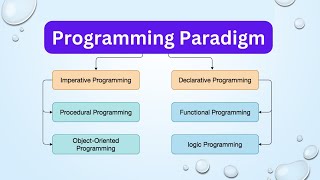
Basic Programming Paradigm: Procedural Programming
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to explore procedural programming, which is about writing step-by-step instructions to solve problems.

What does it mean to write step-by-step instructions?

Great question! It means that our programs will execute one line of code at a time, just like following a recipe in cooking.

Can you give us an example of how that looks?

Sure! For instance, imagine a simple function that calculates the factorial of a number. We would use a loop to multiply numbers sequentially. Remember the acronym 'FLOP' to think of 'Functions, Loops, Operations' in procedural programming.

So, it's like breaking down a big problem into smaller, manageable tasks?

Exactly! At the end of this session, you'll understand how to apply this logic to solve various programming challenges.
Functions in Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss functions, which are pivotal in procedural programming. They help us reuse code and make it easier to understand.

What is a function exactly?

A function is a block of code that performs a specific task and can be reused multiple times. Think of it as a mini-program within your main program!

Can we see an example of a function?

Absolutely! Here's a simple function in Python that calculates the factorial of a number using a loop. It illustrates how we can encapsulate logic within a function.

How do we call this function?

Good question! Once defined, you call the function by its name and pass any required parameters. This makes our code cleaner and more efficient.

So functions help break up the logic too?

Precisely! After explaining this, we'll practice writing and calling functions on our own.
Control Structures in Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into control structures like loops and conditionals, which dictate the flow of our programs.

What do you mean by control structures?

Control structures help us determine how and when to execute certain parts of our code. For example, loops allow us to repeat an action, while conditionals let us execute code based on certain conditions being true.

Can you explain loops a bit more?

Certainly! A loop iterates over a block of code multiple times. Think of a 'For Loop' as a way to say, 'Do this task five times'. Let's practice writing loops to reinforce this concept.

And conditionals help in decision-making within the code, right?

Exactly! We will apply these concepts in our next exercise to build more complex programs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore procedural programming as a foundational programming paradigm that emphasizes writing clear, sequential instructions to execute tasks, with a focus on concepts such as functions and loops. It serves as the basis for understanding more complex programming paradigms.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The Basic Programming Paradigm, primarily procedural programming, focuses on a systematic approach to problem-solving through sequential execution of instructions. This paradigm is central for beginners, as it helps in developing logical thinking and building a solid foundation before moving on to more advanced concepts.
Key Elements of Procedural Programming:
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Programs are designed by taking one step at a time, making the logic straightforward to follow.
- Functions: Reusable blocks of code are created to perform specific tasks, such as calculating the factorial of a number using loops.
- Control Structures: Using loops and conditionals effectively manages the flow of the program.
Procedural programming acts as a bridge to advanced paradigms like Object-Oriented Programming and Functional Programming. Understanding its principles is crucial for software development, enabling developers to structure their code logically and improve maintainability.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Focus of Procedural Programming
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Focuses on step-by-step instructions.
Detailed Explanation
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm that emphasizes a sequence of operations, or procedures. Each procedure is a set of instructions that the computer follows in a linear fashion. This means that the programmer writes down steps for the computer to execute, making the logic straightforward and easy to follow. This style is particularly useful when tasks can be broken down into smaller sub-tasks, which can each be executed in order.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of procedural programming like following a recipe in cooking. The recipe lists each step that you need to perform in a specific order. For instance, you first gather ingredients, then mix them, followed by cooking them, and finally serving the dish. If you follow the steps in order, the result will be successful!
Example: Factorial Calculation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Example: Writing a function to calculate factorial using loops.
Detailed Explanation
Calculating the factorial of a number is a classic example that illustrates procedural programming. For example, the factorial of a non-negative integer n is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. In procedural programming, you typically implement this using a function where you start from 1 and multiply it by each integer up to n in a loop. This step-by-step approach clearly shows how the task can be broken down and completed in an organized manner.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are assembling a toy that requires you to put together parts one at a time. You have a set of instructions that tell you to first connect the legs, then attach the arms, and finally place the head. Following these instructions one step at a time makes sure you create the toy correctly, just like calculating a factorial step by step.
Key Concepts
-
Procedural Programming: A paradigm where developers write step-by-step instructions for the computer to execute.
-
Functions: Blocks of reusable code that perform specific tasks.
-
Loops: Allow for repetitive execution of code based on conditions.
-
Conditionals: Enable decision-making within programs based on boolean expressions.
Examples & Applications
Calculating the factorial of a number using a function and a loop.
Using a conditional to check if a number is even or odd.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For loops and functions, we have a plan, step by step we code, just like we can!
Stories
Imagine you're baking a cake. First, you mix the ingredients step by step, then you have a 'Recipe Function' to repeat for every cake you bake.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'FLOP' for Functions, Loops, Operations in procedural programming.
Acronyms
FLOP
Functions
Loops
Operations; critical concepts in procedural programming.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Procedural Programming
A programming paradigm focused on writing procedures or functions that manipulate data, emphasizing a linear flow of control.
- Function
A reusable block of code that performs a specific task and can accept inputs (parameters) to operate on.
- Loop
A control structure that repeats a block of code multiple times until a specified condition is met.
- Conditional
A statement that executes certain parts of code based on whether a specified condition is true or false.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
