Synchronization in Common RTOS
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to RTOS Synchronization APIs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss synchronization in Real-Time Operating Systems, specifically focusing on the APIs they provide. Why should we care about synchronization?

Is it because it helps tasks work together without messing up data?

Exactly! Synchronization ensures that when multiple tasks access shared resources, they do so without creating conflicts. Let's review the specific APIs for FreeRTOS first. Who can tell me about `xSemaphoreCreateMutex()`?

That's used to create a mutex for critical sections!

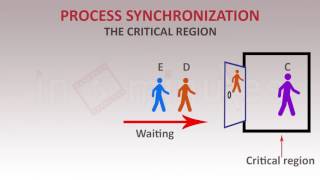
Right! A mutex allows only one task to access the critical section at a time. Remember, think 'only one at a time' to recall what a mutex does.
FreeRTOS Synchronization Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In FreeRTOS, synchronization can also be achieved using `xQueueSend()`. What does this function do?

It allows one task to send data to a queue that another task can read from, right?

Correct! It facilitates communication between tasks. Let's pair that with `xTaskNotify()`, which lets a task notify another task about events. Can anyone summarize how these tools help in synchronization?

They both help to manage task communication and make sure tasks are aware of each other's states.

Well said! Remember 'notify’ for `xTaskNotify()` and 'queue' for `xQueueSend()`. These keywords are great memory aids!
Zephyr OS Synchronization APIs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's turn to Zephyr OS. Who can explain what `k_mutex_lock()` does?

It locks a mutex to ensure only one task can access certain resources!

Exactly! And what about `k_sem_take()`?

That’s used to take a semaphore, waiting until it’s available.

Spot on! Semaphore is another way of managing access. Think 'take' to help memorize its function. Now, how do these APIs contribute to synchronization?

They ensure tasks don’t run into each other while accessing shared resources!
VxWorks Synchronization Functions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss VxWorks. Who can tell me about `semTake()` and `semGive()`?

SemTake waits for a semaphore, and SemGive releases it.

Exactly right! These functions are essential for semaphore operations. Can anyone tell me why we need these synchronization techniques?

To avoid race conditions and ensure data stays consistent!

Correct! Remember 'take' for semaphores to recognize when tasks acquire locks. Great job today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the synchronization APIs provided by popular RTOS such as FreeRTOS, Zephyr, and VxWorks. By examining these APIs, we can observe how they facilitate task synchronization and manage resources effectively, ensuring that concurrent processes can operate without interference.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Synchronization in Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) is crucial for coordinating access to shared resources among concurrent tasks. Different RTOS implementations offer APIs tailored for synchronization, ensuring tasks can execute safely and predictably. This section highlights the synchronization APIs from three prevalent RTOS — FreeRTOS, Zephyr, and VxWorks.
- FreeRTOS Synchronization APIs: Includes functions like
xSemaphoreCreateMutex(), which creates a mutex for protecting critical sections,xQueueSend()to send data to queues, andxTaskNotify()to allow tasks to notify each other upon events. - Zephyr OS APIs: Provides
k_mutex_lock(),k_sem_take()for semaphore operations, andk_msgq_put()for message queue manipulation. These tools ensure tasks are synchronized effectively in Zephyr applications. - VxWorks APIs: Features
semTake()andsemGive()for semaphores, andmsgQSend()for message queues, enabling smooth inter-task communication and resource management in VxWorks environments.
By utilizing these synchronization mechanisms, developers can create real-time applications that prevent race conditions and ensure data integrity during concurrent operations.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
RTOS Synchronization APIs Overview
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
FreeRTOS xSemaphoreCreateMutex(), xQueueSend(), xTaskNotify()
Zephyr OS k_mutex_lock(), k_sem_take(), k_msgq_put()
VxWorks semTake(), semGive(), msgQSend()
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the synchronization APIs used in three common real-time operating systems (RTOS): FreeRTOS, Zephyr OS, and VxWorks. Each of these systems provides specific functions that developers can use to manage synchronization of tasks effectively.
- FreeRTOS: Includes functions such as
xSemaphoreCreateMutex()to create mutexes,xQueueSend()to send items to queues, andxTaskNotify()to allow tasks to notify each other. - Zephyr OS: Uses functions like
k_mutex_lock()to acquire a mutex,k_sem_take()to take a semaphore, andk_msgq_put()to put a message in a queue. - VxWorks: Provides functions such as
semTake()andsemGive()for semaphore operations, andmsgQSend()for sending messages to a queue.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these APIs as different tools in a toolbox. Just like a carpenter has hammers, saws, and screwdrivers for different tasks, developers using RTOS have various synchronization functions to help manage tasks in their applications efficiently.
Key Concepts
-
Synchronization APIs: Essential tools provided by RTOS for managing concurrent task execution.
-
FreeRTOS Functions: Specific APIs such as
xSemaphoreCreateMutex(),xQueueSend(), andxTaskNotify()enabling task synchronization. -
Zephyr API Functions: Functions like
k_mutex_lock()andk_sem_take()to manage synchronization in Zephyr OS. -
VxWorks API Functions: VxWorks functions such as
semTake()andmsgQSend()allowing for robust task synchronization.
Examples & Applications
In FreeRTOS, using xSemaphoreCreateMutex() prevents multiple tasks from entering a critical section simultaneously.
In Zephyr, k_sem_take() can be used to block a task until a resource is available, ensuring safe access.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Mutex protects access with a simple lock, one task in the section, around the block.
Stories
Imagine a busy restaurant where only one chef can access the spice cupboard at a time to prevent chaotic cooking - that's like how a mutex works!
Memory Tools
Remember 'M', 'S', 'Q' for mutex, semaphore, queue — all essential tools for safe task synchronization.
Acronyms
RACE
Remember Access Control Ensures safety while executing tasks.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- FreeRTOS
An open-source RTOS designed for embedded systems, offering tools for synchronization, scheduling, and inter-process communication.
- Mutex
A synchronization primitive that allows only one task to access a resource, preventing conflicts.
- Semaphore
A signaling mechanism to control access to shared resources, can be binary or counting.
- Zephyr
An open-source RTOS aimed at IoT devices, with an emphasis on modularity, scalability, and ease of use.
- VxWorks
A commercial RTOS known for robustness and real-time performance, widely used in embedded systems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
