Case Study 4: Integrated Photonic Sensors for Environmental Monitoring
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Integrated Photonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss integrated photonic sensors and their applications in environmental monitoring. Can anyone tell me what a sensor is?

Isn't a sensor something that detects changes in the environment?

Exactly! Sensors detect various changes, and photonic sensors specifically use light to analyze these changes. Now, what do you think makes photonic sensors unique compared to other types?

I think they might be more sensitive than regular sensors?

Right! Integrated photonic sensors offer high sensitivity and selectivity, which are essential for accurately monitoring gases and pollutants in the environment. Can anyone name a few gases we might want to monitor?

Methane and carbon dioxide are two important ones, especially for climate change!

Great points! These sensors are capable of detecting gases like methane and carbon dioxide, helping us track air quality and emissions. Let's summarize: integrated photonic sensors are vital for environmental monitoring due to their sensitivity and capability to detect key gases.
How Integrated Photonic Sensors Work
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about their importance, let's dive into how these sensors actually work. Can anyone explain the basic mechanism behind gas sensing?

They use lasers, right? The lasers send light out to the gas.

Correct! The lasers emit light at specific wavelengths that interact with the gas. What happens next?

The photodetectors measure how much light is transmitted or reflected?

"Exactly! They analyze the intensity and wavelength shifts to determine the gas concentration. Let's remember: Light emitted, analyzed by sensors to understand the gas concentration.
Applications of Integrated Photonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about some practical applications of these integrated photonic sensors. Who can share where they might be used?

I read that they are used in air quality monitoring to ensure the air we breathe is safe.

Absolutely! They help monitor pollution levels effectively. What about industrial safety?

Are they used to detect gas leaks in factories?

Yes! Proper monitoring can prevent unsafe conditions in workplaces. Let’s summarize today’s session: integrated photonic sensors are critical for a range of applications, including air quality monitoring, industrial safety, and greenhouse gas emission tracking, impacting environmental protection efforts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section examines how integrated photonic sensors are used for environmental monitoring, focusing on gas sensing technologies. These sensors can detect significant environmental threats efficiently and play an essential role in applications such as air quality monitoring and industrial safety.
Detailed
Integrated Photonic Sensors for Environmental Monitoring
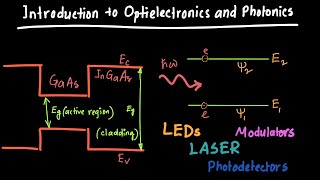
Integrated photonic sensors represent a significant advancement in environmental monitoring technologies, particularly in detecting gases, pollutants, and other substances in the atmosphere. These sensors utilize integrated optoelectronic components, including lasers, photodetectors, and spectrometers, to achieve high sensitivity and selectivity while consuming low power.
Key Applications
- Gas Sensing: The primary application discussed is the use of integrated photonic sensors for detecting gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Methodology: The functioning of these sensors is based on laser technology where lasers emit light at specific wavelengths that interact with the targeted gases. Photodetectors then measure the amount of light transmitted or reflected, and any intensity or wavelength shifts are analyzed to determine the concentration of the gas.
- Impact: The integration of these sensors onto a single chip supports real-time, portable monitoring solutions essential for applications in air quality monitoring, greenhouse gas emission tracking, and industrial safety. They represent a step forward in promoting environmental protection efforts.
Overall, integrated photonic sensors simplify the monitoring process by making it more efficient, accessible, and responsive to current environmental conditions.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Background of Environmental Monitoring
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Environmental monitoring often involves detecting gases, pollutants, and other substances in the air. Integrated optoelectronic sensors offer high sensitivity and selectivity, enabling real-time monitoring with low power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
Environmental monitoring is crucial for maintaining air quality and public health. It involves measuring various gases and pollutants present in the atmosphere. Integrated optoelectronic sensors are special tools that combine optical and electronic components to detect these substances with high accuracy. These sensors are designed to be very sensitive, meaning they can detect even small amounts of pollutants. Additionally, they are selective, which allows them to focus on specific gases while ignoring others. This is important because the air can contain many different substances at once. The sensors operate using low power, making them effective for continuous monitoring without needing frequent battery replacements.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to find a needle in a haystack. A traditional sensor would be like using your hands — it can be done, but it’s slow and you might miss the needle. Integrated photonic sensors are like using a powerful magnet to find the needle quickly and easily. They can detect tiny traces of harmful gases just like a magnet can pull the needle out of the haystack.
Application of Gas Sensing
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Application: Gas Sensing with Integrated Photonic Sensors
● Technology: Integrated Lasers, Photodetectors, and Spectrometers
● Example: Integrated photonic sensors are used to detect gases like methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These sensors are often used in environmental monitoring and industrial safety applications.
Detailed Explanation
Integrated photonic sensors are employed to specifically detect gases critical for environmental monitoring, such as methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The technology behind these sensors includes integrated lasers that produce light at specific wavelengths, photodetectors that capture the light after it interacts with gases, and spectrometers that analyze the light to determine gas concentrations. For example, if a sensor is used to detect methane, the laser will emit light that interacts with methane molecules in the air. The sensor then measures how much light is absorbed or reflected, which correlates with the concentration of methane present.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like smelling food cooking in the kitchen. Just as your nose detects different smells based on how much scent is in the air, these sensors detect gases by analyzing how much light interacts with them. The more intense the smell, the stronger the signal. Similarly, if more light is absorbed by a specific gas, the sensor signals that there is a higher concentration of that gas.
Mechanism of How Integrated Photonic Sensors Work
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● How it Works:
○ Lasers emit light at specific wavelengths that interact with the gas of interest.
○ Integrated photodetectors measure the light that is transmitted or reflected after interacting with the gas.
○ The intensity and wavelength shifts of the light are analyzed to determine the concentration of the gas in question.
Detailed Explanation
The functioning of integrated photonic sensors involves several steps. First, lasers emit light at specific wavelengths that are chosen because they correspond to the absorption characteristics of the target gas. When this light encounters the gas, some of it is absorbed while some is transmitted or reflected. The integrated photodetectors then capture this light. By analyzing the intensity of the light and any shifts in its wavelength after interacting with the gas, scientists can determine the concentration of the gas. If more gas is present, more light will be absorbed, changing the signal detected by the photodetectors.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to understand how humid it is in a room by feeling the air with your hand. If the air is dry, you feel little moisture; if it’s humid, you feel much more. In this analogy, the lasers are like your hand feeling the air, and the photodetectors are like your brain interpreting the sensation. The change in how much light is absorbed and reflected allows the sensor to measure the 'humidity', or in this case, the concentration of the gas.
Impact of Integrated Photonic Sensors
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Impact:
○ The integration of these sensors onto a single chip has enabled real-time, portable monitoring devices.
○ These sensors are used in air quality monitoring, greenhouse gas emission tracking, and industrial leak detection, contributing to more efficient environmental protection efforts.
Detailed Explanation
The development of integrated photonic sensors has significantly impacted environmental monitoring technology. By integrating multiple components onto a single chip, these sensors have become much smaller and easier to transport. This portability allows for real-time monitoring, meaning data can be collected and analyzed almost instantly instead of waiting for samples to be sent off to a lab. These sensors play a vital role in areas such as air quality monitoring, tracking greenhouse gas emissions, and detecting leaks in industrial settings. Their ability to provide immediate data helps organizations respond more effectively to environmental concerns.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a simple weather app on your phone that gives you up-to-the-minute weather information. These integrated photonic sensors function in a similar way for the environment by providing immediate feedback about air quality. Just as you can check the weather in real-time to decide if you need an umbrella, these sensors can alert companies or governments to pollution levels so they can take action quickly.
Key Concepts
-
Integrated Photonic Sensors: Devices combining optical and electronic components for gas detection.
-
Gas Sensing Mechanism: Lasers emit light at specific wavelengths, photodetectors measure interactions with gases.
-
Applications: Used in air quality, industrial safety, and environmental monitoring.
Examples & Applications
Integrated photonic sensors detect gases like methane crucial for monitoring climate change.
Sensors used in factories to enhance safety by detecting harmful gas leaks.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To keep the air clean and bright, photonic sensors help us see the light.
Stories
Imagine a tiny device that sends out a beam of light into the air, it detects invisible gases, shining a bright awareness on pollution. It's like having a superhero for the environment!
Memory Tools
Remember GASP for gas detection: Gases, Analysis, Sensitivity, Photodetection.
Acronyms
GEMS
Gas Environmental Monitoring System refers to the integrated sensors measuring gas concentrations.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Integrated Photonic Sensors
Sensors that integrate optical and electronic components to detect gases and pollutants efficiently.
- Gas Sensing
The process of detecting and measuring the concentration of gases in the environment.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemical compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature and can have harmful health effects.
- Photodetector
A device that detects light and converts it into an electrical signal.
- Spectrometer
An instrument used to measure properties of light across various wavelengths.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
