Numerical Algorithms for Similarity Transformations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Numerical Algorithms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into numerical algorithms that are critical for similarity transformations. Understanding these will enhance our ability to solve complex civil engineering problems. Who can tell me what they remember about similarity transformations?

Similarity transformations help in transforming one matrix into another to simplify computations.

Exactly! We primarily use these transformations for tasks like diagonalizing matrices. Let’s start with the QR Algorithm. It helps find eigenvalues through a series of transformations. Can anyone recall how this algorithm functions?

It uses orthogonal matrices to maintain the column relations during transformations.

Great! The QR algorithm works by iteratively transforming a matrix into an upper triangular form where the eigenvalues are placed along the diagonal. This helps in easier computation.

So, it’s like breaking down the problem into simpler parts that are easier to manage!

Precisely! QR stands for 'Quick Reduction' in terms of effectiveness in handling these transformations. Now, how do we ensure accuracy in these computations?

By using iterative methods to check the convergence?

Exactly! Always check for convergence with these algorithms, especially in iterative processes. To summarize today's key points, we highlighted how similarity transformations are vital and introduced the QR algorithm for eigenvalue computation.
Schur Decomposition Explained
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, let’s explore Schur Decomposition. This algorithm is central for handling any square matrix. Can anyone share its key feature?

Every square matrix can be converted into an upper triangular matrix through this method.

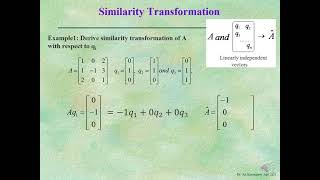
Correct! The matrix gets expressed in the form $ extbf{A} = extbf{Q}^T extbf{T}$, where $ extbf{Q}$ is orthogonal. Why do you think this characteristic is useful in civil engineering?

It simplifies systems of equations we might encounter in structural analysis!

Well said! It helps particularly in reducing computational complexity. Now, how does Schur Decomposition compare with the QR Algorithm we discussed earlier?

QR focuses on finding eigenvalues, while Schur focuses more on transforming without direct eigenvalue extraction.

Exactly! And remember, while both are powerful, Schur is foundational for solving linear algebra problems involving matrix similarity. To summarize, Schur Decomposition is a vital technique for matrix transformations into upper triangular forms, enhancing problem-solving efficiency.
Jordan Reduction Algorithms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss Jordan Reduction Algorithms. While they aren’t used much in practice, what can you tell me about their significance?

They help in symbolic computations and provide insight into systems that are not diagonalizable.

Correct! Jordan forms help when dealing with matrices that have defective eigenvalues. When might we find such a situation in engineering?

In cases of structural systems that have repeated eigenvalues?

Exactly! Understanding these situations helps engineers apply the right computational techniques. Although Jordan reduction can be unstable, it still provides a theoretical foundation we might need for certain problems. Before we finish, what are the main points we've covered today?

We discussed numerical algorithms like QR, Schur Decomposition, and the Jordan Algorithms and their roles in matrix transformations.

Great summary! Remember to consider the strengths and limitations of each algorithm as you encounter practical problems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, several key algorithms for performing similarity transformations in matrices are discussed, including their applications in civil engineering. The QR algorithm, Schur decomposition, and Jordan reduction algorithms are highlighted for their roles in the computational processes involved in matrix similarity transformations.
Detailed
In computational applications, particularly in civil engineering, similarity transformation plays a crucial role in simplifying matrix computations. Algorithms such as the QR algorithm, Schur decomposition, and Jordan reduction are utilized to perform these transformations efficiently. The QR algorithm focuses on calculating eigenvalues through repeated similarity transformations, $ extbf{A} = extbf{Q}^T extbf{A}_k extbf{Q}_k$, converging to an upper triangular matrix where the diagonal contains the eigenvalues. Schur decomposition ensures that every square matrix is unitarily similar to an upper triangular matrix, making it a foundational technique. While Jordan reduction algorithms are typically less favored in numerical practice due to potential instability, they remain relevant within symbolic computation contexts. Overall, understanding these algorithms is vital for engineers working with numerical simulations in software packages like ANSYS, STAAD.Pro, and MATLAB.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Key Algorithms for Similarity Transformations
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In computational civil engineering (e.g., finite element software), algorithms are used to compute similarity-based transformations.
Detailed Explanation
In civil engineering software, several specific algorithms are employed to perform similarity transformations, which are crucial for simplifying complex calculations. These algorithms help in determining eigenvalues and modifying matrices so that they can be more easily analyzed and understood. Key algorithms include the QR Algorithm, Schur Decomposition, and Jordan Reduction Algorithms, each of which has unique applications and properties.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a construction team preparing to analyze the stresses in a building. They have a huge blueprint (the matrix) that doesn't make much sense at first glance. By using tools (algorithms) like the QR Algorithm, they can break down the blueprint into simpler, more manageable sections, making it easier to see where the critical stress points are.
QR Algorithm
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- QR Algorithm:
- Used to compute eigenvalues.
- Based on repeated similarity transformations:
A = Q^T A Q
where A → converges to an upper triangular matrix with eigenvalues on the diagonal.
Detailed Explanation
The QR Algorithm is a computational method used to find the eigenvalues of a matrix. It works by iteratively transforming the matrix A into a form that is closer to an upper triangular matrix. This transformation continues until the matrix converges, meaning the eigenvalues can be easily read from the diagonal of the triangular matrix. The process involves creating two matrices, Q (an orthogonal matrix) and R (an upper triangular matrix), such that A is expressed as the product of these two matrices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of trying to simplify a complicated recipe step by step. The QR Algorithm is like reorganizing the ingredients and steps until you have a clear, concise recipe laid out. Each time you simplify, you're getting closer to the final dish (the eigenvalues).
Schur Decomposition
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Schur Decomposition:
- Everysquarematrixisunitarilysimilartoanuppertriangularmatrix.
- For real matrices, a real Schur form is used:
A=QTQ,
where Q is orthogonal and T is upper quasi-triangular.
Detailed Explanation
The Schur Decomposition is a method that states any square matrix can be transformed into an upper triangular form through a unitary similarity transformation. This means that for a given matrix A, there exists an orthogonal matrix Q such that when you apply the transformation, A can be expressed as the product of Q and an upper quasi-triangular matrix T. This is particularly useful in simplifying the analysis of the matrix, especially for determining eigenvalues.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a complex structure like a tower. The Schur Decomposition method is akin to constructing a model of that tower using simplified shapes (the triangular matrix) so you can easily study its behavior under various loads without all the details of the actual structure overwhelming you.
Jordan Reduction Algorithms
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Jordan Reduction Algorithms:
- Rarely used in numerical practice due to instability.
- Useful in symbolic computation environments (e.g., Mathematica, Maple).
Detailed Explanation
Jordan Reduction Algorithms are designed to transform a matrix into its Jordan form, which is a type of nearly diagonal matrix. However, these algorithms are not commonly used in practical numerical computations because they can be unstable. They are more often applied in theoretical perspectives or within symbolic computation environments, where exact calculations rather than numerical approximations are required.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to draw a perfect curve with a pencil. If your hand is steady, you can easily achieve it. But if your hand shakes, the line might come out jagged. The Jordan Reduction Algorithms are like trying to capture that smooth curve despite the shake — challenging and not always reliable, but potentially insightful when you need the nuanced understanding to draw complex concepts.
Applications in Civil Engineering Software
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These techniques are embedded in modern software like ANSYS, STAAD.Pro, and MATLAB used in civil engineering simulations.
Detailed Explanation
The algorithms discussed are integrated into major engineering simulation software such as ANSYS, STAAD.Pro, and MATLAB. These software applications utilize numerical algorithms for similarity transformations to facilitate structural analysis, dynamic simulations, and the design processes essential for civil engineering projects. By leveraging these algorithms, engineers can efficiently compute complex matrix operations, leading to faster and more accurate analyses.
Examples & Analogies
Using software like ANSYS for a bridge design comparison is like using a high-tech calculator to quickly crunch numbers for your personal budget. Instead of doing everything manually, you let the software handle the heavy lifting of complex calculations, ensuring that you can focus on the design and functionality instead of getting bogged down by the math.
Key Concepts
-
QR Algorithm: An iterative method to find eigenvalues through matrix transformations.
-
Schur Decomposition: A technique that enables upper triangular matrix decomposition of square matrices.
-
Jordan Reduction: A form of matrix reduction for non-diagonalizable matrices that are essential in stability analysis.
Examples & Applications
Example of applying QR Algorithm to find eigenvalues for a matrix in civil engineering simulation.
Use of Schur Decomposition to simplify a complex structural analysis problem.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When you seek to find eigen values true, use QR's magic to guide you through.
Stories
Imagine a builder needing to lift a heavy arch, they apply the Schur method to build an arch, getting just the right shape while keeping it strong.
Memory Tools
Remember J-S-Q: Jordan, Schur, QR, keys to matrix transformation success.
Acronyms
R.A.M
Reducing matrix with Algorithms for Decomposition is a key to ease computations.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- QR Algorithm
An iterative algorithm used to compute eigenvalues by transforming matrices to upper triangular form.
- Schur Decomposition
A mathematical technique that transforms any square matrix into an upper triangular form through orthogonal similarity.
- Jordan Reduction
A method used to express matrices in Jordan canonical form, useful for matrices that are not diagonalizable.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
