Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of ADCs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the importance of Analog-to-Digital Converters, also known as ADCs. Can anyone tell me what ADCs do?

ADCs convert analog signals into digital data!

Exactly! This conversion is crucial for processing information in digital systems. Why do you think this transformation is necessary?

Because computers and digital devices can't process analog signals directly!

That's right! ADCs enable the use of real-world signals in digital technology. They determine the accuracy and resolution of the measurements. Let's remember this with the acronym 'ADC': A for Analog, D for Digital, and C for Conversion!

Is the accuracy of the ADC important?

Absolutely! The better the ADC, the more accurately it reflects the analog signal. We'll dive deeper into the operational aspects and architectures of ADCs in our next session.
Role of ADCs in Technology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone think of applications where ADCs play a fundamental role?

In audio recording, right?

Great example! ADCs are used in audio processing to digitize sound signals for recording and playback. Any other examples?

What about in cameras?

Yes, indeed! Cameras use ADCs to convert light signals into digital images. Understanding where and how ADCs are applied will help us appreciate their significance in electronic devices.

So, they really are everywhere!

You got it! And this chapter will guide you through their critical components and how they function.
Key Concepts in ADC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s outline some key concepts we will cover regarding ADCs. First, can anyone explain what happens during the conversion process?

There are steps like sampling, quantization, and encoding!

Exactly! Those three steps are core to how an ADC functions. We'll also delve into different architectures of ADCs and performance metrics, which help evaluate their effectiveness. Does anyone know what performance metrics might refer to?

Maybe how fast or accurate they are?

That's precisely right! We'll discuss metrics like resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, and more. Remember, understanding these metrics is essential for choosing the right ADC for a specific application.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
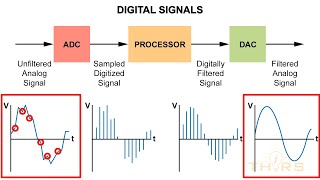
ADCs are essential in mixed signal systems as they transform analog signals into digital formats for processing and communication. This section introduces the importance of ADCs and their impact on measurement accuracy and resolution, setting the stage for a deeper discussion on their principles, architectures, and performance metrics.
Detailed
Introduction to Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC)
Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) are pivotal in mixed signal systems, serving the crucial function of converting real-world analog signals into digital form. This transformation is vital for data processing, storage, and communication in various applications. The effectiveness of ADCs directly influences the precision and fidelity of measurements, particularly in how accurately and finely the analog phenomena can be digitized.
In this chapter, we will explore the operational principles of ADCs, various architectures, and the performance metrics that are essential for evaluating ADC effectiveness across diverse applications. Understanding these aspects is key for engineers and developers aiming to design high-performance systems reliant on accurate analog signal representation.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What are Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) are critical components in mixed signal systems, responsible for transforming real-world analog signals into digital data suitable for processing, storage, and communication.
Detailed Explanation
ADCs serve a fundamental role in modern electronics by converting analog signals—like sound, light, or temperature—into digital data that computers and processors can understand and manipulate. Without ADCs, devices such as smartphones, cameras, and audio systems wouldn't be able to process the real-world signals that they capture.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an ADC as a translator. Imagine speaking to someone in your native language, and they have no idea what you're saying. The translator listens to your words and translates them into another language that the other person understands. Similarly, an ADC takes the 'language' of analog signals and converts it into the 'language' of digital data.
Importance of ADC Effectiveness
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The effectiveness of an ADC determines the accuracy and resolution with which analog phenomena can be measured.
Detailed Explanation
An ADC's effectiveness directly impacts how accurately it can represent analog signals. This includes two key concepts: accuracy (how close the digital output is to the actual analog signal) and resolution (the smallest change in the analog signal that can be detected). High-quality ADCs are crucial in applications where precise measurements are necessary, such as in medical devices or high-fidelity audio equipment.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a high-resolution camera versus a standard one. A high-resolution camera captures more details and colors, allowing you to see finer nuances in the image. Similarly, a very effective ADC can capture the small changes in the analog signal, leading to a clearer and more detailed digital representation.
Overview of the Chapter
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter covers the working principles, key architectures, and performance metrics used to evaluate ADCs across a range of applications.
Detailed Explanation
The chapter provides a comprehensive overview of how ADCs function, the different types of ADC architectures available for various applications, and how to evaluate their performance through specific metrics. Understanding these concepts will help you grasp not just the technical workings of ADCs, but also how to choose the right one for a given application.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine studying different types of cars to understand which one is best for your needs. You would look at how they work (the engine), what designs are popular (different makes and models), and what reviews say about their performance (fuel efficiency, speed, reliability). Similarly, this chapter gives you the tools to understand ADCs in various technical and practical contexts.
Key Concepts
-
Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The process of transforming analog signals into digital format.
-
Sampling: The act of measuring analog signals at intervals to create discrete data.
-
Quantization: The mapping of sampled analog values to specified levels.
-
Encoding: The conversion of quantized data into binary.
-
Nyquist Theorem: The principle that sampling frequency must meet specific criteria for accurate representation.
Examples & Applications
In smartphones, ADCs convert sound waves from the microphone into digital signals that can be processed.
In medical devices, ADCs convert signals from sensors monitoring physiological parameters into digital data for analysis.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
ADCs take signals from the light and sounds, turn them digital, making data abound.
Stories
Imagine a musician playing a song. The microphone captures the sound waves, and an ADC transforms those waves into digital packets, preserving every note for perfect playback.
Memory Tools
Remember 'S-Q-E' for the ADC process: Sampling, Quantization, and Encoding.
Acronyms
ADC
for Analog
for Digital
for Conversion – the essential function of an ADC.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AnalogtoDigital Converter (ADC)
A device that converts continuous analog signals into discrete digital data.
- Resolution
The smallest change in input that can be detected by the ADC, measured in bits.
- Sampling
The process of measuring an analog signal at distinct intervals.
- Quantization
Mapping continuous values measured in sampling to a finite number of discrete levels.
- Encoding
The process of converting quantized levels into a binary format for digital representation.
- Nyquist Theorem
A principle that states the sampling frequency must be at least twice the highest frequency of the analog signal to avoid loss of information.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
