Importance of Soil Classification in Pavement Design
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Assessment of Load-Bearing Capacity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we're discussing the assessment of load-bearing capacity in pavement design. Can anyone tell me why this is important?

It’s important because we need to know if the soil can support the weight of the pavement and traffic.

Exactly! The classification helps us identify the strength of the soil underneath the pavement. What types of soils do you think are better for load-bearing?

Well-graded gravels and sands would be better, right? They usually have higher strength.

Yes, you’re correct! These soils are ideal because they provide better stability. Great job! Let's remember this with the acronym 'GWS' for Gravels, Well-graded sands, which signifies good load-bearing capacity.

What happens if we choose a weaker soil?

Choosing a weaker soil may lead to pavement failures. It could sag or crack under heavy loads. Anyone remember why knowing soil strength affects our design choices?

Because we need to ensure the pavement can withstand the traffic without getting damaged!

Exactly! Summarizing today, we've learned that assessing load-bearing capacity through soil classification is vital for designing durable pavements. Remember GWS for strong soil!
Predicting Behavior Under Load
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s address how different soils behave under load. Can anyone describe what this means?

I think it means that different types of soils react differently when cars drive over them.

That's right! Some may compress, while others might expand. Why is it crucial to predict these behaviors?

If we don't predict them, the pavement could get damaged over time.

Spot on! Consider using the mnemonic ‘DESERT’ for Different Engaged Soils Encourage Reactions to Traffic, which can remind you of how essential it is to assess soil types.

Are there any particular soils we should be worried about?

Yes, expansive clay soils can cause major issues like heave. Understanding these behaviors lets us design pavements that are more resilient. To recap, predicting soil behavior is key to avoiding future pavement problems!
Material Selection and Drainage Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about material selection. How does soil classification assist us in choosing the right materials?

It helps us know what additives or stabilizers we might need to make the pavement stronger.

Correct! For instance, if we classify soil as clayey, we might consider lime stabilization. Now, why are drainage considerations tied to our soil classifications?

Because some soils drain better than others? We don’t want water pooling under the pavement.

Absolutely! Remember the acronym ‘PACE’ for Permeable And Compactable Environments which refers to adequate drainage conditions to ensure longevity of pavement.

How do we know what kind of drainage is needed?

Great question! We analyze the permeability of the soil type, which is also crucial. To summarize today—soil classification is vital for making informed choices about materials and drainage!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section highlights the crucial role of soil classification in pavement design, emphasizing its impact on load-bearing capacity, behavior under traffic loads, material selection, drainage considerations, and construction feasibility. Understanding these aspects ensures appropriate design interventions and enhances pavement stability and longevity.
Detailed
Importance of Soil Classification in Pavement Design
Soil classification plays a significant role in pavement design. It assists engineers in several key areas:
- Assessment of Load-Bearing Capacity: Classifying soil types aids in identifying their strength, crucial for determining their suitability as subgrade and sub-base layers. Stronger soils support heavier loads, while weaker soils may require additional support or treatment.
- Predicting Behavior Under Load: Different soil types behave distinctly under traffic loads; some may compress while others may yield or even expand. Understanding these behaviors allows engineers to predict pavement performance over time.
- Material Selection: Proper soil classification is vital for selecting the right stabilizers or replacement materials when needed. This ensures that the materials chosen complement the soil's characteristics, improving overall pavement durability.
- Drainage Considerations: Soil classification is also based on its permeability, influencing drainage design significantly. Well-drained soils prevent water accumulation that could undermine pavement integrity.
-
Construction Feasibility: Some soil types may require extensive treatment or may not be suitable for construction at all. Knowing this beforehand can save time and resources during the construction phase.
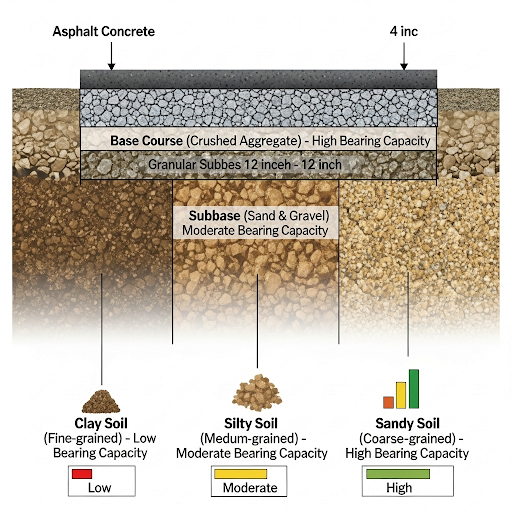
In summary, understanding soil classification helps engineers to make informed decisions that enhance pavement design, leading to improved performance and extended service life.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Assessment of Load-Bearing Capacity
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Classification helps in identifying soil strength and suitability for subgrade and sub-base layers.
Detailed Explanation
Soil classification is vital for understanding how much weight the soil can support. Engineers classify soil to determine its strength, which is crucial for building safe and effective pavements. This classification process helps pinpoint whether the soil can adequately support layers of pavement and under which conditions it might be problematic.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a table: if the table legs are strong and sturdy, it can hold heavy books without a problem. But if the legs are weak, the table might collapse under the weight. Soil works similarly; knowing its load-bearing capacity allows engineers to design safe roads just like we ensure furniture is sturdy enough for use.
Predicting Behavior Under Load
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Different soil types exhibit different behaviors under repeated traffic loads.
Detailed Explanation
Different soils react differently when subjected to pressure, especially from vehicles. Some soils may compress and change shape, which can lead to pavement failures, while others remain stable. Understanding these behaviors helps engineers predict how the pavement will perform over time and under various conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge compared to a solid piece of wood. If you press on the sponge, it squashes down, but it can bounce back. In contrast, if you place weight on wood, it won't change shape at all. Knowing how different soils act under load helps in making smart decisions about where to build roads.
Material Selection
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Proper classification aids in selecting appropriate stabilizers or replacement materials if required.
Detailed Explanation
Soil classification helps engineers determine what materials would work best to enhance or replace existing soil, ensuring stability and durability. For example, if the soil is too weak, they might choose to mix in stabilizers like lime or use stronger materials to enhance the subgrade.
Examples & Analogies
Consider baking a cake: if you find out your flour is too old and doesn’t provide enough structure, you might add some fresh flour or a binding agent like eggs to ensure it comes out right. Similarly, engineers can enhance soil with better materials so that it forms a strong base for the pavement.
Drainage Considerations
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Soils are classified based on permeability, affecting drainage design.
Detailed Explanation
Different soils allow water to pass through them at different rates, known as permeability. This aspect is critical because good drainage minimizes water-related damage to pavements. Classification enables engineers to forecast and design drainage solutions that will effectively manage water and protect the pavement.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how water flows through a sponge versus a brick. Water goes through a sponge easily, while the brick holds the water on the surface. By understanding how different soil types behave, engineers can implement effective drainage methods similar to how you would choose different materials to manage spills effectively.
Construction Feasibility
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some soils may require significant treatment or are completely unsuitable for construction.
Detailed Explanation
Not all soils are equal when it comes to construction; some may need extensive treatment, while others might be completely unsuitable. Soil classification gives engineers a heads up about potential challenges. If the soil isn't compatible with construction efforts, plans can be adjusted to either modify the soil or choose a different site.
Examples & Analogies
Just like in cooking, if a recipe calls for fresh vegetables, but you only have spoiled ones, you need to adjust your recipe or find fresh ones. Similarly, if soil classifies as unsuitable, construction projects may need alternatives to ensure their success.
Key Concepts
-
Assessment of Load-Bearing Capacity: The evaluation of soil’s strength to support pavement.
-
Predicting Behavior Under Load: Understanding how different soils respond to traffic loads.
-
Material Selection: Choosing appropriate materials based on soil classification.
-
Drainage Considerations: The significance of soil permeability in drainage design.
Examples & Applications
A well-graded sand has a high load-bearing capacity and is ideal for subgrade.
Clay soils may require stabilization to improve their load-bearing capacity and drainage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Strong soil helps pave the way, keep it dry, and it will stay!
Stories
Imagine a city where roads are built on marshy soil; they sink and crack. But in another town, roads made from stable gravel stand strong!
Memory Tools
Remember 'PLAM' for soil classifications – Predict, Load, Analyze, Material, ensuring you cover all bases!
Acronyms
GWS for strong soil types
Gravels
Well-graded sands.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- LoadBearing Capacity
The ability of soil to support the weight of structures above it.
- Permeability
The capacity of soil to transmit water through its pores.
- Subgrade
The soil layer that provides support for pavement structures.
- Stabilizers
Materials added to soil to improve its strength and stability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
