Introduction to Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Basics of Operational Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’ll introduce Operational Amplifiers, or Op-Amps. Who knows what an operational amplifier is?

Is it something that amplifies signals?

Exactly! Op-Amps are high-gain voltage amplifiers that amplify the difference between two input voltages.

What do you mean by two inputs?

Great question! Each Op-Amp has a non-inverting input, which keeps the signal's original polarity, and an inverting input, where the signal is inverted. Can anyone tell me why this is useful?

Maybe to compare different signals?

Exactly! By amplifying the difference between the inputs, we can achieve effective signal processing.

Remember this: Op-Amp = Differential Input + High Gain. Let’s summarize this part. Op-Amps amplify the difference between - and + inputs. You got it?
Characteristics of Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss the key characteristics of Op-Amps. Can anyone name one characteristic?

They have a high gain?

Correct! In an ideal situation, Op-Amps have infinite open-loop gain. But in reality, what do we know about their gain?

It’s finite, right?

Right! It’s typically in the range of 10^4 to 10^5. Now, they also have infinite input impedance. Why is this beneficial?

So they don’t draw any current from the input?

Exactly! This allows the Op-Amp to measure signals without altering them. Remember: Ideal Op-Amps = Infinite Gain + Infinite Input Impedance.
Applications of Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into the applications of Op-Amps. What are some ways we use these amplifiers?

They can amplify signals?

Absolutely! Op-Amps are used as voltage amplifiers to boost weak signals. They are also used in filters. Can anyone name a type of filter?

Low-pass filters?

Correct! Op-Amps help create active filters that can eliminate unwanted frequency component. They can also function as comparators and oscillators.

How do they work as comparators?

Great question! They compare two input signals and output a high or low voltage based on that comparison. So, Op-Amps are essential not just for amplification, but in various circuit designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Operational amplifiers (Op-Amps) are high-gain voltage amplifiers with a differential input and single-ended output, playing a crucial role in analog electronics. They amplify the voltage difference between two inputs and are characterized by their differential input, high gain, and single-ended output.
Detailed
Introduction to Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps)
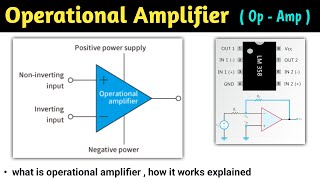
Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps) are fundamental components in analog signal processing, characterized by their ability to amplify the difference between two input voltages applied at their terminals. More specifically, they feature:
- Differential Input: Op-Amps amplify the voltage difference between the inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) inputs.
- High Gain: They can provide theoretically infinite gain in an open-loop configuration, making them ideal for amplifying weak signals.
- Single-Ended Output: Outputs a single amplified signal corresponding to the input difference.
These characteristics make Op-Amps invaluable in various applications such as amplification, filtering, and signal comparison, establishing them as building blocks in numerous electronic circuits.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is an Operational Amplifier?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An operational amplifier (Op-Amp) is a high-gain voltage amplifier with a differential input and a single-ended output. Op-Amps are crucial components in analog electronics and signal processing applications. The basic operation of an Op-Amp is to amplify the difference between the two input voltages (non-inverting and inverting inputs).
Detailed Explanation
An operational amplifier, or Op-Amp, is a device used in electronics to boost voltage signals. It has two inputs: the non-inverting input, where the signal comes in and remains unchanged, and the inverting input, where the signal is flipped in polarity when processed. The main job of an Op-Amp is to take the voltage difference between these two inputs and amplify it. They are important in various applications, such as audio systems and signal processing, because they can make weak signals stronger and more usable.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an Op-Amp as a referee in a football game. The referee is positioned to see the play from two angles (the two inputs). Based on the difference in perspectives (the voltage difference), the referee makes a call (the amplified output). Just like the referee amplifies the action on the field so everyone understands what happened, the Op-Amp amplifies voltage differences in electric signals.
Key Characteristics of Op-Amps
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Key Characteristics:
○ Differential Input: Op-Amp amplifies the difference between the voltage applied at the inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) terminals.
○ High Gain: Ideally infinite gain in an open-loop configuration.
○ Single-Ended Output: A single output terminal is used to provide the amplified signal.
Detailed Explanation
Op-Amps have several key characteristics that define their behavior and utility in electronic circuits. Firstly, they have a differential input, which means they specifically amplify the voltage difference between the two inputs instead of the individual voltages. This is crucial because it allows for versatile applications like filtering and signal conditioning. Secondly, the gain of an Op-Amp is ideally infinite when no feedback is applied, meaning that even the slightest difference at the inputs can result in a large output change. Lastly, Op-Amps have a single-ended output, which means there is one output terminal conveying the amplified signal, simplifying the connection in various circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a volume control on a stereo system. The Op-Amp's differential input is like having two settings: one for the left speaker and one for the right. When you turn up the volume, you amplify the difference in sound levels, notably an improvement for any setting that's too quiet. The high gain means even a slight adjustment in volume can make a big change in output sound. The single-ended output can be thought of as the final volume knob that provides one uniform sound output for the entire system.
Key Concepts
-
Differential Input: Op-Amps amplify the difference in voltage between their two input terminals.
-
High Gain: Ideally infinite gain allows Op-Amps to amplify even the smallest signals.
-
Single-Ended Output: Op-Amps produce a single output signal based on the difference in input voltages.
Examples & Applications
Op-Amps can amplify the audio signals from a microphone before sending them to speakers.
In a temperature sensing application, Op-Amps can amplify small voltages generated by thermocouples for better measurement.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Op-Amps, high and bright, amplify with all their might!
Stories
Imagine an Op-Amp as a referee in a game, deciding who scores by amplifying the difference between two players' scores.
Memory Tools
Remember AGI – Amplify, Gain, Input, for recalling Op-Amps' key characteristics.
Acronyms
DHS
Differential inputs
High gain
Single output.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Operational Amplifier (OpAmp)
A high-gain voltage amplifier with a differential input and single-ended output.
- Differential Input
The difference between voltages applied at the inverting and non-inverting inputs of the Op-Amp.
- High Gain
The ability to amplify voltages significantly, ideally infinite in open-loop configuration.
- SingleEnded Output
An output signal produced from one terminal in response to an amplified input.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
