Type Conversion: The process of changing one data type to another.
Examples & Applications
An integer value example: 15. A string example: 'Goodbye'. A boolean example: True.
Converting from an integer to a string: Changing the number 123 to '123' for storage in a string variable.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Values are numbers and words we use, in programming's dance, they set the right cues.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a land of code, a variable named 'X' changed its mode. It started as 10 and then was a string, showing how data can evolve, like a mystical thing.
Memory Tools
To remember data types: I - Integer, F - Float, C - Character, S - String, B - Boolean (IFCSB).
Acronyms
V.C.T
Variable can change
Constant is fixed
Type Compatibility is key!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Values
Actual data stored in variables or constants, such as numbers and strings.
- Data Types
Classifications that specify the nature of data that can be stored, such as integers, strings, and booleans.
- Variable
A named storage location that can hold values which may change during the program execution.
- Constant
A named storage location with fixed values that do not change.
- Type Compatibility
The requirement that values must match the data type of the variable where they are stored.
- Type Conversion
The process of converting values from one data type to another.
- Boolean
Logical values representing true or false.
- Integer
Whole numbers without decimals.
- String
A sequence of characters.
- Float
Numbers that include decimals.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
