Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of ADCs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the importance of Analog-to-Digital Converters, or ADCs. Can anyone tell me why ADCs are critical in mixed signal systems?

They convert real-world analog signals into digital data?

Exactly! ADCs create a bridge between analog inputs and digital systems. Why do you think accurate conversion is so important?

Because digital processing needs precise data to function correctly?

Well put! The effectiveness of an ADC significantly affects the accuracy of our measurements.
Balancing ADC Specifications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss how to select an ADC for a specific application. Can anyone think of the key specifications that we need to consider?

I think speed and resolution are important!

Absolutely, never forget about power and noise performance as well! What applications can benefit from different balances of these specifications?

Audio recording would need high resolution, while RF sampling needs high speed!

Right again! Each application has unique requirements guiding ADC selection.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The conclusion emphasizes the significance of Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) in mixed signal systems. It highlights the importance of understanding their architectures, specifications, and application domains to design systems that effectively balance speed, resolution, and power requirements.
Detailed
In summary, ADCs form the core of mixed signal systems, essential for the accurate digital representation of analog inputs. Grasping the various architectures and performance metrics of ADCs enables better system design that can effectively meet the demands of specific applications. Selecting the correct ADC requires a careful examination of factors such as speed, resolution, power consumption, and noise performance. This understanding is paramount for creating high-performance solutions in diverse fields ranging from audio recording to complex sensor integration.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
ADCs in Mixed Signal Systems
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
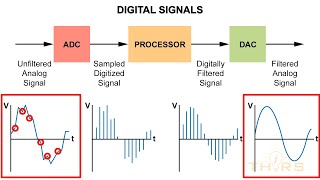
ADCs are at the heart of mixed signal systems, enabling accurate digital representation of analog inputs.
Detailed Explanation
Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) play a crucial role in mixed signal systems, which are systems that process both analog and digital information. By accurately converting analog signals—like sound, light, or temperature—into digital format, ADCs allow systems to interpret real-world inputs in a way that computers and digital devices can understand and process.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an ADC as a translator for a phone conversation between two people who speak different languages. One person speaks in analog (the original language), while the other understands only digital (the translated text). The ADC ensures that what is being said is accurately conveyed from one language to the other.
Understanding ADC Specifications
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding their architectures, specifications, and application domains is critical for designing high-performance systems.
Detailed Explanation
Knowing the different types of ADC architectures, their specifications like resolution and speed, and the domains in which they can be applied is essential for designing effective systems. Each application might require different characteristics from an ADC, influencing its design and selection process. For instance, audio processing requires high resolution, while RF sampling needs high speed.
Examples & Analogies
When choosing a car, you need to consider what you'll be using it for. A family car needs space and comfort, while a sports car focuses on speed and performance. Similarly, selecting an ADC requires understanding the specific requirements of your application to choose the best fit.
Balancing Performance Factors
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Selection of the appropriate ADC involves balancing speed, resolution, power, and noise performance according to the target application.
Detailed Explanation
Choosing the right ADC is a balancing act. If a system needs to process data quickly (speed), or if it needs to capture very fine details (resolution), these demands can sometimes conflict with other factors like power consumption or noise levels. Designers must weigh these aspects to achieve the best possible performance for the task at hand.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like planning a meal. If you're hosting a dinner party, you might want to offer fancy dishes (high resolution), but you also need to prepare everything in time (speed). However, you must do it within your budget (power consumption), ensuring it’s enjoyable without overwhelming your guests (noise performance).
Key Concepts
-
ADC: Vital in converting analog signals to digital formats.
-
Performance metrics: Essential to consider when designing or selecting ADCs for specific applications.
-
Architecture selection: Balancing speed, resolution, and power is crucial based on the target application.
Examples & Applications
An ADC in a digital voltmeter uses high-resolution converters to provide precise voltage readings.
A Flash ADC is used in high-speed data acquisition systems where instantaneity is critical.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For ADCs in systems mixed, a bridge they create, converting signals from analog to digital straight!
Stories
Imagine a concert hall where musicians play analog sounds. An ADC listens and translates those sounds into digital waves, allowing us to store and play them back later!
Memory Tools
Remember the ABCs of ADC: A = Analog input, B = Binary output, C = Conversion process.
Acronyms
Remember the acronym S.R.A.P. for ADC specifications
= Sampling rate
= Resolution
= Accuracy
= Power.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AnalogtoDigital Converter (ADC)
A device that converts continuous analog signals into discrete digital data.
- Mixed Signal Systems
Systems that combine both analog and digital signals.
- Resolution
The number of bits in the output of an ADC, determining how finely the input range is divided.
- SignaltoNoise Ratio (SNR)
The ratio of the signal power to the noise power; higher SNR indicates better accuracy.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
