Summary of Key Concepts
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore operational amplifiers, or Op-Amps, which are essential in many analog circuits. Can anyone tell me what they think an Op-Amp does?

I think it amplifies signals, right?

Exactly! Op-Amps amplify the difference between two input signals. What types of inputs do you think they have?

Isn't it one inverting and one non-inverting input?

Yes, those are the two types of inputs! It’s important to remember that the inverting input will flip the signal's polarity while the non-inverting input maintains it. Here’s a mnemonic to remember: IN for 'Inverting' means ‘Inverted’ and NON for 'Non-Inverting' means ‘Normal’.

That's helpful!
Ideal vs. Practical Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss the ideal characteristics of Op-Amps. Can anyone name one?

Infinite gain?

Correct! Infinite gain means that the Op-Amp can boost signals indefinitely under ideal conditions. What about input impedance?

It should be infinite too, right?

Spot on! It should ideally draw zero currents from the input. But how do practical Op-Amps differ from this ideal model?

They have a finite gain and some offset voltage?

Exactly! Though imperfections exist, they still perform remarkably well in real-world applications.
Applications of Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into how Op-Amps are used in circuits. Who can give me an example of where they might be applied?

Maybe in filters or amplifiers?

Absolutely right! Op-Amps are widely used for amplification, filtering signals, and even in oscillators. Remember the acronym 'AFO'— Amplification, Filtering, Oscillation.

That's easy to remember!

Good! Additionally, Op-Amps serve roles in comparators which help compare signals. Can you think of a practical use of a comparator?

I think in a temperature control circuit, it can turn a heater on or off, right?

Exactly! They are key in automation systems for comparison tasks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section provides an overview of operational amplifiers, emphasizing their unique characteristics, including infinite gain and high input impedance. It also highlights their versatility in applications such as amplification, filtering, and integration, while noting the differences between ideal and practical Op-Amps.
Detailed
Summary of Key Concepts
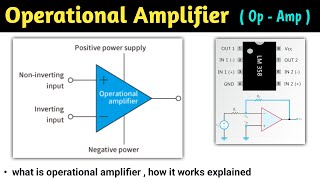
Operational amplifiers, commonly referred to as Op-Amps, are fundamental components in analog electronics. They serve as high-gain voltage amplifiers with differential inputs, amplifying the voltage difference between inverting and non-inverting terminals. The ideal characteristics of Op-Amps include infinite gain, infinite input impedance, and zero output impedance, making them theoretically perfect for amplifying and processing signals.
However, practical Op-Amps have finite gain, non-zero offset voltage, and may exhibit various limitations. Despite these imperfections, they still provide excellent performance and find extensive applications in numerous analog circuit designs such as voltage amplifiers, active filters, comparators, oscillators, and integrators. An understanding of both their ideal traits and real-world performance is crucial for engineers working with these versatile devices.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Operational Amplifiers
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Operational amplifiers are high-gain, differential-input, single-output devices used extensively in analog circuits.
Detailed Explanation
Operational amplifiers, commonly known as op-amps, are specialized electronic devices that amplify voltage signals. They have a unique configuration with two inputs (differential input) and one output. This design allows them to amplify the difference between the two input voltages. Because of their high gain, they can significantly increase weak signals, making them essential in various electronic applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an op-amp like a microphone amplifier. Just as a microphone captures quiet sounds and sends them to a speaker to be amplified, an op-amp takes small electrical signals and boosts them so that they can be processed further in electronic circuits.
Ideal Characteristics of Op-Amps
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Ideal characteristics include infinite gain, infinite input impedance, and zero output impedance.
Detailed Explanation
In theory, ideal op-amps have several perfect characteristics: they can gain signals infinitely, meaning any small input difference can be amplified immensely. They also have infinite input impedance, which means they do not draw any current from the source, preventing any disruption. Similarly, they have zero output impedance, allowing them to act as perfect voltage sources. However, these characteristics are theoretical and help understand how they work compared to real devices.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a classroom where a teacher can perfectly hear every whisper from each student (infinite gain) without the students ever needing to speak louder (infinite input impedance). The teacher can then calmly project the most crucial points to the entire class without any loss of clarity (zero output impedance).
Applications of Op-Amps
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Op-Amps have a wide range of applications, including amplification, filtering, and integration.
Detailed Explanation
Op-Amps find their use in many electronic circuits. They can amplify signals to make them usable, filter out unwanted frequencies, and perform mathematical operations like integration. Other applications include acting as comparators, generating oscillations, and summing inputs. This versatility makes them the backbone of analog signal processing.
Examples & Analogies
Consider an op-amp like a multitool for electronics. Just as a Swiss Army knife can perform various tasks from cutting to screwing, op-amps can adapt to many functions in circuits, whether it's amplifying a sound signal or filtering noise out of a feed.
Real-World Characteristics of Op-Amps
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Real-world op-amps come with finite gain and non-zero offset voltage, but they still offer excellent performance in most applications.
Detailed Explanation
While ideal op-amps have perfect characteristics, real op-amps have limitations. For instance, they have finite gain, meaning their amplification is strong but not infinite. Additionally, there's a small offset voltage, which means there's often a tiny difference in voltage when the outputs should theoretically be zero. Despite these imperfections, real op-amps are designed to perform exceptionally well in practical applications and deliver reliable results.
Examples & Analogies
Think of real op-amps like a professional athlete. Perfect athletes can perform flawlessly in every competition (ideal characteristics). However, even real professional athletes have their strengths and weaknesses and may not always perform at their peak (finite gain and offset voltage). Yet, they still achieve remarkable feats and excel in their competitions.
Key Concepts
-
Differential Input: Op-Amps amplify the difference between two input signals.
-
High Gain: Op-Amps can achieve significant amplification, ideally infinite.
-
Applications: Used in filtering, amplification, and signal processing.
Examples & Applications
Voltage amplifiers that boost weak signals for clearer audio output.
Active filters used in audio devices to remove unwanted frequencies.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Op-Amp, Op-Amp, boosting with ease, amplifying signals as we please!
Stories
Imagine a town where Op-Amps run everything, comparing the sounds of bells, amplifying the softest whispers to reach every ear.
Memory Tools
Remember 'AFO' for Op-Amp applications: Amplification, Filtering, and Oscillation.
Acronyms
IDEAL
Infinite Gain
Differential Input
Effortlessly Amplify
Low Output Impedance.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Operational Amplifier (OpAmp)
A high-gain voltage amplifier with differential inputs and a single output.
- Inverting Input
The input terminal of an Op-Amp where the signal is inverted.
- NonInverting Input
The input terminal of an Op-Amp where the signal remains in its original polarity.
- Ideal Characteristics
Theoretical attributes of Op-Amps such as infinite gain and input impedance.
- Practical Characteristics
Real-world attributes of Op-Amps which exhibit finite gain and non-zero offset voltage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
