Technology - 9.3.2.1
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
High-Speed Fiber Optic Communication
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore high-speed fiber optic communication. Can anyone tell me what role integrated optoelectronic systems play in this technology?

They convert electrical signals to optical signals, right?

Exactly! Integrated lasers, photodetectors, and modulators are crucial for this process. Think of it as the conversion process where data gets encoded onto light waves. We can remember this process using the acronym LPM: Lasers, Photodetectors, Modulators. Who can explain how this process works?

Well, first lasers generate the optical signals, and then modulators encode the information onto those signals.

After that, it travels through the optical fibers, and at the receiver end, the photodetector converts it back to an electrical signal!

Great summary! Let's recap: high-speed communication is enabled by integrating these components, which leads to lower power consumption and better performance in systems like 5G. Remember LPM today!
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about Optical Coherence Tomography, or OCT. What can you tell me about its applications?

I know it's used for imaging tissues, especially in eye care.

Correct! OCT provides high-resolution images that help diagnose conditions like glaucoma and retinal diseases. How does it work?

It uses a light source that emits low-coherence light aimed at the tissue, and then detects the reflected light.

Exactly! The time delay of the reflected light is measured to create those detailed images, allowing for earlier diagnosis. Why is this significant in healthcare?

Because earlier diagnosis can improve patient outcomes!

Absolutely! So, remember OCT’s role in modern medicine, as it showcases how optoelectronic systems enhance diagnostic capabilities.
LiDAR in Autonomous Vehicles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's examine how integrated optoelectronic systems are crucial for LiDAR technology in autonomous vehicles. Can anyone explain how LiDAR works?

LiDAR uses lasers to send light pulses that bounce back from objects, right?

That's exactly right! The sensors calculate distances based on how long it takes for the pulses to return. What do we call the data produced from this process?

A 3D point cloud that represents the car’s environment!

Perfect! This technology makes self-driving cars safer, as they can create real-time maps. Remember, LiDAR combines sensors and lasers to enhance vehicle perception—key for navigation and obstacle avoidance!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Integrated optoelectronic systems combine optical and electronic components to create high-performance technologies across various fields. This section highlights several applications, such as high-speed fiber optic communication, medical imaging through Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), and the use of LiDAR in autonomous vehicles, showcasing the transformative impact of these technologies in real-world scenarios.
Detailed
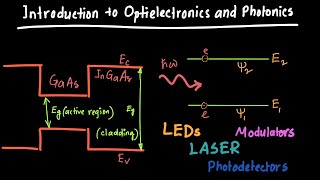
Technology in Integrated Optoelectronic Systems
This section delves into the technological advancements in integrated optoelectronic systems, emphasizing their role in a multitude of applications. These systems blend optical components with electronic circuits, enabling functionalities unattainable by using either discipline alone. Noteworthy applications discussed include high-speed fiber optic communications, where data is transmitted over vast distances through optical fibers with integrated lasers, photodetectors, and modulators. Additionally, the section explores the use of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in medical imaging, explaining how these systems allow for high-resolution imaging crucial for diagnosing various diseases. Another critical application is seen in the use of LiDAR technology in autonomous vehicles, which relies on integrated optoelectronic systems to generate real-time 3D maps of the environment by measuring distances using laser light. These examples illustrate the profound influence integrated optoelectronic systems have across several sectors, paving the way for future innovations.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Technology: Integrated Light Sources, Detectors, and Scanners
● Example: Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique used for high-resolution cross-sectional imaging of tissues, especially in ophthalmology for eye imaging. It has applications in diagnosing retinal diseases, glaucoma, and assessing tissue structure in cardiology.
Detailed Explanation
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) utilizes a combination of light sources, detectors, and scanning techniques for imaging. It is particularly beneficial in the medical field, especially in ophthalmology, where it provides detailed scans of the eye's internal structures. OCT works similarly to ultrasound, but instead of sound waves, it uses light to create images at a microscopic level. This system is crucial for early diagnosis and monitoring diseases that affect tissues, like eye diseases and heart issues.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a camera to take a picture of a small object in detail. Just as the camera focuses and increases resolution to capture all details, OCT uses light to scan tissues and produce high-resolution images. A real-life application is during an eye exam when doctors use OCT to check for diseases like glaucoma, which can damage vision if not caught early.
How OCT Works
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● How it Works:
○ An integrated light source (typically a superluminescent diode or swept source laser) emits low-coherence light.
○ This light is directed at the tissue, and the reflected light is captured by photodetectors.
○ The time delay between the reflected light and the incident light is measured to produce high-resolution images of internal structures in the tissue.
Detailed Explanation
The mechanism of OCT involves emitting low-coherence light from an integrated light source and directing it towards the tissue being examined. When this light hits the tissue, some of it is reflected back. The photodetectors then measure the time it took for the light to return. By analyzing these time delays, high-resolution cross-sectional images of the tissue can be generated. This allows doctors to observe internal structures without needing to perform invasive procedures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how echolocation works for bats; they emit sound pulses, and by listening to the echoes, they determine the size and distance of objects around them. OCT operates on a similar principle but uses light instead of sound. When doctors examine the eye with OCT, they send light waves into the eye, and by measuring the returning light, they can visualize the eye's internal layers clearly.
Impact of OCT Technology
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Impact:
○ Integrated optoelectronic systems have allowed for the miniaturization and cost reduction of OCT devices, making them more accessible in clinical settings.
○ The precision of OCT has enabled early detection of diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, improving patient outcomes.
Detailed Explanation
The integration of optoelectronic systems in OCT technology has significantly reduced the size of the devices, making them less expensive and easier to use in hospitals and clinics. These advances have democratized access to such important diagnostic tools, allowing more patients to benefit from early disease detection. Early detection through OCT enables timely interventions, leading to better treatment outcomes for conditions that could severely affect vision.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how smartphones have become more compact and affordable over time—a crucial evolution that makes technology accessible to many people. Similarly, with the advancements in OCT technology, doctors can provide essential eye imaging at a fraction of the previous costs, enabling wider screening for diseases that could lead to vision loss if not caught in time.
Key Concepts
-
Integration of Optical and Electronic Components: The combination of these technologies enables more efficient and compact devices.
-
High-Speed Communication: Optical communication uses light to transmit data efficiently over long distances.
-
Non-Invasive Medical Imaging: OCT allows for detailed imaging of internal tissues, crucial for early disease detection.
-
LiDAR Technology: This technology is essential for environment mapping in autonomous navigation.
Examples & Applications
High-Speed Fiber Optic Communication: Systems employing integrated lasers, photodetectors, and modulators for data transmission.
OCT in Ophthalmology: Non-invasive eye scanning used for diagnosing retinal and eye diseases using light-based imaging.
LiDAR in Autonomous Vehicles: Laser-based distance measurement systems that create real-time maps for self-driving car navigation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
OCT helps doctors see, imaging tissues, quick and free.
Stories
Imagine a doctor using a magic flashlight (OCT) that reveals the hidden details of your eye without any pain.
Memory Tools
Remember LPM for Light, Photo, Modulate when learning about fiber optics.
Acronyms
For LiDAR, think of (L)ight (D)ata (A)ccuracy (R)ealtime.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Integrated Optoelectronic Systems
Systems that combine optical and electronic components to perform complex functions that are challenging with just optics or electronics.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
A non-invasive imaging technique used for high-resolution cross-sectional imaging of tissues.
- LiDAR
Light Detection and Ranging; a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to measure distances and create detailed maps.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
