Application: Gas Sensing with Integrated Photonic Sensors
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Integrated Photonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re exploring integrated photonic sensors, which are pivotal in detecting gases in our environment. They combine light and electronic components to provide real-time monitoring.

How do these sensors work, exactly?

Great question! They operate by emitting laser light at specific wavelengths that interact with the gases. The changes in the light can inform us about the gas concentration.

So, when the gas interacts with light, what happens?

When the light interacts, it can either be absorbed or scattered, and these changes are analyzed by photodetectors to determine gas concentrations.

That sounds very precise! What kind of gases can these sensors detect?

They can detect several gases like methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds, which are significant for environmental monitoring.

What’s the impact of these sensors then?

Their integration into portable devices fosters real-time monitoring of air quality and contributes to environmental protection efforts. Summarizing today's concept: Integrated photonic sensors are not only accurate but crucial for our safety in monitoring harmful gases.
Components of Gas Sensing Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into the components of gas sensing systems. What components do you think these integrated sensors use?

I guess they need lasers? What else?

Correct! Lasers are key components, but they also use photodetectors and spectrometers. Each has a unique function. Can anyone explain why?

I think lasers create the light, and photodetectors capture the data from gas interactions?

Exactly! And spectrometers help analyze the wavelengths of light to determine concentration. Memorize it as LPS: Lasers, Photodetectors, Spectrometers.

So, if they all work together, they can provide accurate measurements, right?

Absolutely! This collaboration between components allows for effective monitoring of gas concentrations, ensuring the integrity of our environment.

What do you mean by real-time monitoring?

Real-time monitoring means that these sensors can provide instantaneous data on gas concentrations, which is vital for detecting leaks or pollution swiftly.
Applications of Gas Sensing Technologies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s explore where gas sensing technologies are applied. Who can name some applications?

Maybe in detecting air pollution?

That's right! They are widely used in air quality monitoring, but also for tracking greenhouse gas emissions and in industrial safety.

Could they be used internally in buildings as well?

Definitely! Integrated sensors can monitor indoor air quality, ensuring safe living environments.

How effective are they compared to traditional methods?

They are significantly more sensitive and selective, providing quick, real-time data. Summing up, these sensors not only enhance safety in industrial contexts but also support global environmental health efforts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Integrated photonic sensors play a vital role in gas sensing applications, utilizing lasers, photodetectors, and spectrometers to detect gases for environmental monitoring. The ability to analyze light interactions with gases provides real-time data crucial for safety and environmental protection.
Detailed
Application: Gas Sensing with Integrated Photonic Sensors
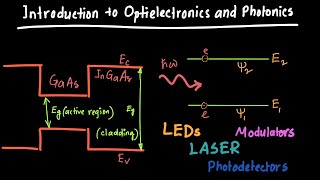
Integrated photonic sensors are revolutionizing gas detection through their convenience and efficiency. These sensors utilize a combination of lasers, photodetectors, and spectrometers to monitor the presence of gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The process begins with lasers emitting light at specific wavelengths, which interacts with the target gas. Photodetectors then measure the light that has been transmitted or reflected after this interaction. By analyzing the intensity and wavelength shifts of this light, it is possible to determine the concentration of the gas.
This innovative approach allows for real-time monitoring, providing portable devices that can be used in air quality assessments, tracking greenhouse gas emissions, and detecting industrial leaks. The compact integration of these systems onto a single chip contributes significantly to efficient environmental monitoring. This advancement is essential as it promotes more effective environmental protection efforts, combining high sensitivity with selectivity.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Gas Sensing
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Integrated photonic sensors are used to detect gases like methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These sensors are often used in environmental monitoring and industrial safety applications.
Detailed Explanation
Integrated photonic sensors specialize in identifying various gases in the environment. They can detect gases like methane, which is key for natural gas safety; carbon dioxide, which is vital for monitoring air quality and greenhouse gases; and volatile organic compounds, which can be harmful pollutants. The sensors are crucial in environmental monitoring, tracking pollutant levels, and ensuring industrial safety by detecting harmful gas leaks.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a smoke detector in your home. Just like it detects smoke to alert you about potential fire danger, integrated photonic sensors detect specific gases in the air to warn about air quality problems or leaks, helping keep the environment and workplaces safer.
How Gas Sensing Works
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Lasers emit light at specific wavelengths that interact with the gas of interest. Integrated photodetectors measure the light that is transmitted or reflected after interacting with the gas. The intensity and wavelength shifts of the light are analyzed to determine the concentration of the gas in question.
Detailed Explanation
The gas sensing process begins when a laser emits light at specific wavelengths intended for detecting particular gases. When this light encounters the gas molecules, it interacts with them. Depending on the nature of the gas, the light may be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted differently. The integrated photodetectors then measure these changes in light: the amount of light that passes through or bounces back. By analyzing the intensity and shifts in light wavelengths, the sensor can calculate how much of the gas is present — this helps produce accurate readings of gas concentrations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a radio tuning into a specific station. Just as you adjust the dial to find the right frequency for your favorite song, these sensors are 'tuned' to specific wavelengths to detect particular gases. The better the tuning, the clearer the song (or, in this case, the gas concentration reading) you receive.
Impact on Environmental Monitoring
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The integration of these sensors onto a single chip has enabled real-time, portable monitoring devices. These sensors are used in air quality monitoring, greenhouse gas emission tracking, and industrial leak detection, contributing to more efficient environmental protection efforts.
Detailed Explanation
By integrating multiple sensing components into a single chip, these photonic sensors have become compact and portable. This means that they can provide real-time monitoring easily, making it doable for cities or industries to track air quality, measure greenhouse gas emissions, or detect industrial leaks more efficiently. Their portability allows them to be deployed in various locations, enabling proactive measures in environmental protection.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how smartphones have changed communication. Just as your smartphone combines multiple functions — calling, texting, internet browsing — into one portable device, integrated photonic sensors combine multiple gas detection features into one small unit. This compact technology empowers communities and industries to manage air quality and safety seamlessly, just like smartphones have revolutionized daily communication.
Key Concepts
-
Integrated Photonic Sensors: Devices that combine optical and electronic elements for gas detection.
-
Gas Detection Mechanism: Involves laser light interacting with gases and analyzed through shifts in wavelength.
-
Real-time Monitoring: The capability to provide immediate results on gas concentrations.
Examples & Applications
An example application of integrated photonic sensors is in industrial safety, where they help detect gas leaks.
Air quality monitoring in cities is another practical use of these sensors, which monitor pollutants.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sensors they pick, with light they flick, measuring gases, a clever trick!
Stories
Imagine a small team of photonic sensors in a factory that sense methane leaks. They shine their laser light to check the air - if it shifts, they sound the alarm!
Memory Tools
Remember 'LPS' for gas detection: Lasers emit light, Photodetectors receive signals, Spectrometers analyze the data.
Acronyms
GAS
Gases (what they detect)
Analysis (how they do it)
Sensors (the technology used).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Integrated Photonic Sensors
Devices that combine optical and electronic components to detect gases and monitor environmental conditions.
- Gas Concentration
The amount of a specific gas present in a given volume of air.
- Photodetectors
Devices that measure and convert light signals into electrical signals for further analysis.
- Spectrometers
Instruments used to measure the spectrum of light, crucial for identifying gas concentrations.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that can significantly affect air quality and are often found in industrial emissions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
