Introduction to Operational Amplifiers
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Characteristics of Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the essential characteristics of operational amplifiers. Can anyone tell me what makes an Op-Amp different from other amplifiers?

I think they have differential inputs?

Exactly! An Op-Amp amplifies the difference between the voltage at its two inputs, the inverting and non-inverting terminals. This is a key feature. Who can tell me about the gain?

Isn't the gain supposed to be infinite in theory?

That's correct! In ideal situations, the open-loop gain is infinite. This allows for very high amplification. Think of the acronym 'DIGS' — Differential input, Infinite gain, Single-ended output. It summarizes their key characteristics!

What does single-ended output mean?

Great question! It means there's only one output terminal that provides the amplified signal based on the inputs. Let’s recap: Op-Amps amplify voltage differences and ideally have infinite gain and a single output.
Applications of Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've grasped the Op-Amp's characteristics, let's talk about where we use them. What applications can you think of?

They amplify signals, right?

Yes! They are widely used for amplification. What about filters? Does anyone know how Op-Amps are used in that context?

I think they can create different types of filters based on frequency?

Correct! Op-Amps are crucial in designing active filters like low-pass and high-pass filters. Remember the mnemonic 'FAVC': Filter, Amplification, Voltage comparators, and Continuous waveforms. What about oscillators?

They can generate signals continuously, like sine waves?

Exactly! Op-Amps indeed create oscillating signals. So, we’ve established they are pivotal for amplification, filtering, and oscillation.
Types and Comparisons of Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now dive into the types of Op-Amps. Who can name one type and its purpose?

Precision Op-Amps are for high accuracy applications.

Great! Precision Op-Amps are designed for high accuracy with low offset voltage. And what about general-purpose Op-Amps?

They are versatile, used for things like signal amplification.

Correct! They cover broad requirements. In comparison, how do Op-Amps differ from transistor amplifiers?

Op-Amps have higher gain and input impedance?

Exactly! Op-Amps provide high gain, ideal input impedance, and low output impedance, while maintaining lower complexity. This makes them excellent for integrated circuits.
Practical Design Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Before we finish, let's look at practical design considerations when working with Op-Amps. What might we need to keep in mind?

We should consider the power supply requirements, right?

Absolutely! Most Op-Amps require dual power supplies for proper operation. What about feedback resistors?

They are important for setting the gain?

Correct! Feedback resistors are critical in stabilizing the circuit. And why is stability important?

To prevent the Op-Amp from oscillating unexpectedly?

Exactly! Improper design can lead to instability. So, power supply, feedback, and stability are key elements in Op-Amp design!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Op-Amps are high-gain voltage amplifiers with differential inputs and single-ended outputs. This section covers their key characteristics, structure, ideal and practical performance, applications, and types, providing a foundational understanding of Op-Amps in analog circuit design.
Detailed
Introduction to Operational Amplifiers
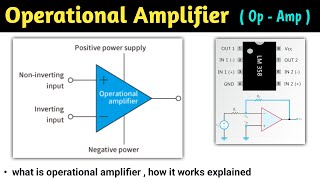
Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps) are high-gain voltage amplifiers widely used in various analog electronics and signal processing applications. They have two inputs — inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) — and a single output, which allows them to amplify the voltage difference between the inputs.
Key Characteristics
- Differential Input: Op-Amps amplify the voltage difference between the inverting and non-inverting terminals.
- High Gain: Theoretically, Op-Amps can have infinite gain in an open-loop configuration.
- Single-Ended Output: There is a single output terminal for the amplified signal.
Op-Amp Structure Overview
- Comprises input terminals, an output terminal, and power supply terminals that often require a dual power supply (positive and negative).
- Built using multiple transistors to provide necessary amplification via a voltage gain stage.
Ideal vs. Practical Characteristics
- Ideal: Infinite open-loop gain, infinite input impedance, zero output impedance, infinite bandwidth, and zero offset voltage.
- Practical: Real Op-Amps exhibit finite gain, finite input impedance, and non-zero offset voltage, which still yields excellent performance in many applications.
Applications
Op-Amps find application in:
- Amplification (voltage and current amplifiers)
- Filters (active filters for various signal types)
- Comparators (comparison of input signals)
- Oscillators (generation of continuous waveforms)
- Integrators/Differentiators (calculating integrals and derivatives)
- Summing Amplifier (combining multiple inputs).
Types
Includes General-Purpose, Precision, High-Speed, and Low-Noise Op-Amps tailored for different application needs.
Comparison with Other Amplifiers
Op-Amps are characterized by high gain and input impedance while maintaining low complexity compared to transistor amplifiers.
Key Equations
Several key equations relate to Op-Amp functionality, highlighting gain calculations and their operational role in circuits.
Practical Considerations
Must account for power supply requirements, feedback resistor selection, and stability during circuit design.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is an Operational Amplifier?
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An operational amplifier (Op-Amp) is a high-gain voltage amplifier with a differential input and a single-ended output. Op-Amps are crucial components in analog electronics and signal processing applications. The basic operation of an Op-Amp is to amplify the difference between the two input voltages (non-inverting and inverting inputs).
Detailed Explanation
Operational amplifiers are specialized electronic components that amplify voltage. Unlike regular amplifiers, Op-Amps look at two different input voltages, known as the inverting input and the non-inverting input. Their main job is to amplify the difference between these two voltages, which is essential for many applications in electronics, like filters and comparators. This means they can take a small voltage difference and make it much larger.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Op-Amps like a referee in a debate between two speakers. The referee listens to both sides (input voltages) and announces who is speaking louder or who has a stronger point (the amplified output). This ability to discern between two inputs and amplify the difference is what makes Op-Amps so useful.
Key Characteristics of Op-Amps
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Key Characteristics:
○ Differential Input: Op-Amp amplifies the difference between the voltage applied at the inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) terminals.
○ High Gain: Ideally infinite gain in an open-loop configuration.
○ Single-Ended Output: A single output terminal is used to provide the amplified signal.
Detailed Explanation
The key characteristics of Operational Amplifiers greatly define how they function in circuits. 'Differential Input' means they measure the difference between two inputs rather than working on one signal alone. 'High Gain' implies they can immensely amplify even tiny voltage differences. Though ideally, they have infinite gain, practical applications often work with very high but finite gains. Lastly, 'Single-Ended Output' indicates that Op-Amps output their results through one terminal, producing a single amplified signal based on the monitored differences.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a pair of scales to weigh two different objects. The scales can show how much heavier one object is than the other—that's the differential input. If you could somehow amplify the reading infinitely, you'd get an incredibly detailed measurement, similar to the high gain of an Op-Amp. And just as scales provide one outcome from two inputs, an Op-Amp provides one output signal from two input voltages.
Op-Amp Inputs and Outputs
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Input Terminals:
○ Inverting (-): Signal input where inversion occurs.
○ Non-Inverting (+): Signal input where the signal remains unchanged in polarity.
● Output Terminal:
○ The output terminal provides the amplified signal, which depends on the input signal and the gain of the op-amp.
Detailed Explanation
Operational Amplifiers have specific terminals to process input signals. The inverting input (-) is where the signal flips polarity when amplified, meaning if the input is positive, the output will be negative and vice versa. The non-inverting input (+) maintains the voltage's positive or negative sign when it produces the output. The output terminal then delivers the result, which is the amplified difference influenced by the characteristics of the Op-Amp.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seesaw at a playground. If one side pushes down (like the inverting input), the other side rises, but inversely (the output). If both sides are balanced (non-inverting), the seesaw stays level. The seesaw represents the balance and amplification of signals at Op-Amps, where one side is modified while the other side remains unchanged.
Power Supply Requirements
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Power Supply Terminals:
○ Op-Amps typically require a dual power supply (positive and negative) to drive the output to the necessary voltage levels.
Detailed Explanation
To operate effectively, most Op-Amps need two power supply voltages, one positive and one negative. This is known as a dual power supply configuration. This setup is necessary to enable the Op-Amp to produce a wide range of output voltages, accommodating both positive and negative signals for various applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a car engine that needs both gasoline and diesel to perform well. If it had only one type of fuel, it wouldn’t be able to function at its best. Similarly, Op-Amps need both types of power supplies to amplify input signals across a full spectrum effectively. Without them, their performance can be limited.
Internal Structure of Op-Amps
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Internal Structure:
○ Transistors: Op-Amps consist of multiple transistors to provide the necessary amplification.
○ Voltage Gain Stage: The primary amplification mechanism in an op-amp.
Detailed Explanation
Inside an Operational Amplifier, transistors form the core structure for amplifying signals. These transistors work together to create what’s called the voltage gain stage, wherein they take small input differences and produce larger output signals. Essentially, they are the builders of the Op-Amp, allowing it to achieve its function efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a team of workers building a large wall. Each worker (transistor) plays a role in lifting and placing bricks (the input signals). If everyone works together effectively, they can build a sturdy, high wall (the amplified output). This teamwork is similar to how transistors in an Op-Amp collaborate to achieve amplification.
Key Concepts
-
Differential Input: The fundamental feature of Op-Amps that allows amplification of voltage differences.
-
Infinite Gain: The ideal characteristic where an Op-Amp can amplify signals indefinitely in a theoretical scenario.
-
Applications: A wide range including amplification, filtering, integration, and oscillation.
-
Op-Amp Structure: Comprised of multiple transistors and requires dual power supplies for operation.
-
Practical Differences: Real-world Op-Amps have finite gain and non-zero offset voltage which affect performance.
Examples & Applications
An Op-Amp is used in audio applications to amplify small audio signals before sending them to speakers.
A summing amplifier configuration of an Op-Amp can add multiple audio signals to create a mixed output for live sound systems.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Op-Amp's aim is to amplify, the voltage gap is its sweet tie.
Stories
Imagine two friends, Inverting and Non-Inverting, both vying for attention. The Op-Amp is the referee, ensuring the louder voice prevails, amplifying the difference in their sounds.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A D-SF I' for Op-Amps: Amplify, Differential, Single-ended, Finite, Infinite (gain).
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'A-F-D-C' to recall
Amplification
Filtering
Differentiation
Comparison.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Operational Amplifier (OpAmp)
A high-gain voltage amplifier with differential inputs used extensively in analog signal processing.
- Differential Input
The ability to amplify the difference between two input voltages (inverting and non-inverting).
- High Gain
The property of ideally providing infinite amplification in an open-loop configuration.
- SingleEnded Output
An output configuration where the amplified signal is provided through one terminal.
- Finite Gain
The real-world limitation of Op-Amps where gain is typically between 10,000 to 100,000.
- Input Impedance
A measure of how much resistance an Op-Amp presents to the input signal.
- Offset Voltage
A small voltage difference that exists between the inputs when the output is zero.
- Feedback Resistors
Components used to determine the gain of an op-amp circuit by applying feedback.
- Active Filters
Circuits that utilize Op-Amps to pass certain frequencies while attenuating others.
- Summing Amplifier
An Op-Amp configuration that outputs a weighted sum of multiple input signals.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
