Concurrent & Parallel Programming
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Concurrency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss concurrency. Can anyone tell me what concurrency means?

Isn't it about executing tasks at the same time?

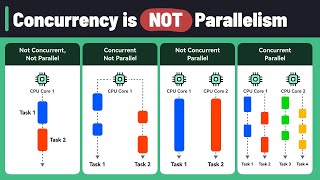
Great start! Concurrency is about managing multiple tasks simultaneously, but it's important to note that they may not run at the exact same time; rather, they interleave execution. Think of it like a busy chef preparing multiple dishes by switching between them.

So, it's like how we multitask in our daily lives?

Exactly! Now, can anyone name scenarios where we might want to use concurrency in programming?

What about a server handling multiple client requests?

Spot on! Concurrency is essential in web servers to handle multiple requests efficiently. Remember, a keyword here is 'management of multiple tasks.'
Understanding Parallelism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's delve into parallel programming. Who can explain what it means?

I think it's about executing multiple tasks at the same time.

Correct! Parallelism involves executing multiple computations simultaneously. This can be done on multi-core processors. Can anyone give a real-world example of when we would use parallelism?

Processing large datasets in data analysis?

Yes! Data analysis often benefits from parallel processing. By dividing the data among multiple processors, we can significantly reduce processing time.

So the larger the data, the more we can benefit from parallelism?

Indeed! Performance is key when data size increases. Remember, concurrency manages tasks, while parallelism executes them simultaneously.
Threads and Processes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the technical implementation—threads and processes. Who can explain the difference between the two?

I think processes are independent, while threads share resources of the same process?

Yes! Processes are isolated, while threads within the same process share resources, making threads lighter on resource use. This is why multithreading can enhance performance but also introduces complexity.

What challenges or issues arise with multithreading?

That's a great point! Potential issues include race conditions and deadlocks. Race conditions happen when multiple threads access shared data concurrently, leading to inconsistent results.

How can we avoid these issues?

Using proper synchronization techniques like locks or semaphores. Always remember: 'Safe choices make reliable threads.'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Concurrent and parallel programming are advanced programming paradigms that utilize threads and processes to improve performance. This section emphasizes their differences, use cases, and significance in modern software development, especially for resource-intensive applications.
Detailed
Concurrent & Parallel Programming Overview
This section explores concurrent and parallel programming, which are vital paradigms in contemporary software development aimed at enhancing performance, especially in computation-heavy tasks.
- Definitions:
- Concurrency: Refers to the ability of a system to manage multiple tasks simultaneously by interleaving their execution, allowing for efficient resource utilization.
- Parallelism: Involves executing multiple tasks simultaneously using multiple processors or cores to increase computational speed.
- Importance: With the rise of multi-core processors and the need for high-performance applications, understanding these concepts is crucial for software developers. Concurrency helps in managing tasks effectively while parallelism accelerates data processing.
- Technical Concepts:
- Use of threads and processes to achieve efficiency.
- Implementation of async-await syntax to manage asynchronous operations effectively.
- Challenges such as race conditions, deadlocks, and how to mitigate them.
In summary, mastering concurrent and parallel programming is essential for developing scalable solutions in today's fast-paced technological landscape.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Concurrent & Parallel Programming
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Use of threads, processes, async-await, etc.
• Boosts performance for computation-heavy tasks.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the key concepts of concurrent and parallel programming. Concurrent programming refers to the ability of a system to manage multiple tasks simultaneously. It allows different tasks to make progress without waiting for each other. Parallel programming, on the other hand, involves executing multiple tasks at the same time, typically on multiple processors. This is particularly useful in computation-heavy tasks, which can benefit from divide-and-conquer strategies.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a restaurant kitchen during dinner rush. Various chefs are working on different dishes at the same time (parallel programming), while a waiter takes orders, processes them, and updates the customers—ensuring all tasks progress without delay (concurrent programming).
Threads and Processes
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Threads are smaller units of a process and share the same memory space.
• Processes are independent and have their own memory space.
Detailed Explanation
In programming, threads and processes are crucial for building concurrent and parallel applications. A process is an independent program that has its own memory space. In contrast, a thread is a smaller part of a process that can run concurrently and shares memory with other threads within the same process. This sharing of memory can lead to better performance but also poses risks like data contamination if not managed correctly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a factory (process) where different assembly lines (threads) work on the same product. Each assembly line utilizes shared resources like tools or materials (memory), but they operate within their own segment of the overall process.
Asynchronous Programming
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Async-await is a programming construct that simplifies working with asynchronous code.
• Helps write non-blocking code where other tasks can run without waiting.
Detailed Explanation
Asynchronous programming allows a program to execute tasks without blocking the main thread. The async-await model enables developers to write code that pauses execution while waiting for an operation to complete (like a network call), without freezing the entire application. This is particularly powerful in web development, where a user interface needs to remain responsive even while data is being fetched.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a waiter taking multiple orders in a busy restaurant. Instead of waiting for the kitchen to prepare each dish before taking the next order, the waiter takes all orders and then checks back later, allowing for uninterrupted service.
Key Concepts
-
Concurrency: Managing multiple tasks simultaneously through interleaving their execution.
-
Parallelism: Simultaneous execution of tasks using multiple processors.
-
Threads: Lightweight processes that share the same resources.
-
Processes: Independent programs with their own memory space.
-
Race Condition: Occurs when multiple threads change shared data concurrently.
-
Deadlock: A situation where threads wait for each other, leading to a standstill.
Examples & Applications
Using threads in a web server to handle multiple client requests at the same time.
Parallel processing of large data sets using frameworks like Apache Spark.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To run many tasks with ease, concurrency is the key; it juggles them with grace, while parallelism sets the pace.
Stories
Imagine a chef who cooks several meals at once—he manages each task concurrently but uses different chefs to cook each meal in parallel.
Memory Tools
Remember 'C3P2': Concurrency is like 3 chefs managing tasks, while Parallelism, like 2 chefs cooking simultaneously.
Acronyms
Use 'TAP' for Threads, Asynchronous, Parallel—key terms to keep in mind.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Concurrency
The ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously, often by interleaving their execution.
- Parallelism
The simultaneous execution of multiple computations, typically utilizing multiple processors.
- Thread
The smallest unit of processing that can be scheduled by an operating system, sharing the same resources of a process.
- Process
An independent program that is executed in its own memory space.
- Race Condition
A situation in which two or more threads access shared data and try to change it at the same time, leading to unpredictable results.
- Deadlock
A situation where two or more threads are waiting for each other to release resources, resulting in all involved threads being blocked.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
